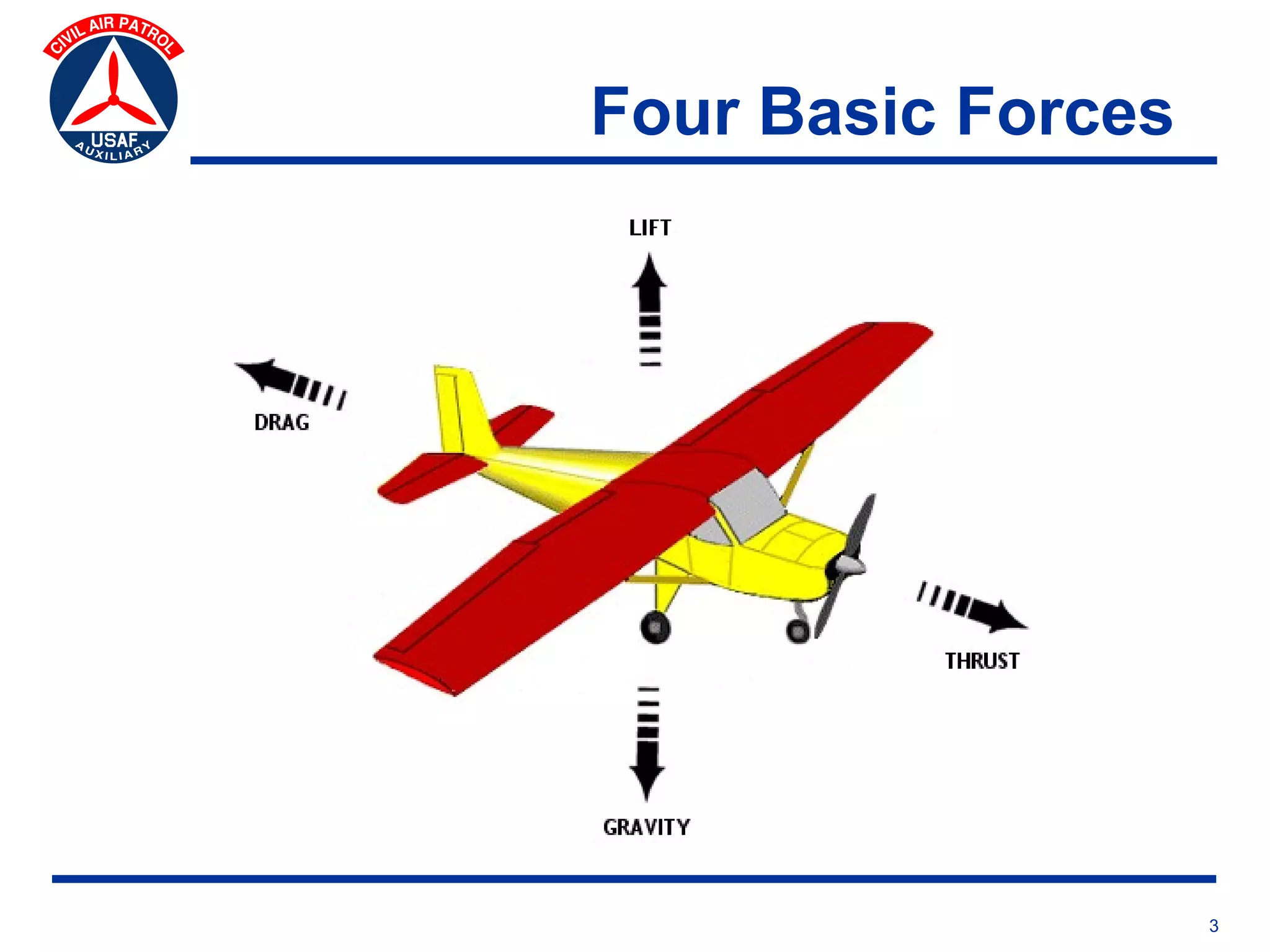
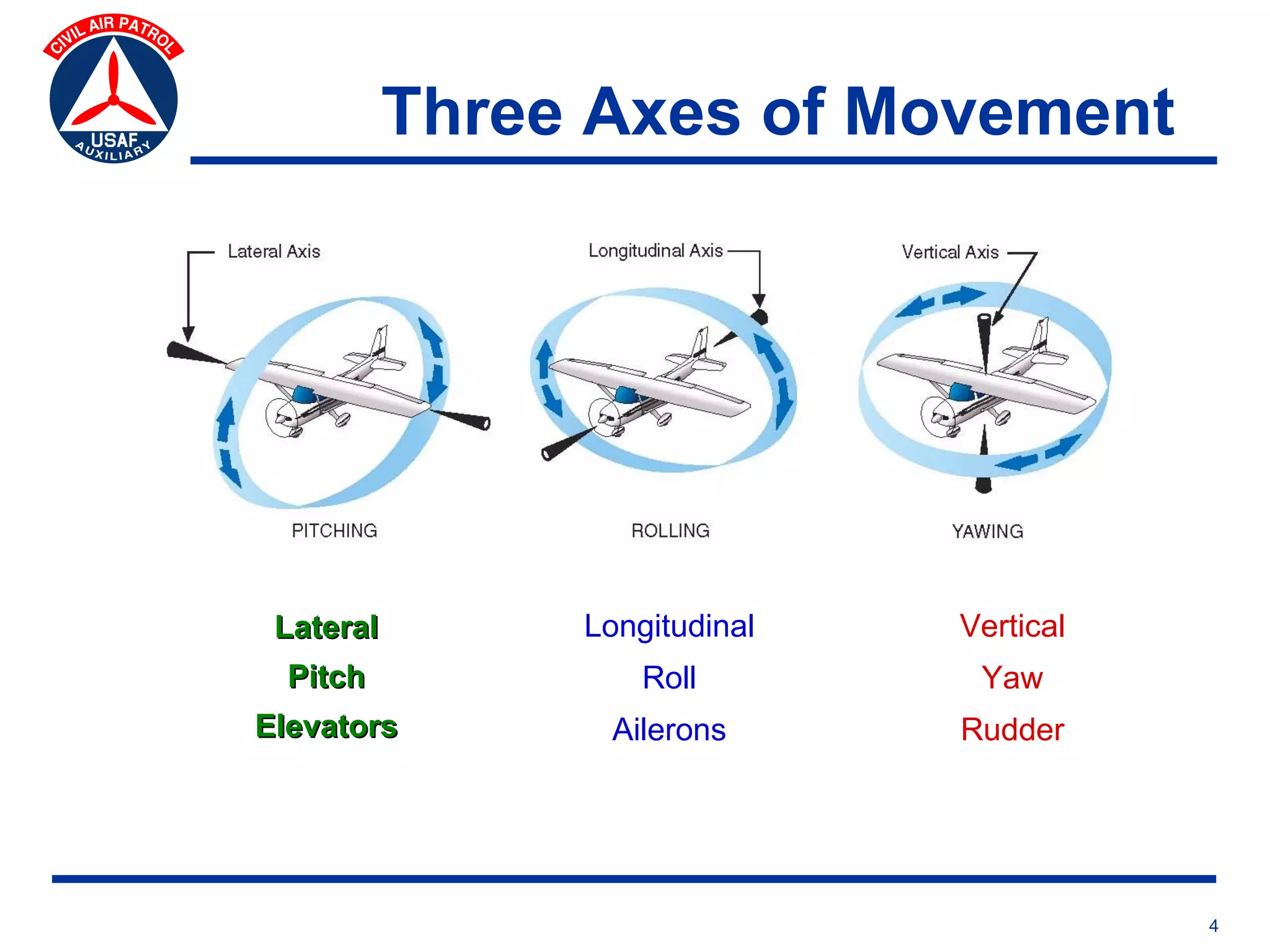
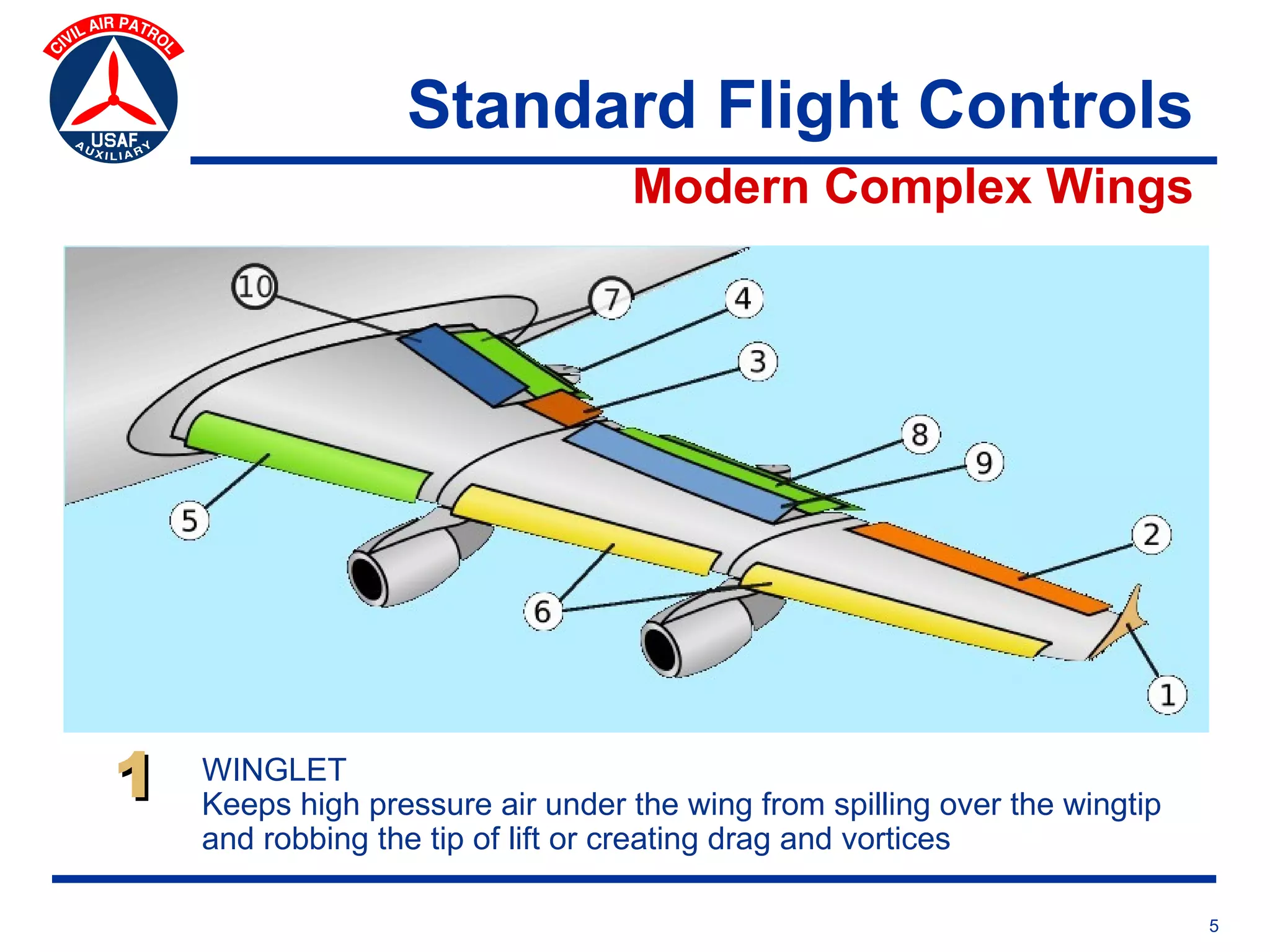
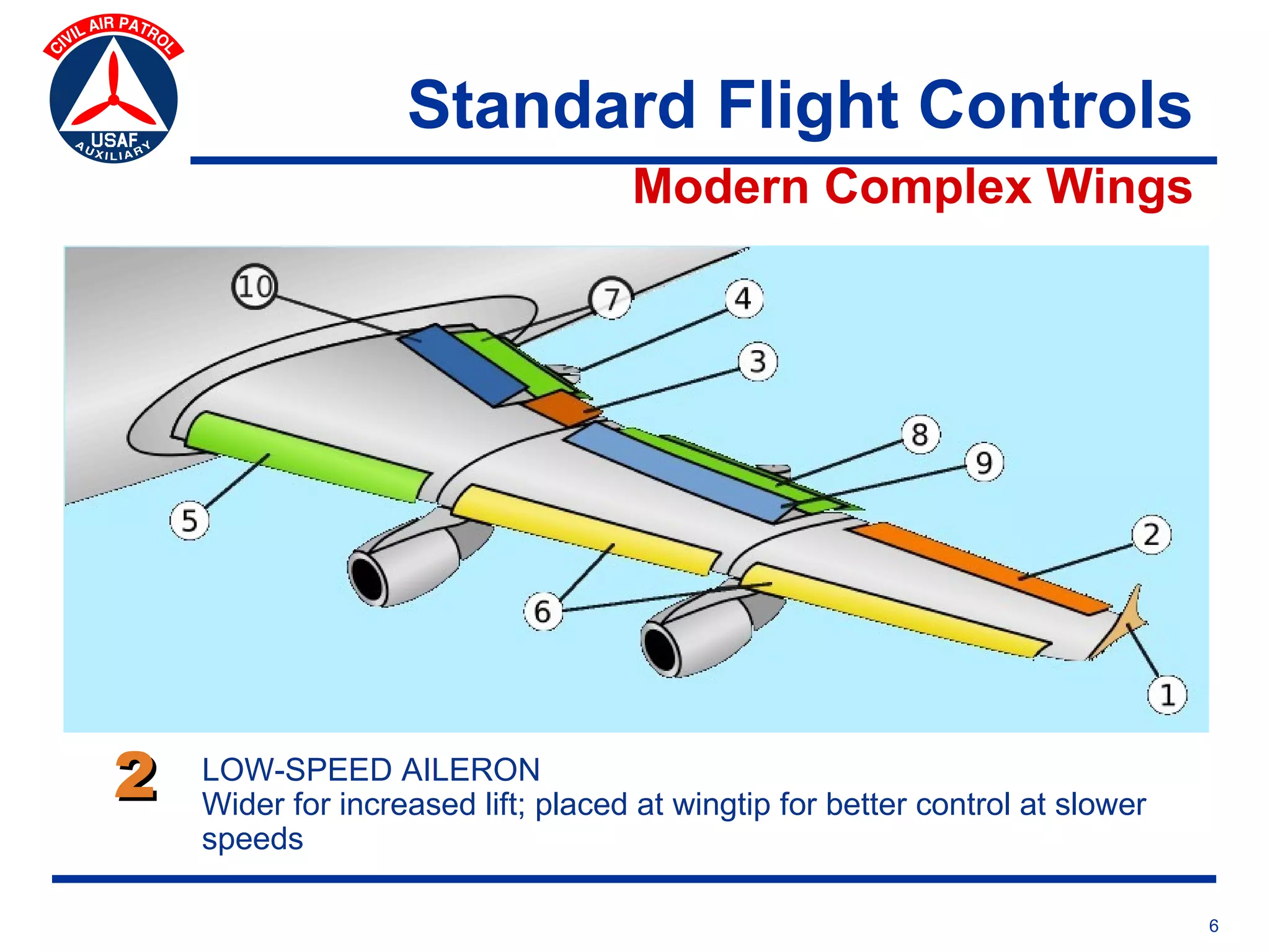
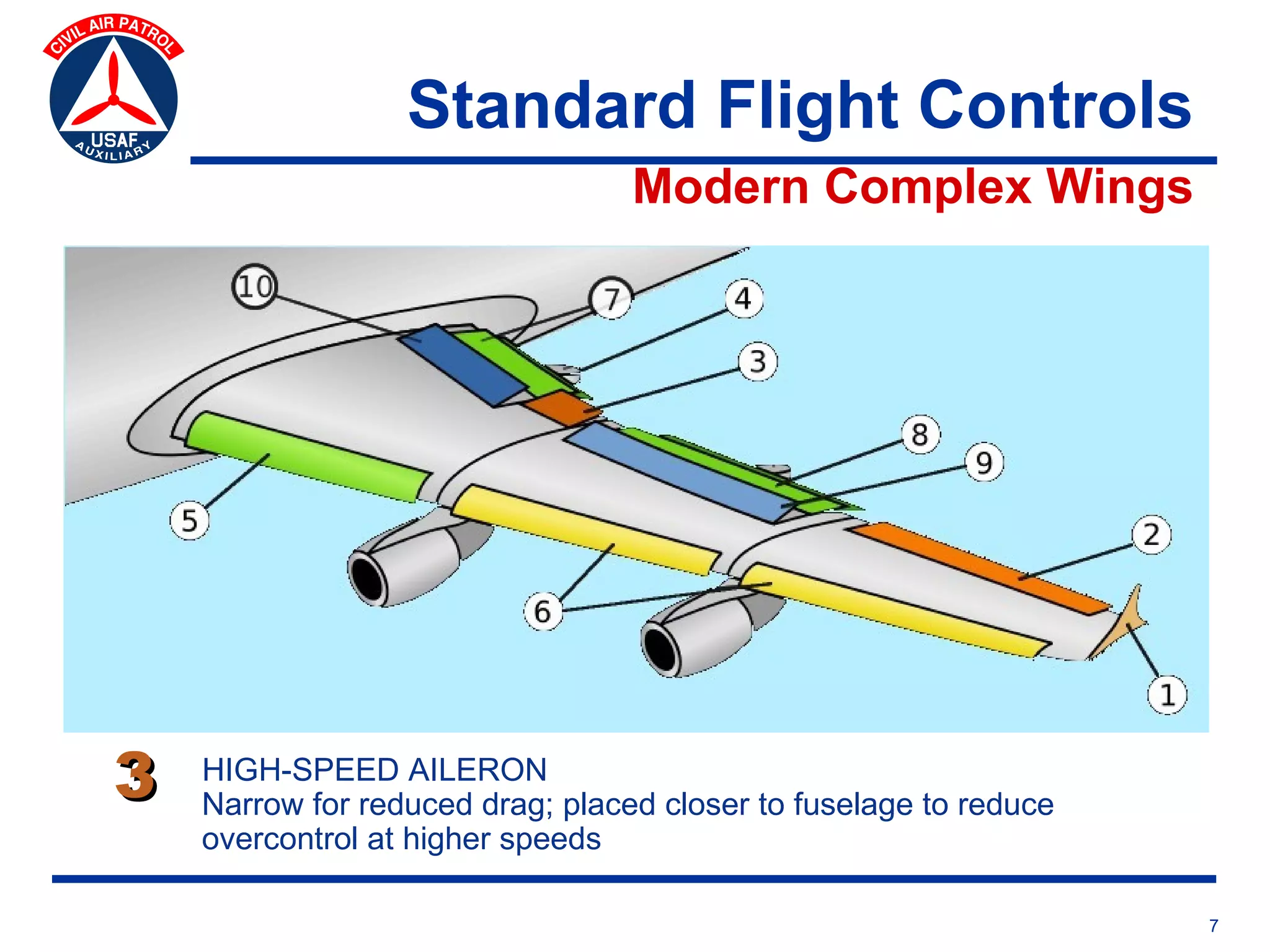
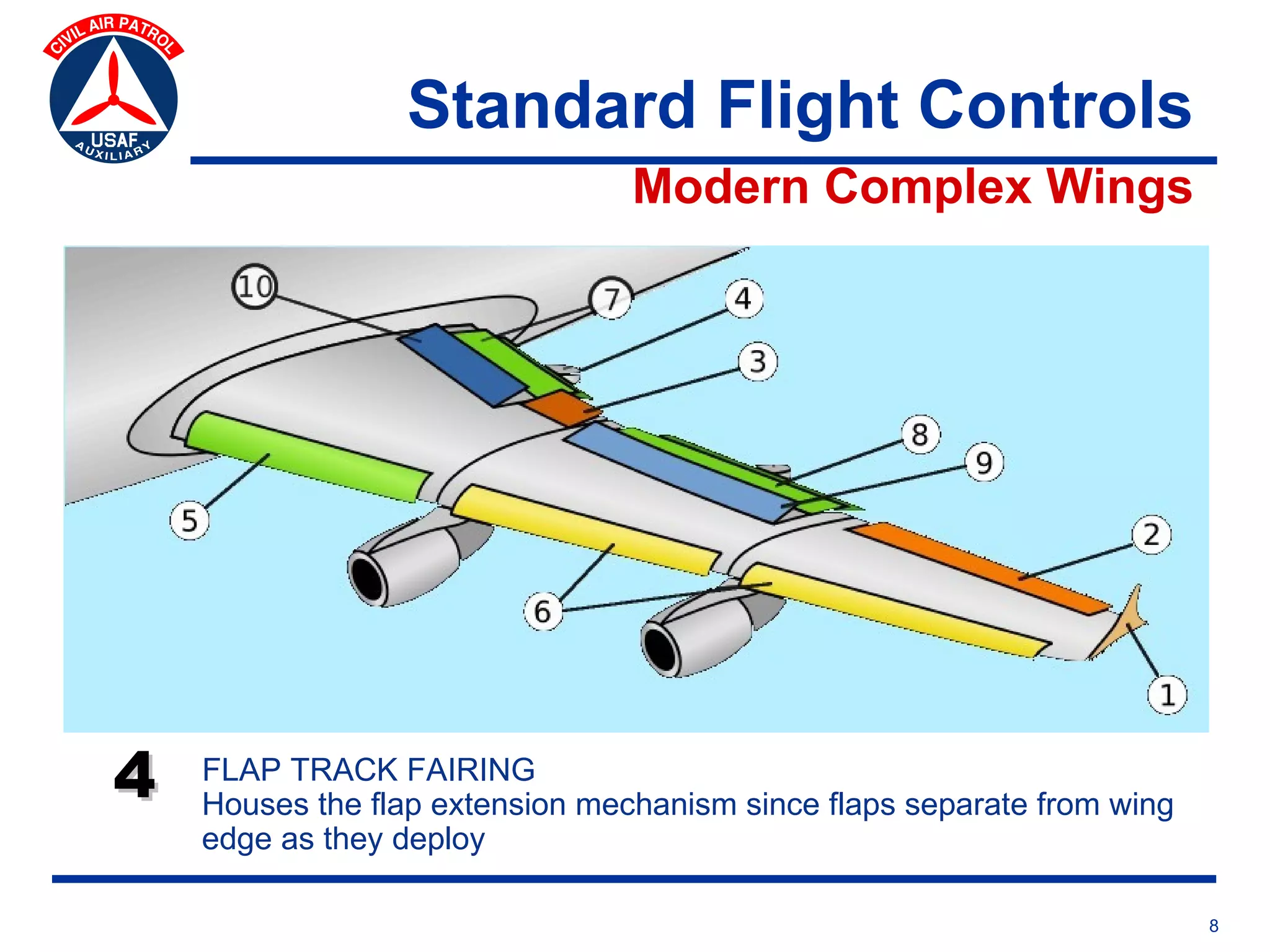
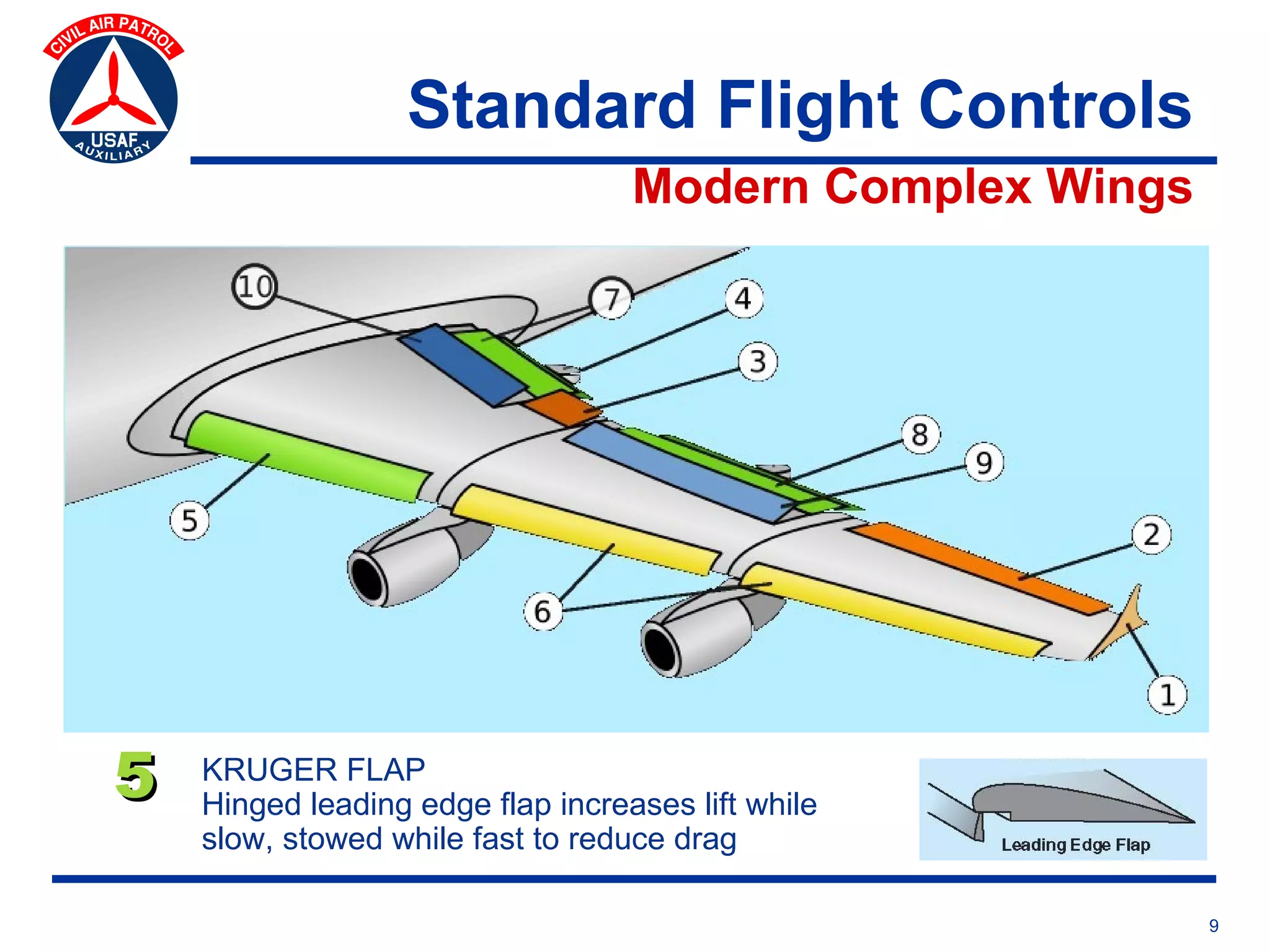
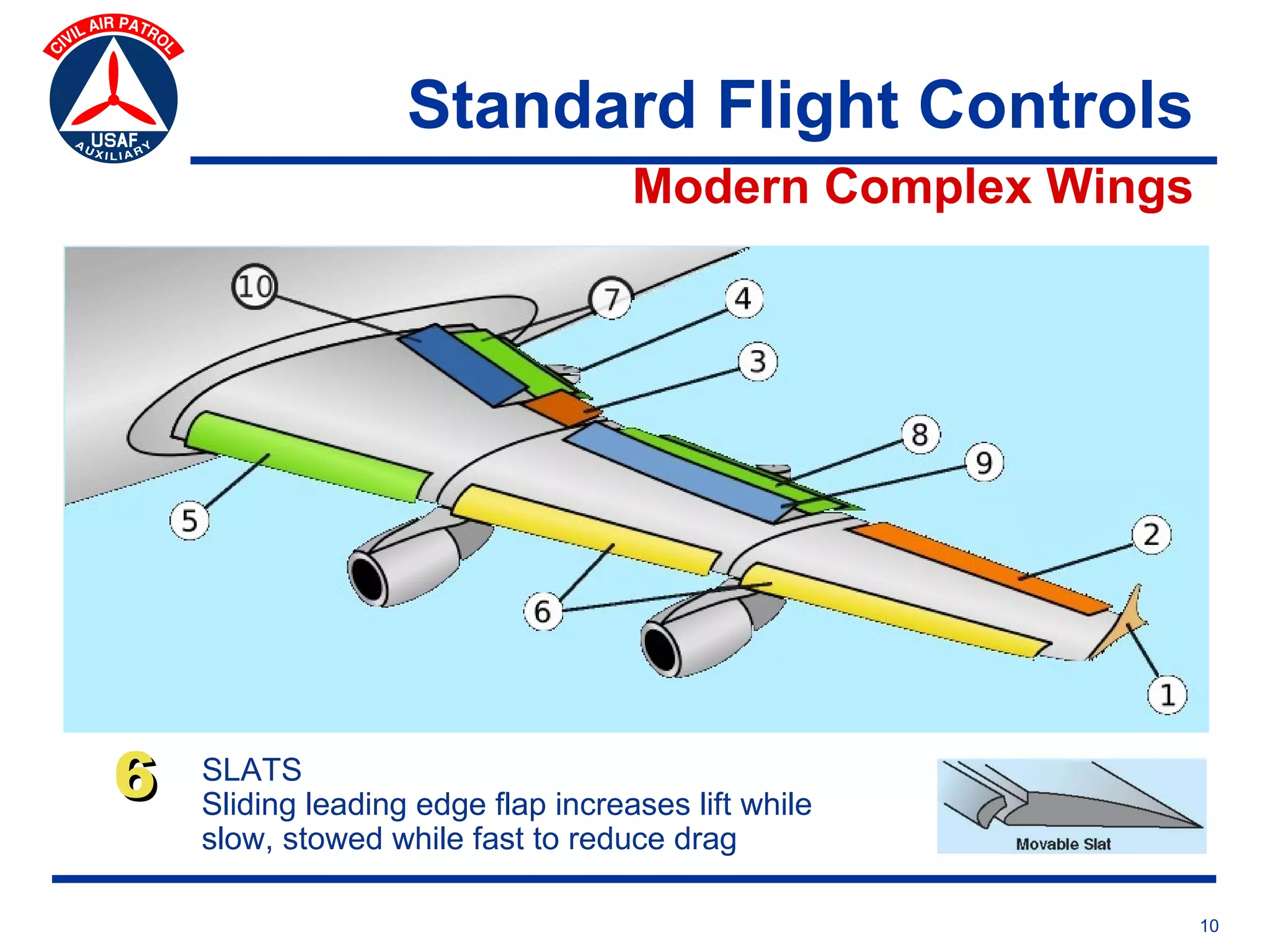
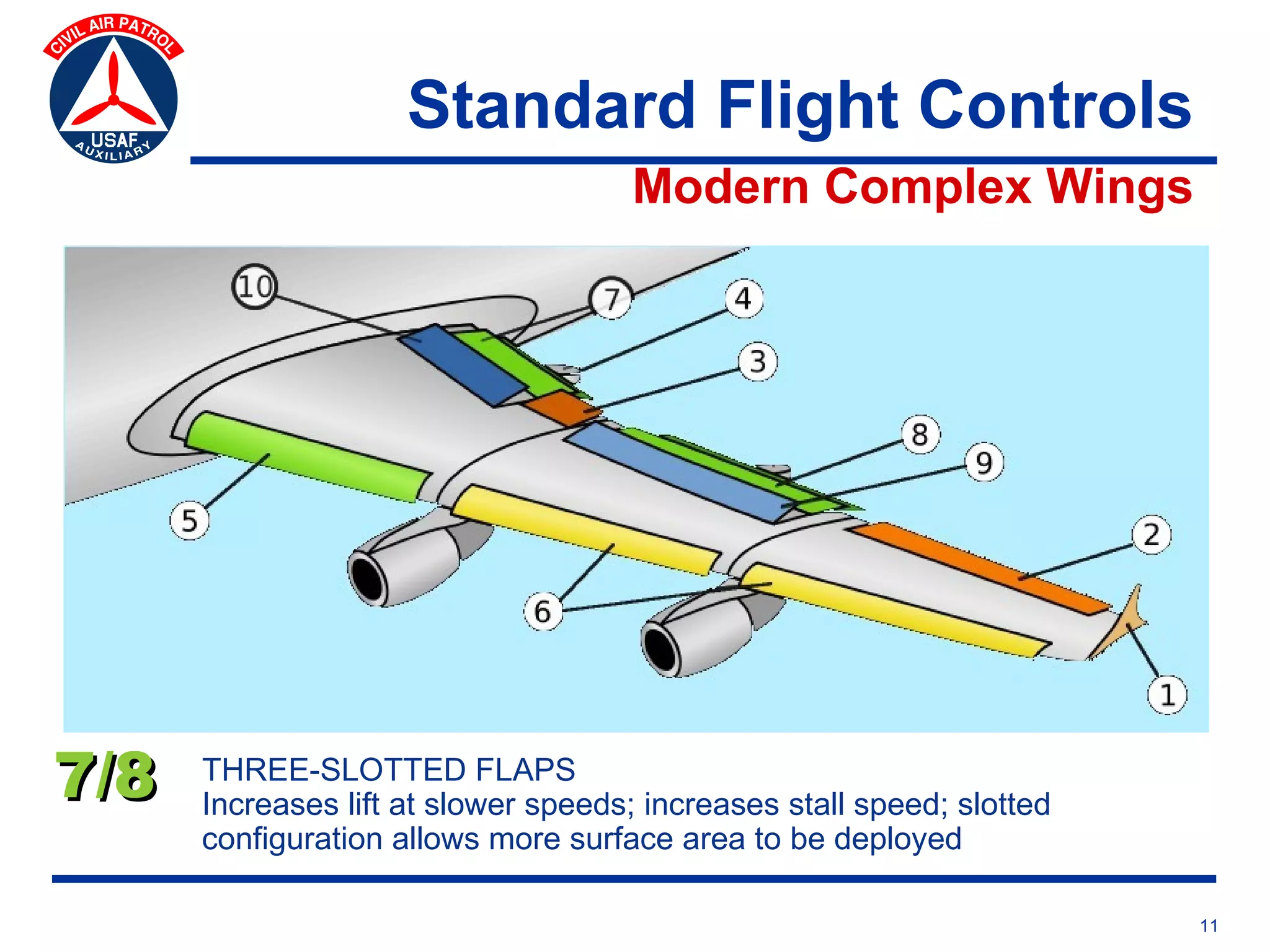
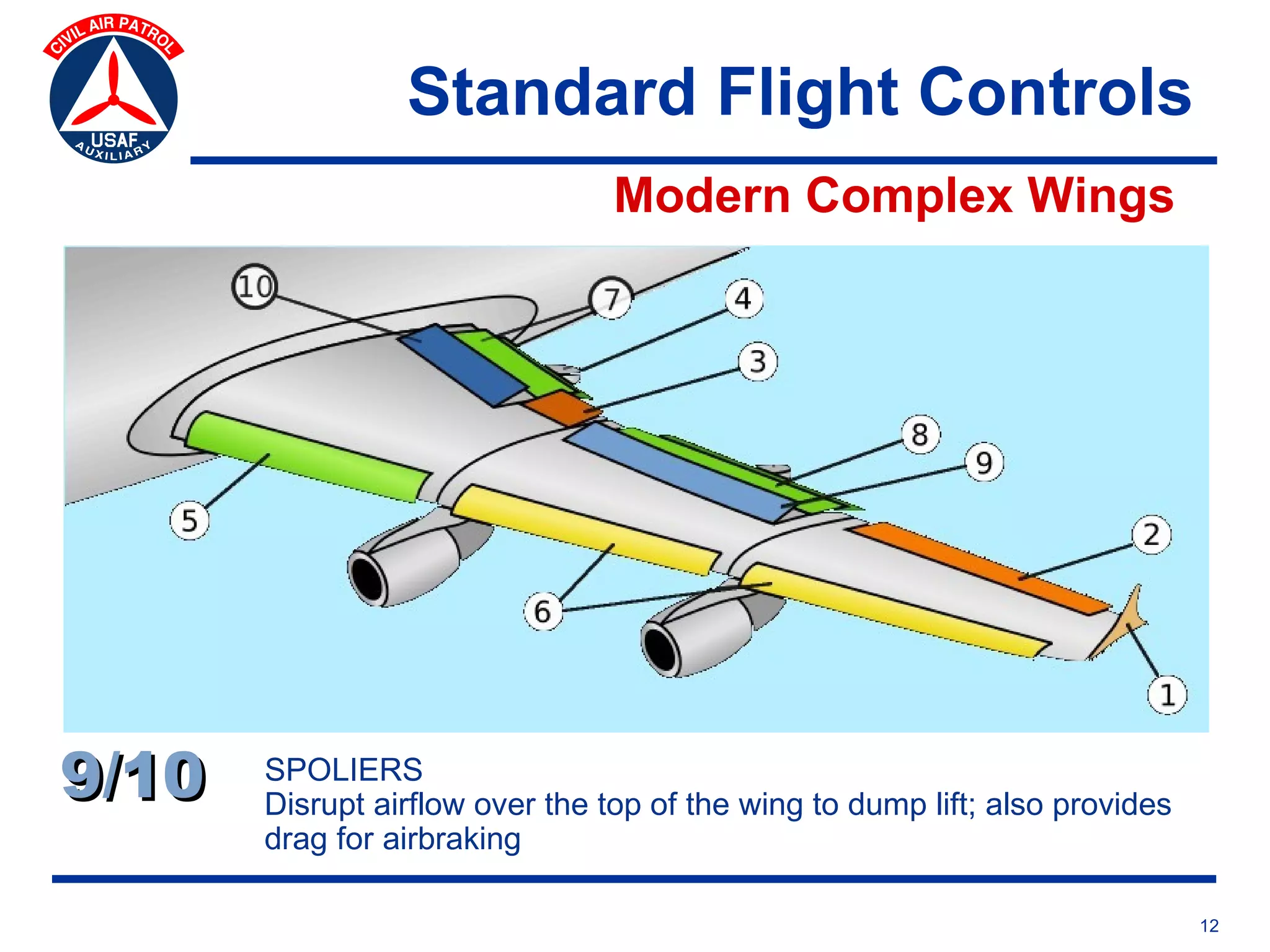
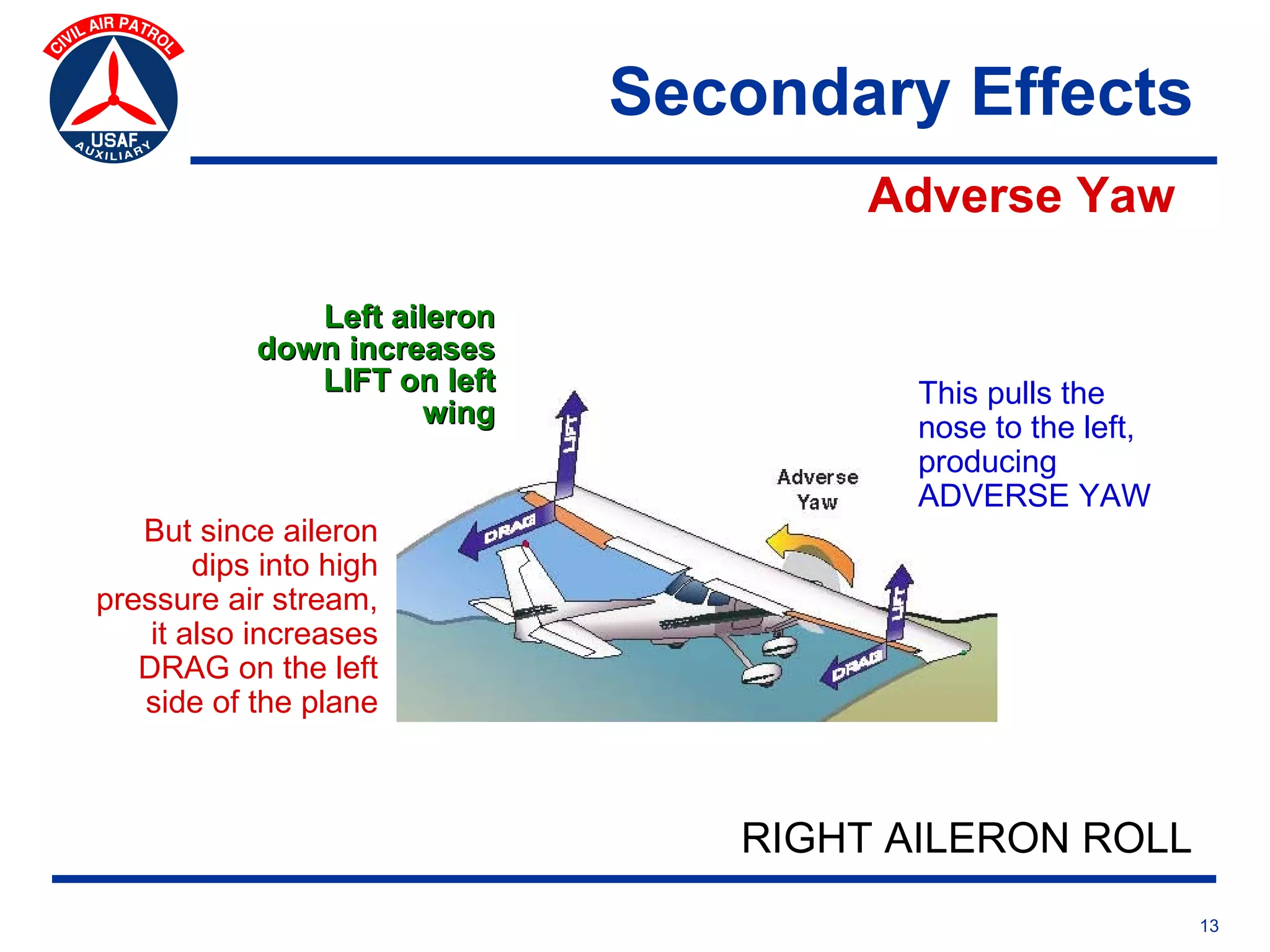
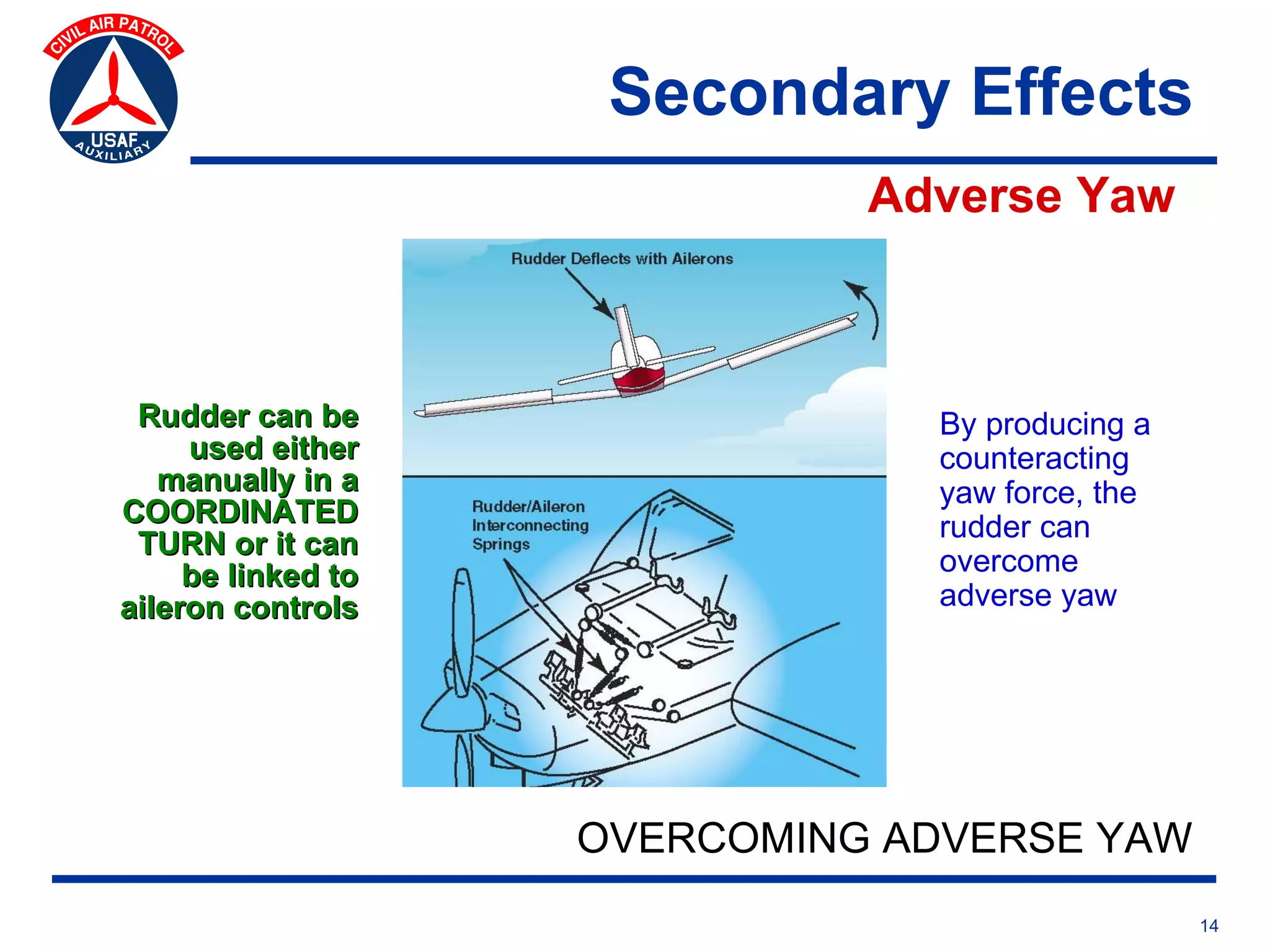
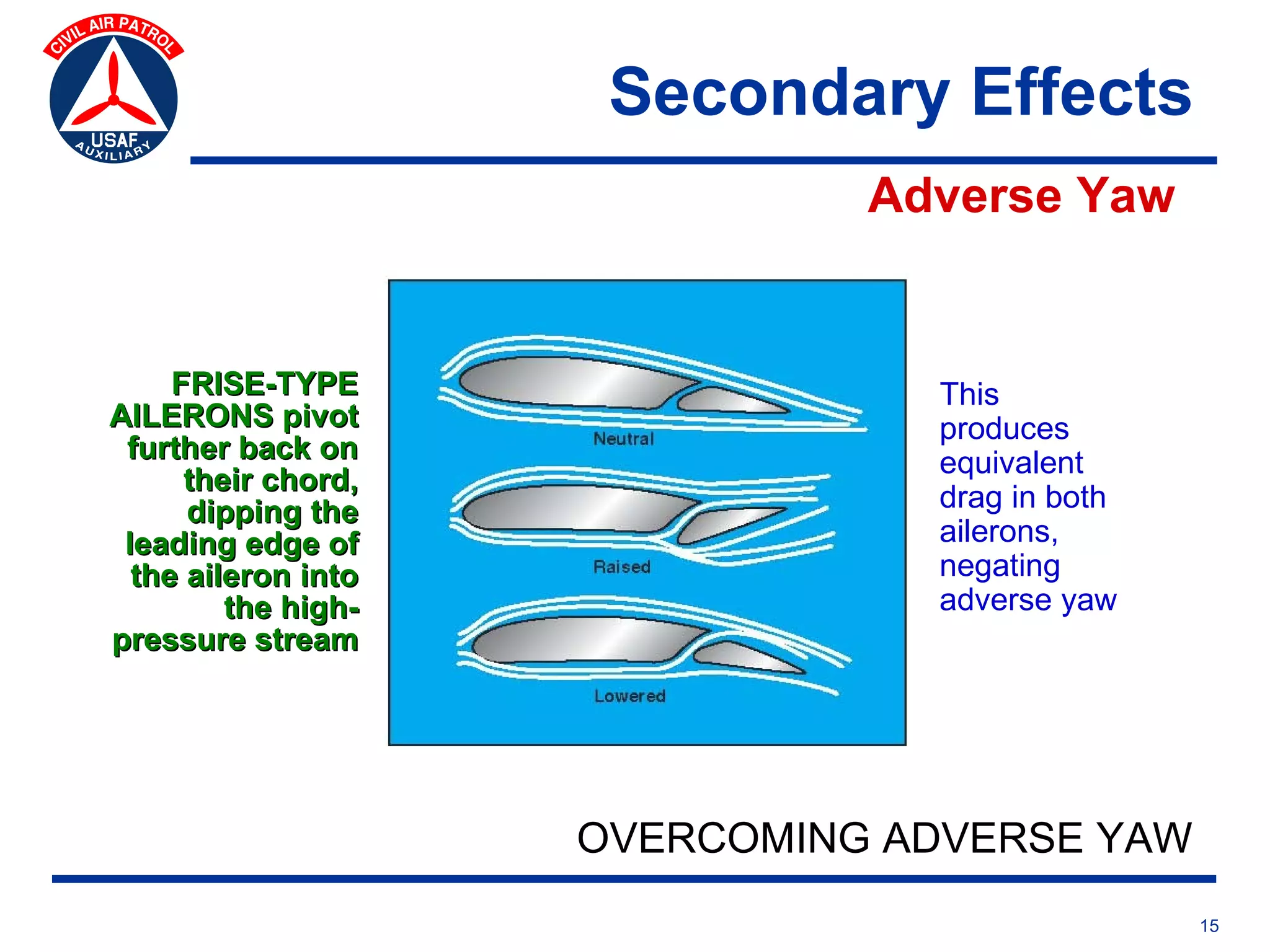
This document provides an overview of advanced flight controls. It begins by outlining four learning objectives related to describing aerodynamic forces, standard flight controls, secondary effects of controls, and alternative control types. It then defines the four basic aerodynamic forces and three axes of aircraft movement. Standard flight controls like ailerons, elevators, and rudders are illustrated. Secondary effects like adverse yaw are described. Finally, alternative control types such as stabilators, tailerons, spoilerons, and ruddervators are defined and their advantages and disadvantages discussed.