This document provides information about various aircraft instruments including:
- The airspeed indicator which uses ram air from the pitot tube and static air, and displays airspeeds like Vso and Vfe. Blockages of the pitot tube or static vent can cause errors.
- The altimeter which uses only static air input and displays various altitudes like indicated, pressure, and density altitude. Not updating the altimeter setting can cause errors.
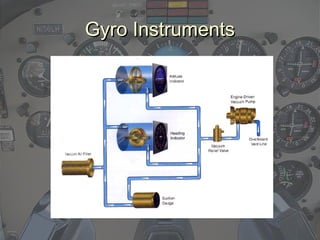
- Gyroscopic instruments like the attitude indicator and heading indicator which function based on the principles of rigidity in space and precession.
- The turn coordinator and inclinometer which indicate aircraft bank and slip/skid.
- The magnetic compass