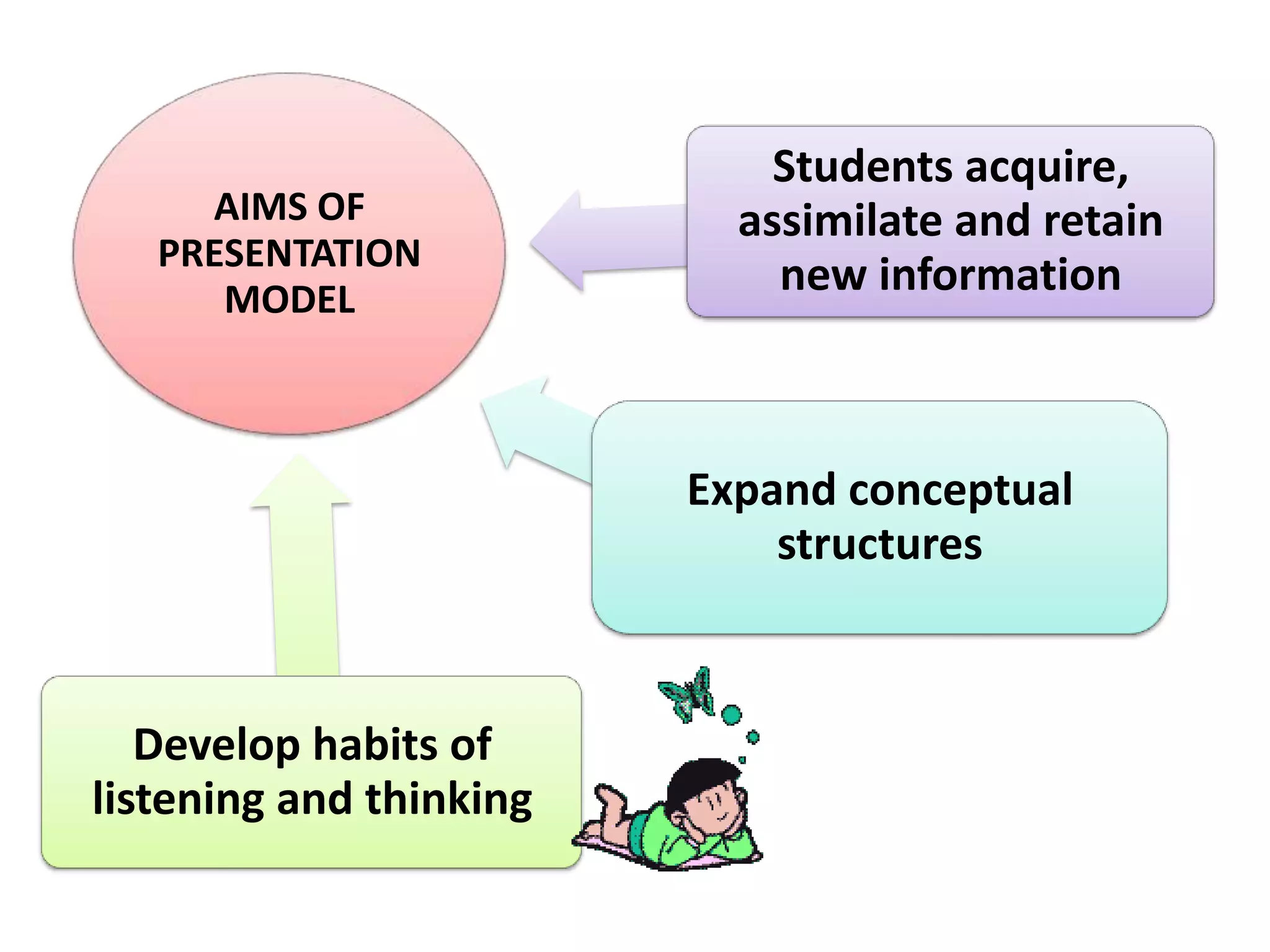
The document provides an overview of the presentation model of teaching. It discusses key aspects of the model including its aims to develop listening and thinking habits in students and help them acquire, assimilate, and retain new information. The model involves 4 major phases: clarifying lesson aims, presenting an advance organizer, presenting new information, and checking student understanding. It also discusses the importance of student prior knowledge, structuring lessons, using advance organizers, managing time and space, and assessing student learning.