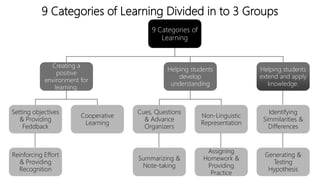
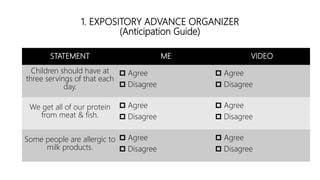
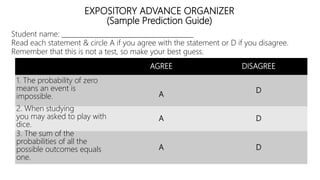
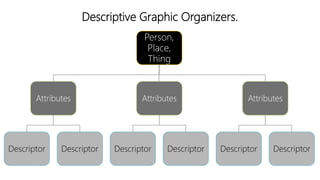
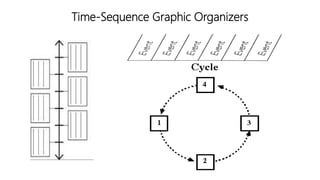
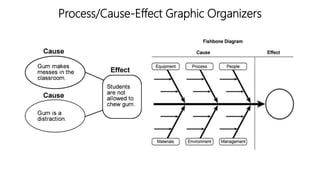
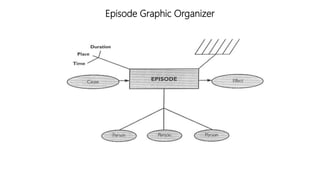
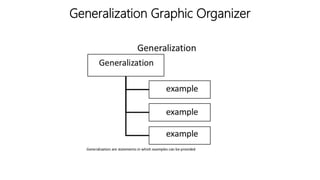
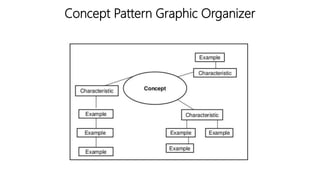
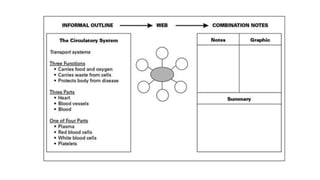
The document discusses principles of teaching and instructional strategies. It outlines three principles of teaching according to Donovan and Bransford: addressing prior knowledge, developing conceptual and factual knowledge, and promoting self-awareness of learning. Nine categories of instructional strategies are also described, divided into three groups: creating a positive learning environment, helping students develop understanding, and helping students apply knowledge. Specific strategies discussed include setting objectives, feedback, cooperative learning, cues and questions, non-linguistic representations, note-taking, homework, identifying similarities and differences, and generating hypotheses.