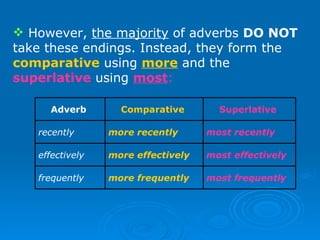
The document discusses the rules for forming comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs in English. It provides five rules for making comparatives and superlatives of adjectives based on their syllable structure and ending. It also explains that most adverbs do not take comparative and superlative endings, and instead use 'more' and 'most' as well as some irregular forms. The document provides examples of intensifiers that can be used with comparatives and expressions for making positive and negative comparisons.