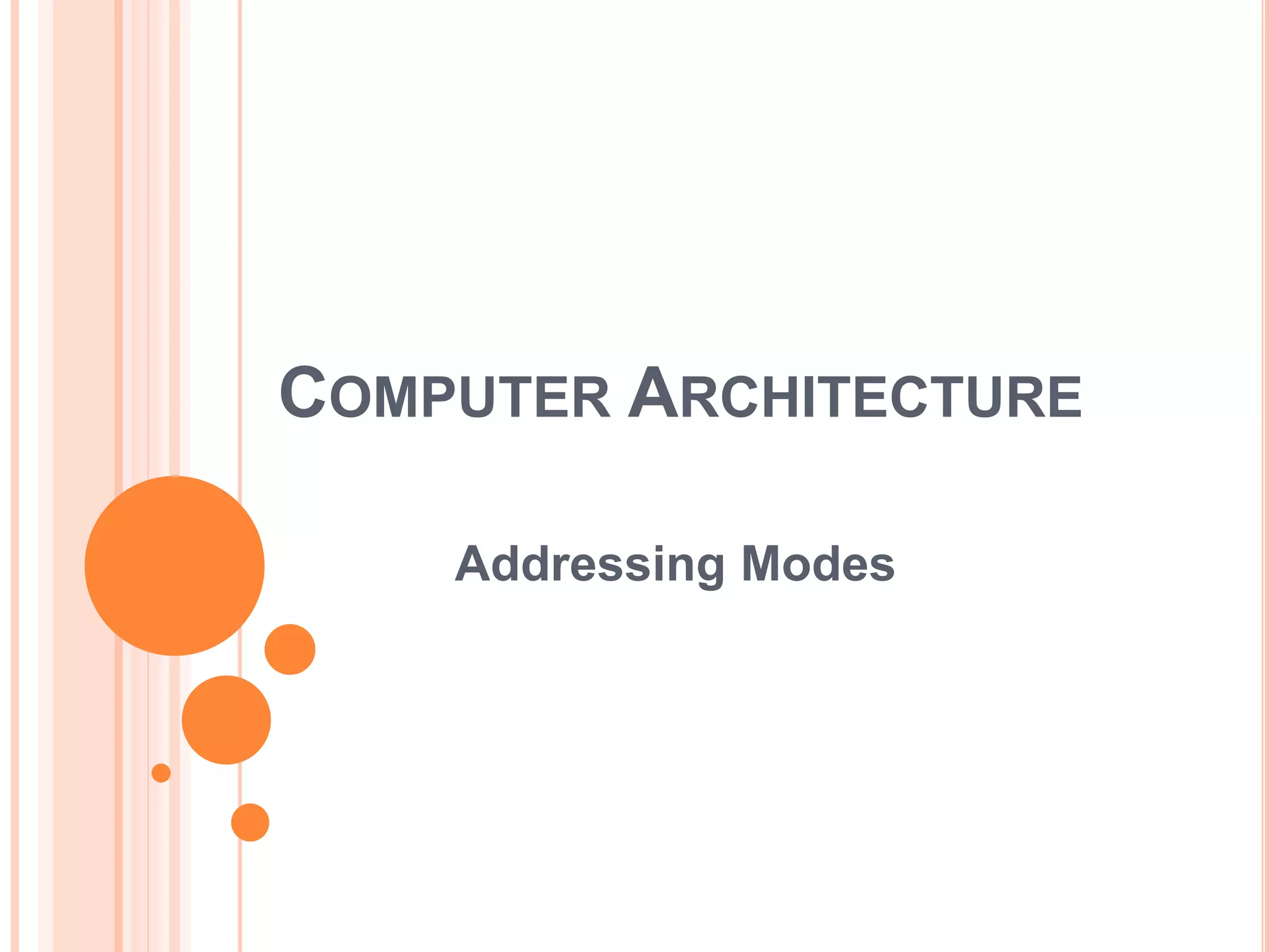
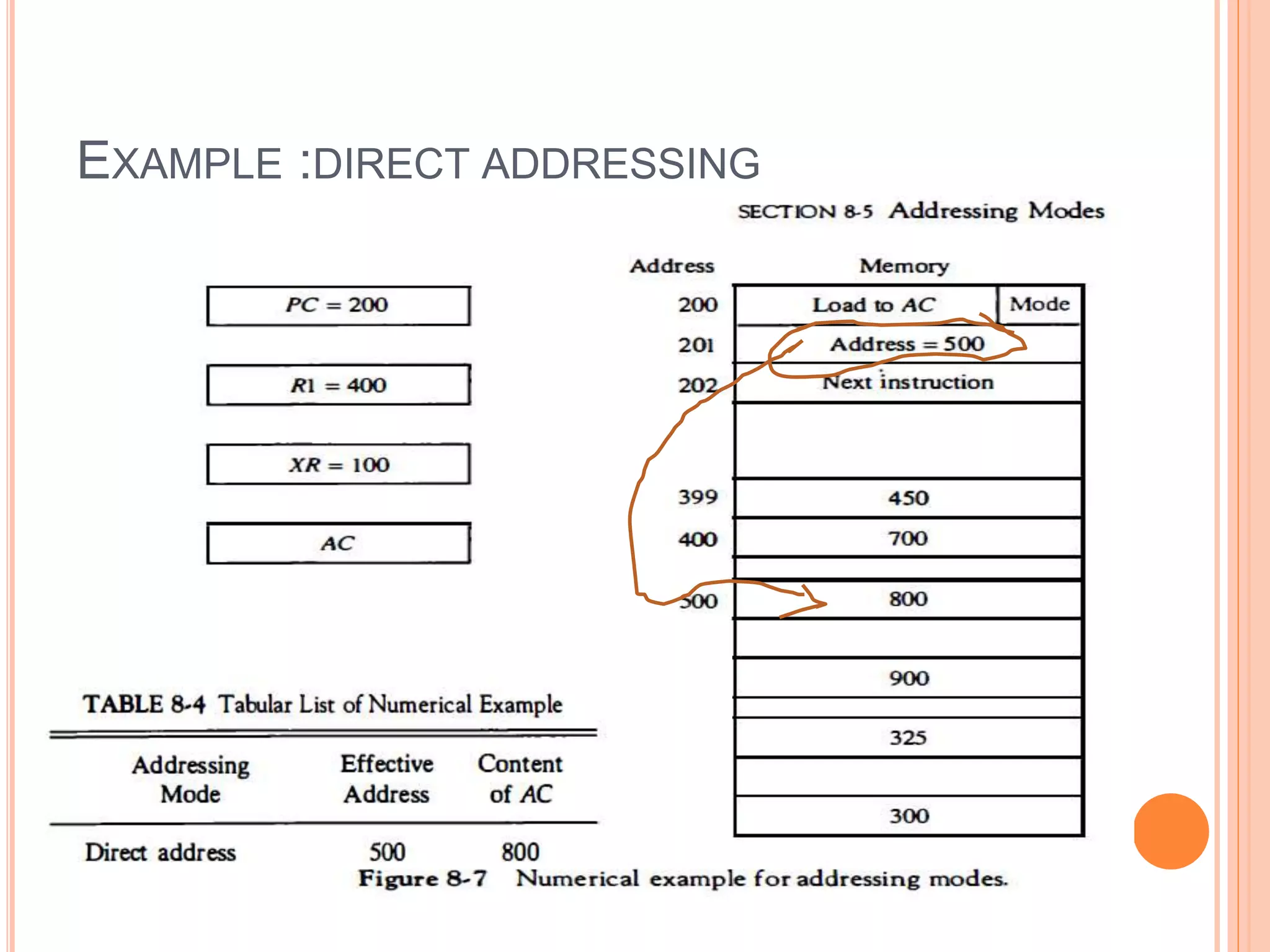
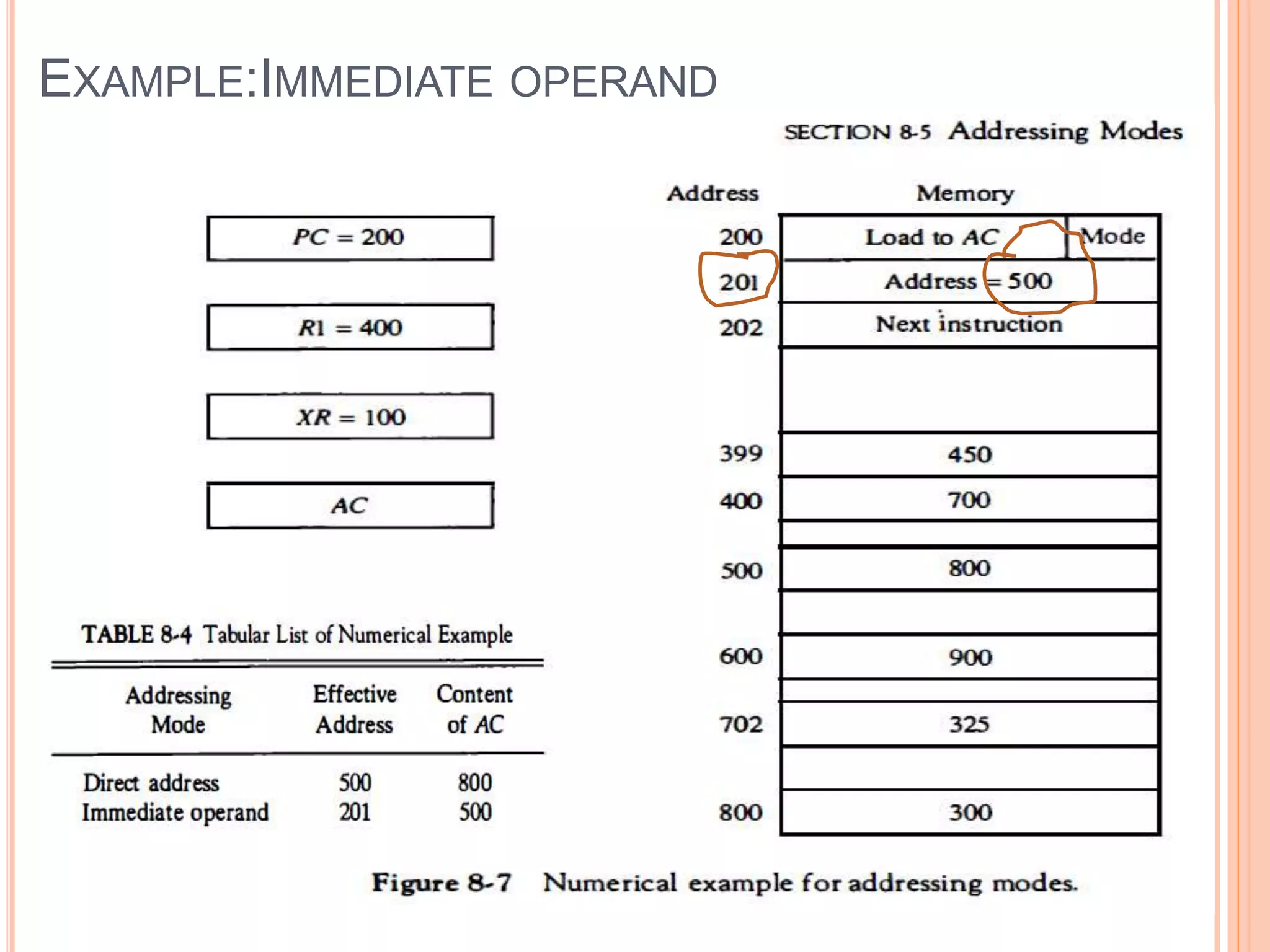
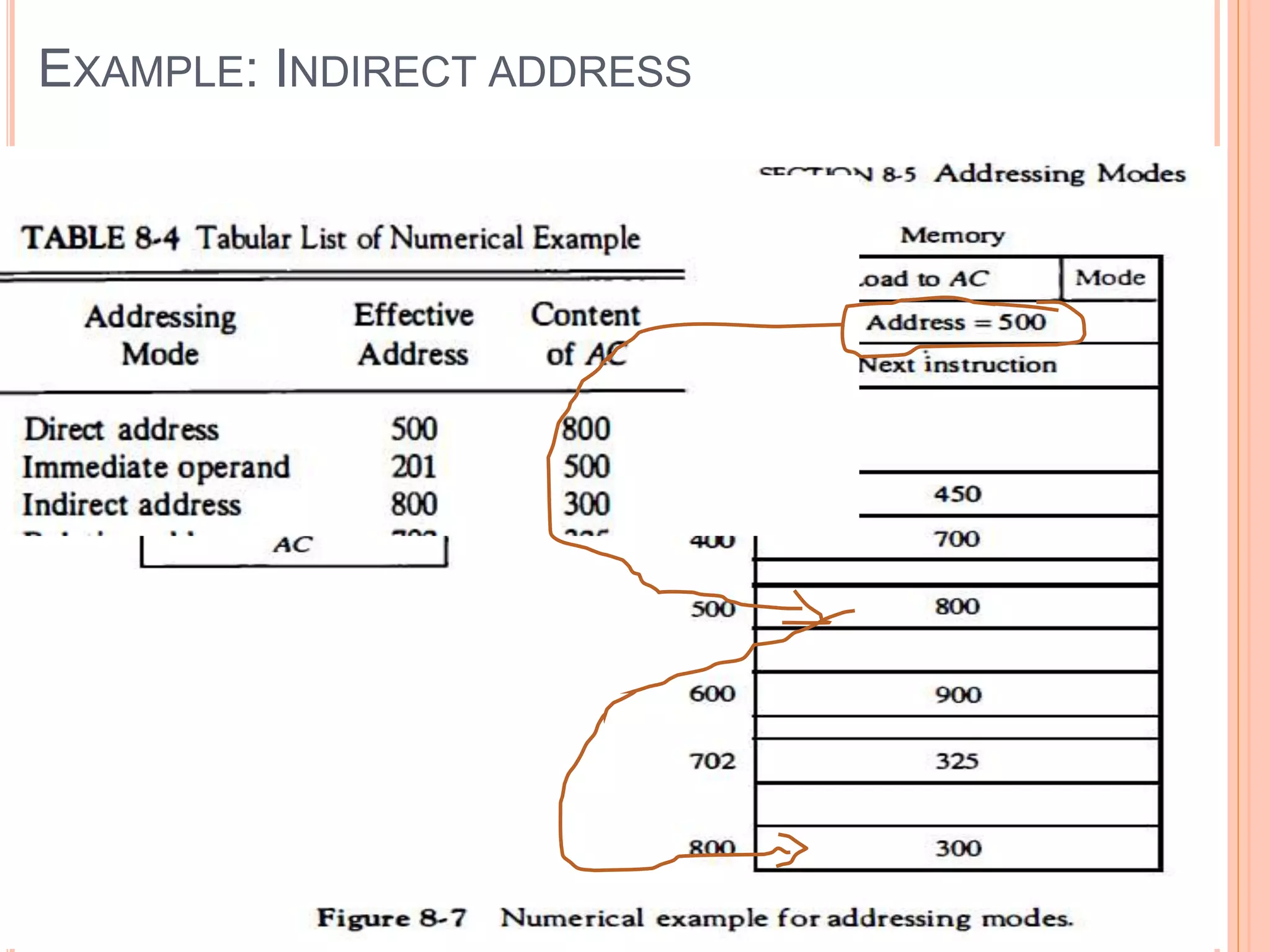
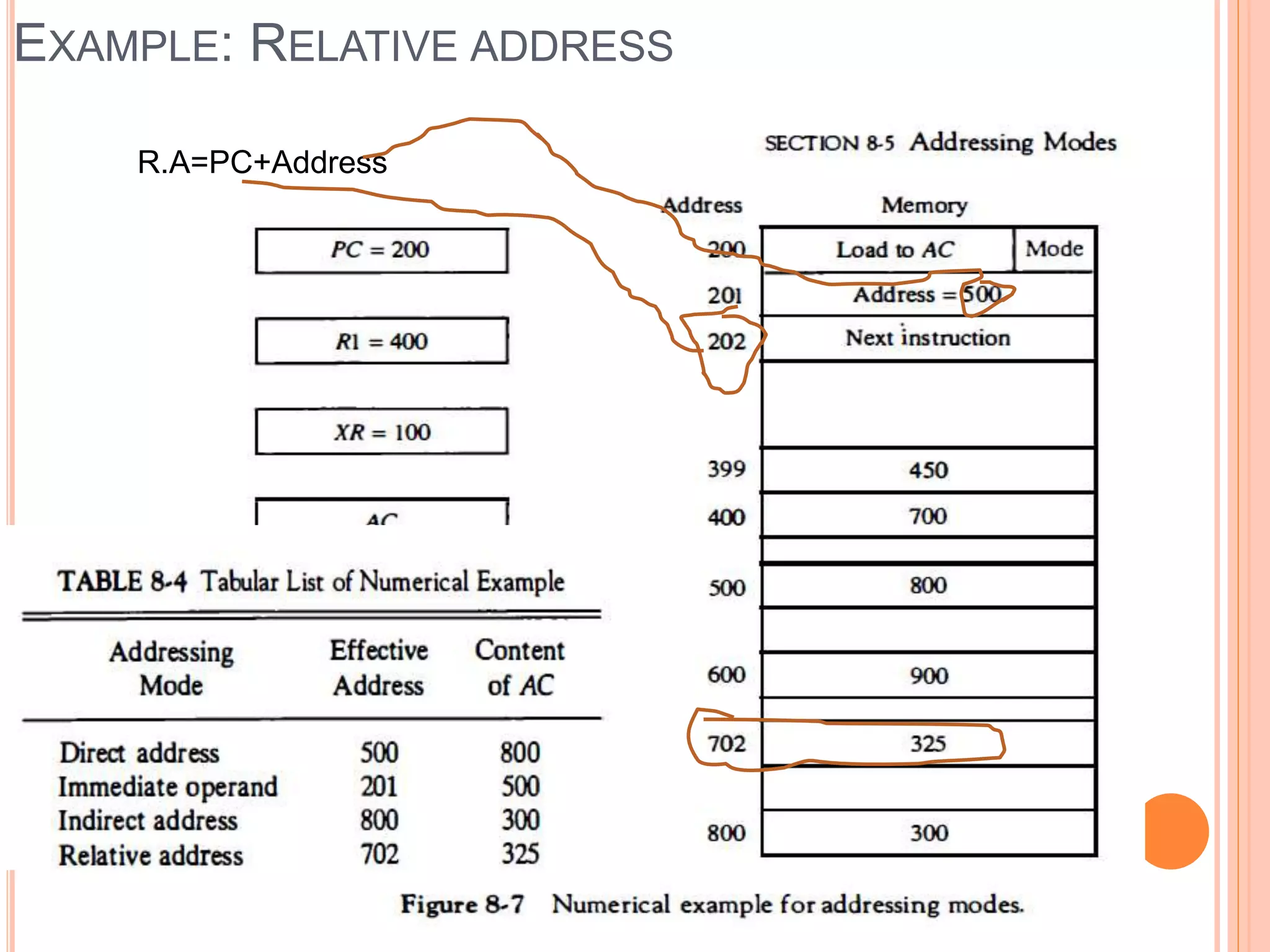
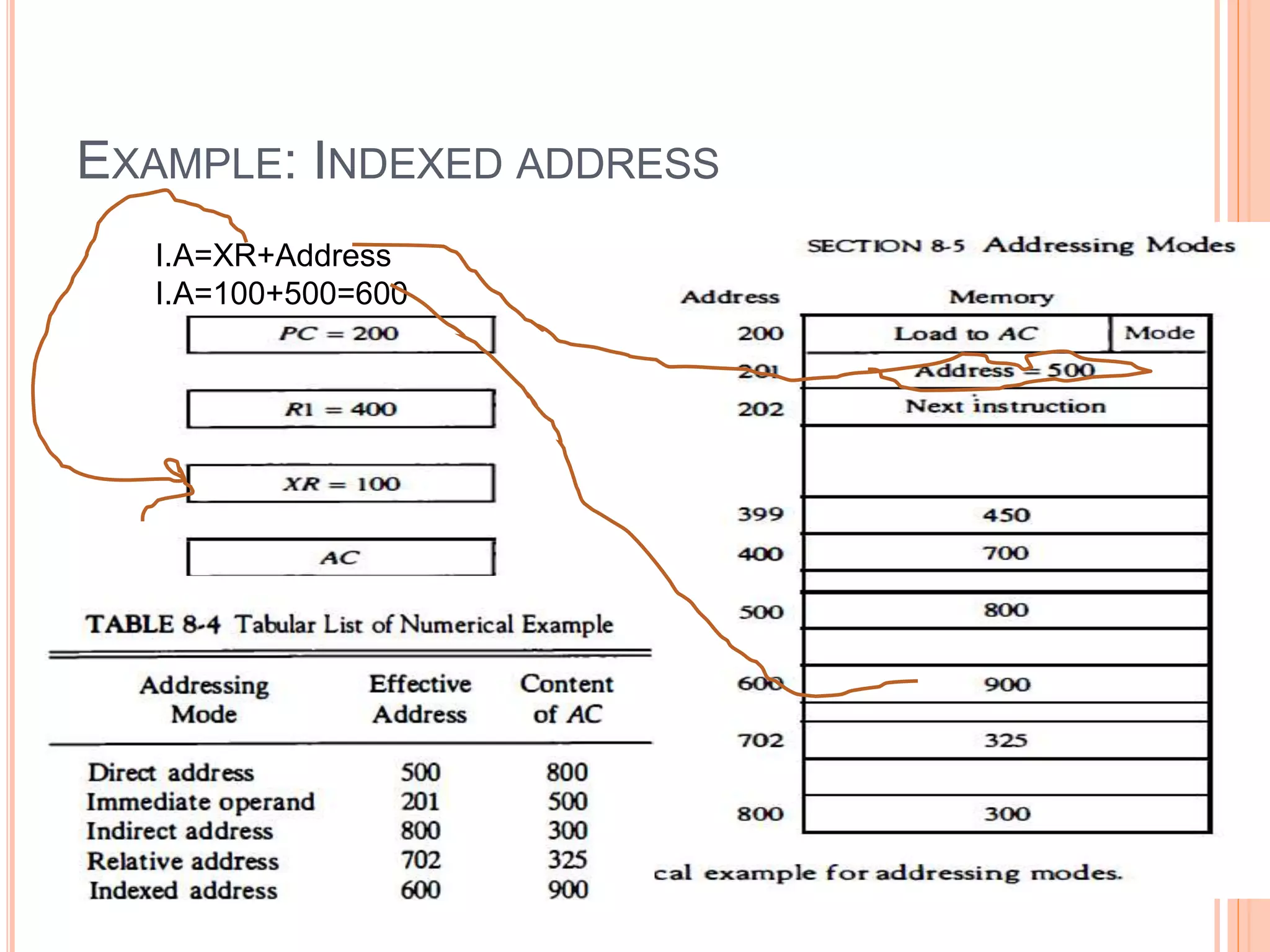
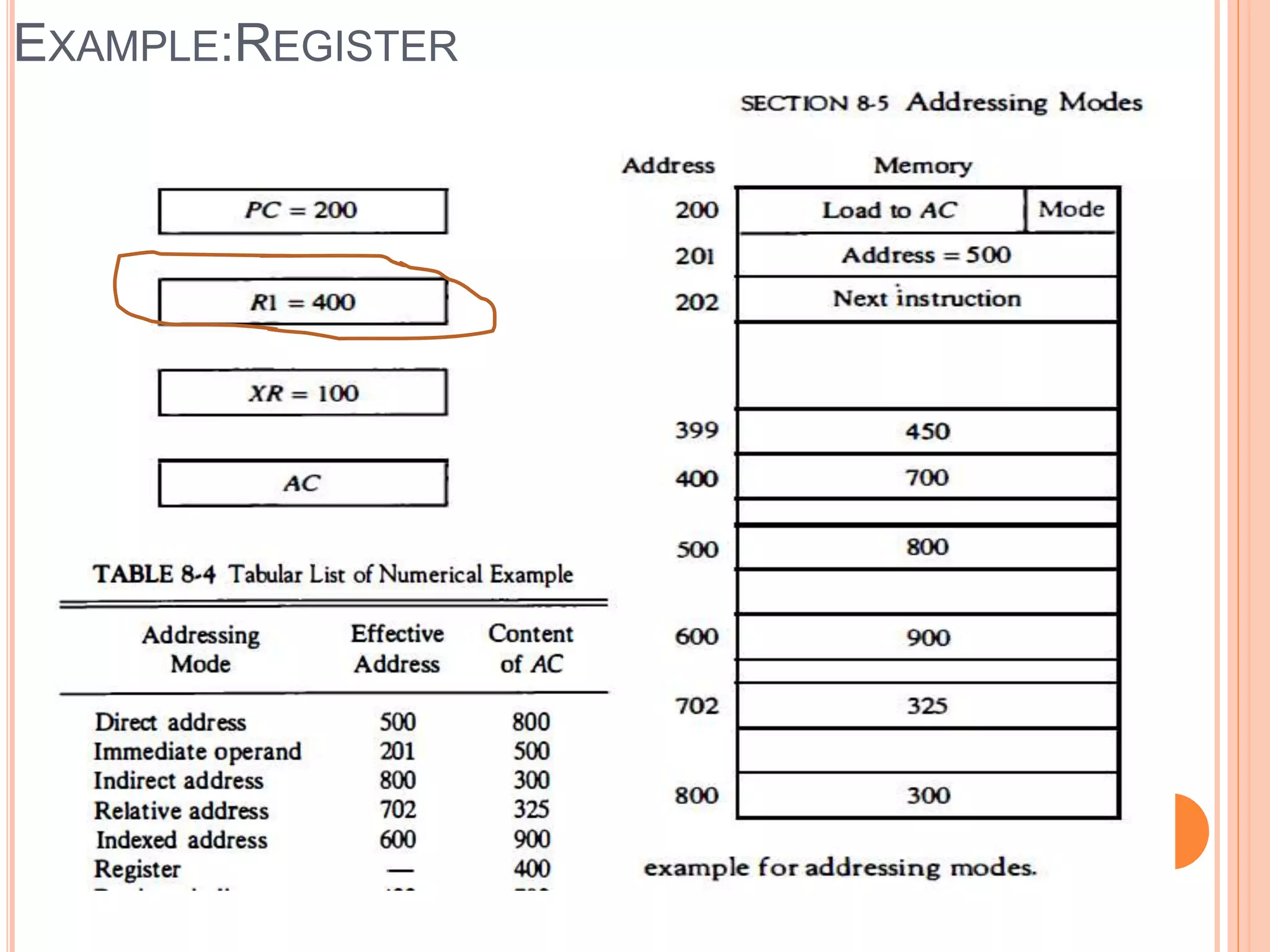
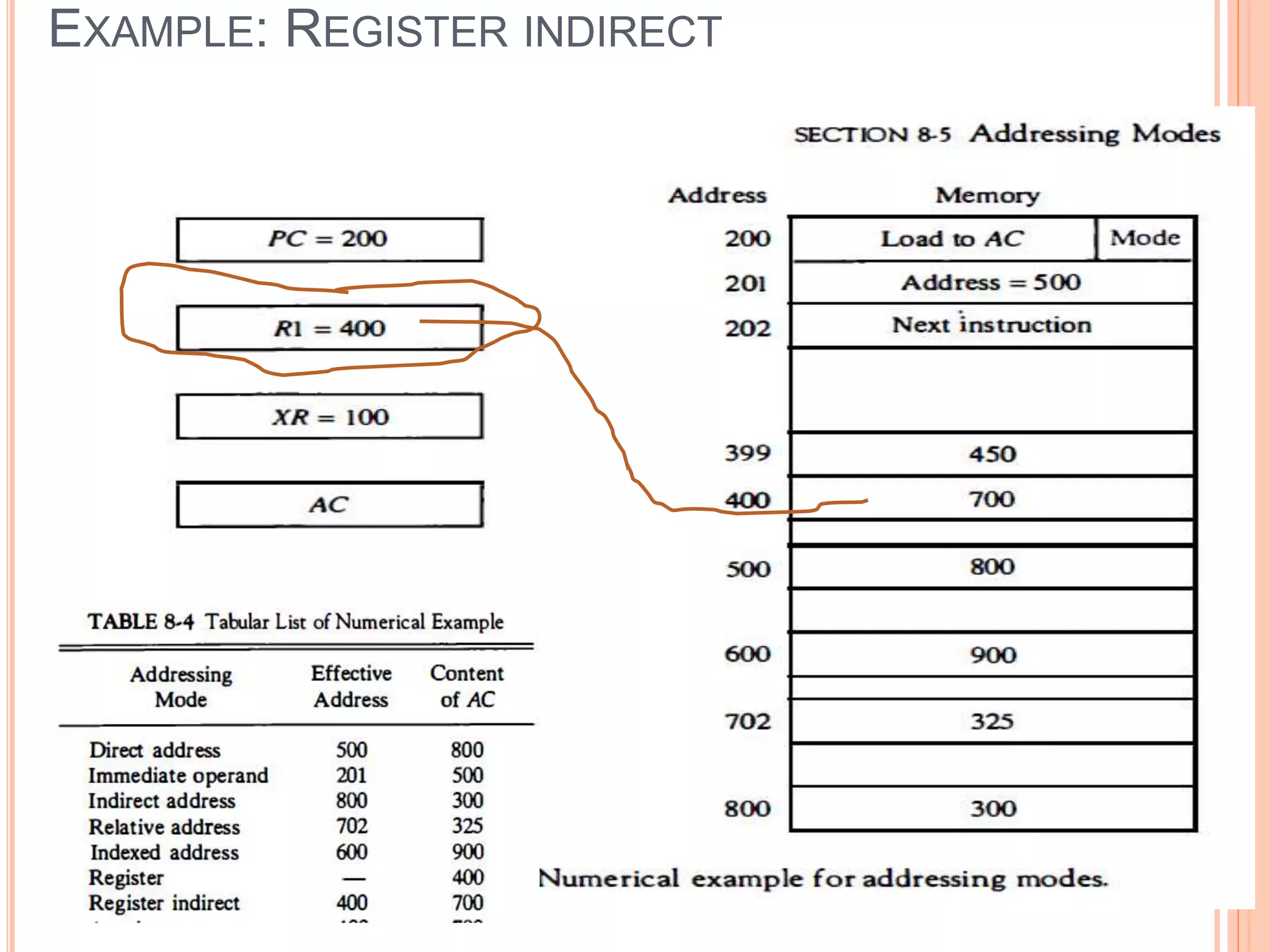
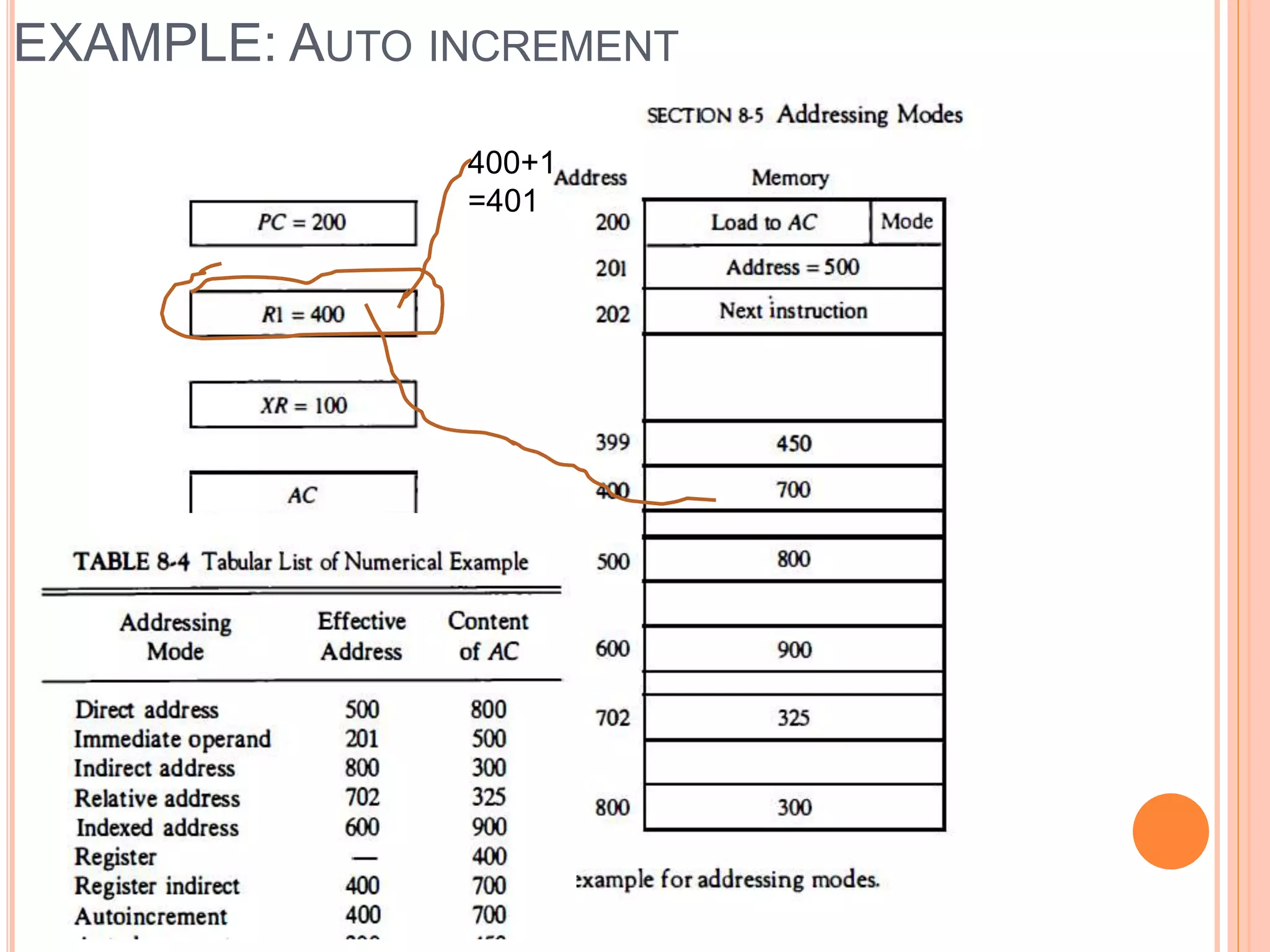
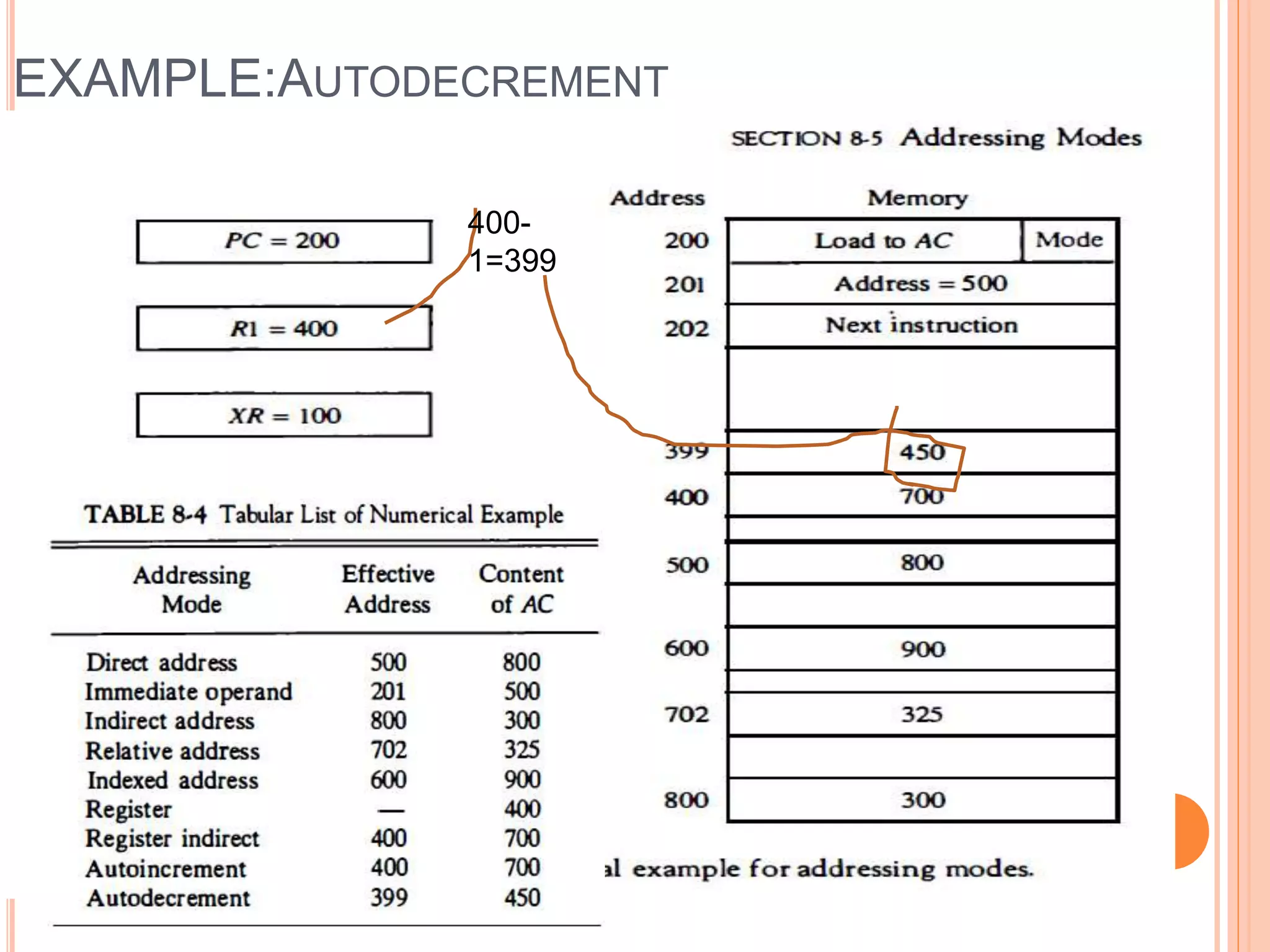
Addressing modes specify rules for interpreting or modifying instruction addresses to reference operands. There are several types of addressing modes including implied, where operands are specified implicitly; immediate, where the operand is in the instruction; and register, register indirect, direct, indirect, base register, relative, indexed, auto increment, and autodecrement addressing modes. Examples are provided to illustrate how each mode calculates the effective address.