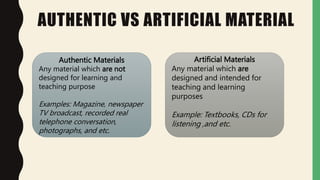
This document provides an overview of language learning materials and material development. It defines what materials are, discusses the forms materials can take (printed, non-printed, self-access), and their roles. It also covers the differences between authentic and non-authentic materials, advantages and disadvantages of each. Additionally, it examines evaluating and adapting textbooks, factors in textbook development, and criteria for evaluation. The document concludes with discussing the nature of material development and considerations for preparing materials for language programs.