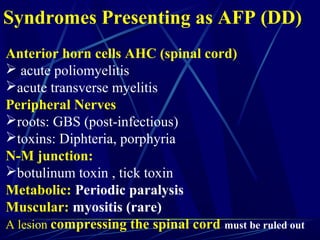
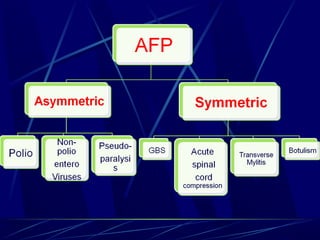
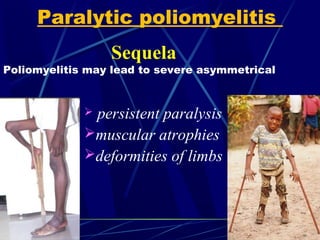
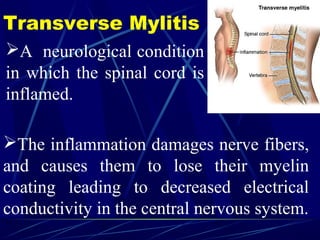
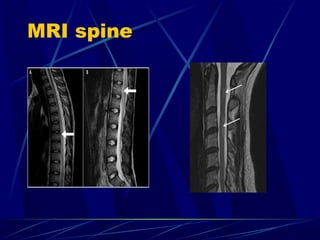
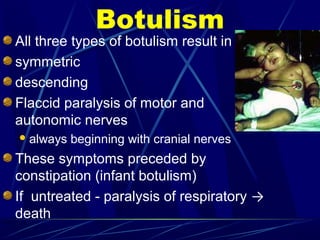
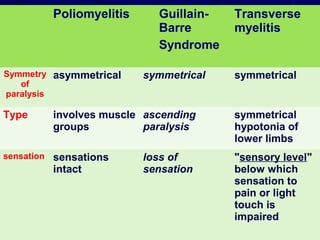
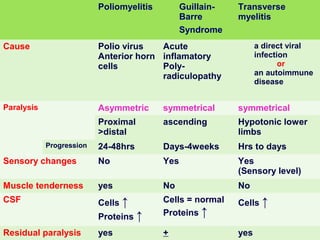
Acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) is characterized by sudden onset of weakness or paralysis over a period of 15 days in patients under 15 years old. The most common causes of AFP are poliomyelitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and transverse myelitis. Poliomyelitis is caused by poliovirus and typically causes asymmetric flaccid paralysis. Guillain-Barré syndrome is an acute post-infectious polyneuropathy that causes progressive symmetric paralysis. Transverse myelitis involves inflammation of the spinal cord that damages nerve fibers and causes symmetric paralysis, sensory loss, and autonomic dysfunction below the level of inflammation.