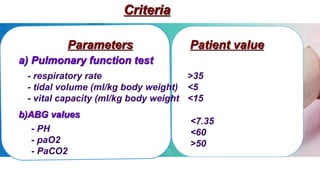
A mechanical ventilator is a machine that assists patients who are unable to breathe on their own by mechanically controlling oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange. It is used to maintain ventilation and oxygenation for patients with conditions like respiratory failure, respiratory distress syndrome, or neurological impairment. Nurses caring for patients on ventilators monitor vital signs and respiratory status, ensure proper ventilator settings are used, turn patients to prevent bed sores, and suction airways when needed.