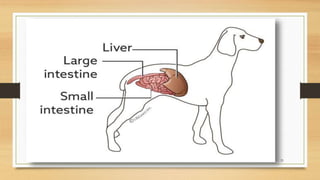
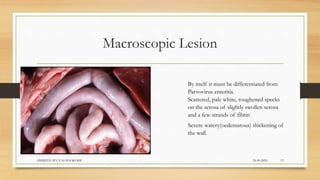
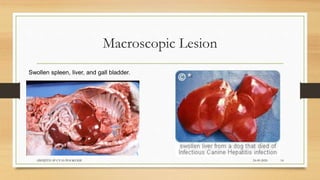
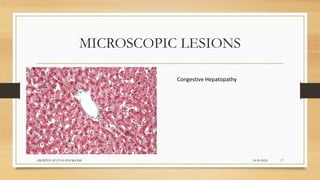
Infectious canine hepatitis is a contagious viral disease of dogs caused by canine adenovirus-1. Clinical signs vary from mild fever and congestion to severe depression, reduced white blood cells, and bleeding disorders. The virus replicates in the liver, causing liver damage and hemorrhaging. Diagnosis is based on clinical signs, virus isolation from body fluids, antigen detection, and histopathology showing intranuclear inclusion bodies in hepatocytes. Vaccination provides effective prevention and control of the disease.







![CLINICAL SIGNS
• Most infections are asymptomatic.
• In systemic infections, there are 3 overlapping syndromes which are usually seen in puppies less
than 6 months old.
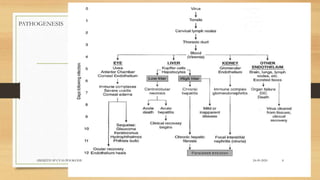
• Per-acute disease. Dog is found dead either without apparent preceding illness or after an illness
lasting only 3 or 4 hours. Due to massive destruction of hepatocytes.
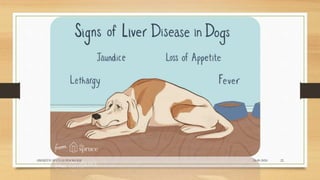
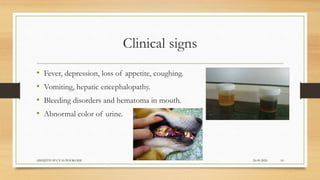
• Acute disease. Dogs that survive the viremic phase. Fever, depression, vomiting, bloody diarrhea,
petechial and ecchymotic hemorrhages of the gums, pale mucous membranes, and jaundice.
• Mild cases.
• Clinical signs in uncomplicated ICH last 5-7 days prior to improvement.
• Encephalitis. Common in foxes [fox encephalitis] but less common in dogs.
24-09-2020ABHIJITH SP CVAS POOKODE 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ichabhijith-200924054913/85/Infectious-Canine-Hepatitis-9-320.jpg)
![Clinical Signs
• Kidney [glomerulonephritis]. Chronic kidney lesions result from immune
complex reactions after recovery from acute or subclinical disease.
• Disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC]. A frequent complication
of ICH, it begins in the early viremic phase of the disease.
• DIC may be triggered by exposure of subendothelial collagen and
subsequent platelet aggregation and/or inability of the damaged liver to
remove activated clotting factors.
• The urine gets abnormal colour due to liver damage and kidney damage.
24-09-2020ABHIJITH SP CVAS POOKODE 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ichabhijith-200924054913/85/Infectious-Canine-Hepatitis-11-320.jpg)


![Why Blue Eye?
• This type III hypersensitivity may be seen during the convalescent phase in about 20% of
clinical cases of infectious canine hepatitis, or 2-3 weeks following vaccination with
modified live canine adenovirus. It is characterized by an anterior uveitis with severe damage
to corneal endothelium, causing profound corneal oedema.
• On or about day 4, virus enters the aqueous humor from the blood and replicates in corneal
endothelial cells.
• By day 7. Severe anterior uveitis and corneal edema develop. Circulating immune complexes
deposited on corneal endothelium [immune complex hypersensitivity] results in complement
activation, neutrophil chemotaxis, frustrated phagocytosis, and corneal endothelial damage.
• Disruption of the corneal endothelium results in accumulation of edematous fluid in the
corneal stroma.
24-09-2020ABHIJITH SP CVAS POOKODE 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ichabhijith-200924054913/85/Infectious-Canine-Hepatitis-16-320.jpg)
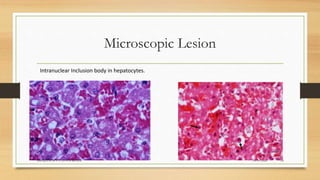
![DIAGNOSIS
• 1.Tentative Diagnosis-Based on clinical signs, history, vaccination schedule
and details from owner.
• 2. Virus isolation in cell culture: Urine, blood, tissue homogenates, etc.
• 3. Antigen detection in tissues: Fluorescent antibody test; PCR.
• 4. Gross and histopathology; hematology [leukopenia].
• 5. Paired sera: Employs virus neutralization, ELISA, or hemagglutination-
inhibition tests.
24-09-2020ABHIJITH SP CVAS POOKODE 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ichabhijith-200924054913/85/Infectious-Canine-Hepatitis-19-320.jpg)