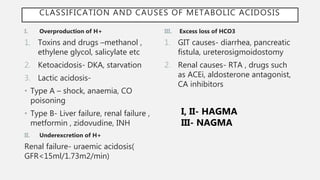
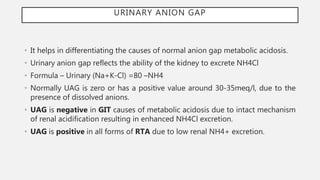
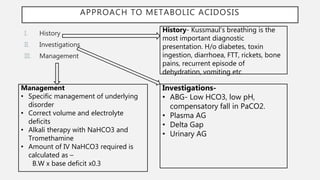
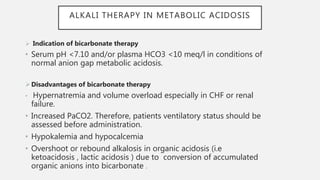
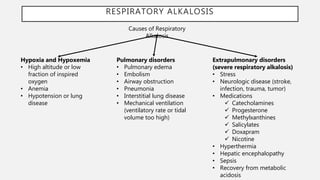
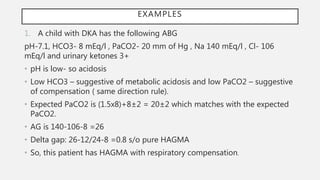
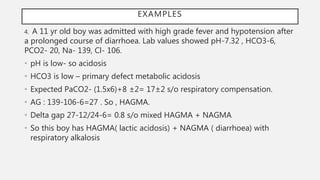
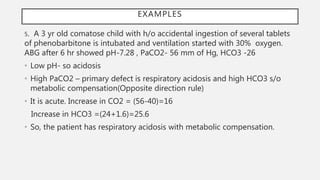
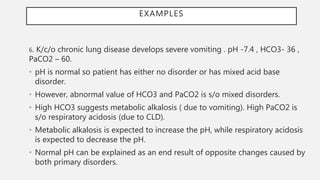
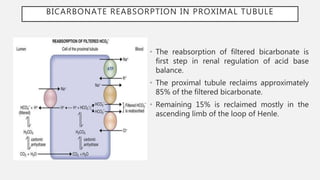
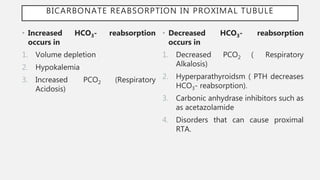
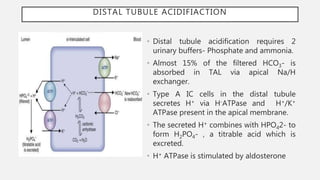
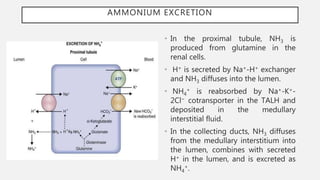
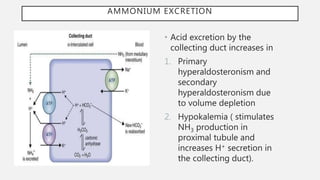
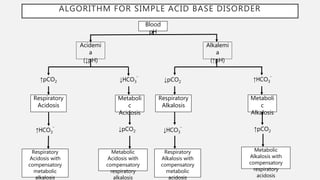
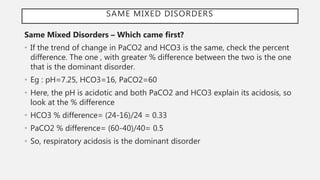
This document discusses acid-base disorders. It begins by explaining that the human body maintains a slightly basic pH through various buffering mechanisms. It then describes the bicarbonate buffer system and how the lungs, kidneys, and buffers work to regulate pH. It discusses the causes, classifications, and clinical features of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. Key points include how to interpret arterial blood gases, calculate anion and urine gaps, and determine compensations and mixed disorders. The document provides an in-depth overview of acid-base physiology and pathophysiology.

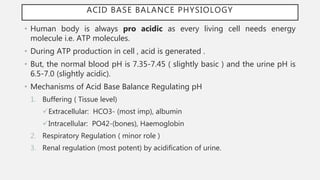
![BUFFERS
• Buffers are substances that attenuate the change in pH that occurs when acids
or bases are added to the body.
• Extracellular buffers accomplish buffering of metabolic causes and intracellular
buffers to that of respiratory causes.
• The pH at which a buffer is 50% dissociated is its pKa ( ionization constant
of acid).
• The best physiologic buffers have a pKa close to 7.40 .When a pH is lower
than pKa of a buffer ,there is more acid than base and vice versa.
• pH of body fluids is calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbach equation
which expresses the relationship among pH , pKa and the concentrations of an
acid and its conjugate base. This relationship is valid for any buffer.
• Equation: pH = 6.1 + 𝑙𝑜𝑔
[𝐻𝐶𝑂3
−]
[𝐶𝑂2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abgfinal-220624095507-9bd7cba1/85/Acid-Base-Disorders-3-320.jpg)






![COMPENSATIONS
Disorder Primary Event Compensation
Metabolic Acidosis ↓ [HCO3
¯] ↓ pCO2
Metabolic Alkalosis ↑ [HCO3
¯] ↑ pCO2
Respiratory Acidosis
Acute (<24 hours) ↑ pCO2 ↑ [HCO3
¯]
Chronic (3-5 days) ↑ pCO2 ↑↑ [HCO3
¯]
Respiratory Alkalosis
Acute (<24 hours) ↓ pCO2 ↓ [HCO3
¯]
Chronic (3-5 days) ↓ pCO2 ↓↓ [HCO3
¯]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abgfinal-220624095507-9bd7cba1/85/Acid-Base-Disorders-19-320.jpg)


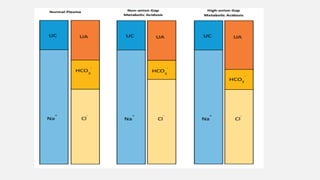
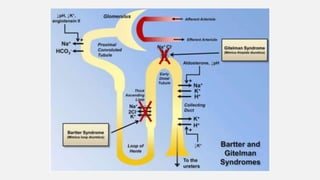
![PLASMA ANION GAP
• Plasma Anion gap is the difference between measured cations (Na+) and the
measured anions (Cl-+ HCO3
-). It is also the difference between unmeasured
cations (K , Mg , Ca) and the unmeasured anions ( albumin, phosphate, urate,
sulfate).
• Formula : Na – (Cl – HCO3)
• Normal value 8-12 meq/l or 12±2meq/l
• A 1g/dl decrease in albumin concentration decreases anion gap by 2.5 meq/l. So,
anion gap corrected for albumin is
[Na]-[Cl+HCO3]+2.5(4-albumin)
• High anion gap metabolic acidosis(HAGMA)-AG is high as HCO3 gets
overconsumed to neutralise accumulated acids and increase in unmeasured
anions.
• Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis(NAGMA)- AG is normal as HCO3 loss is
accompanied by Cl reabsorption ( hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abgfinal-220624095507-9bd7cba1/85/Acid-Base-Disorders-23-320.jpg)