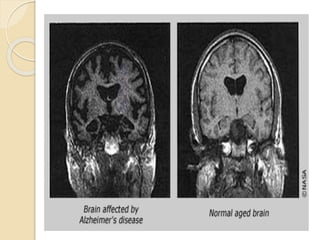
- Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive dementia characterized by cognitive decline and behavioral changes. It is the most common type of dementia and risk increases with age.
- The pathology of AD involves beta-amyloid plaques and tau neurofibrillary tangles in brain regions critical for memory and cognition. This leads to deficits in the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
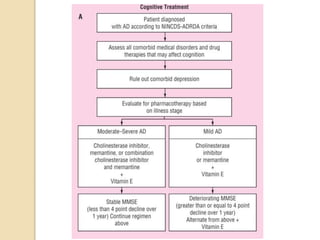
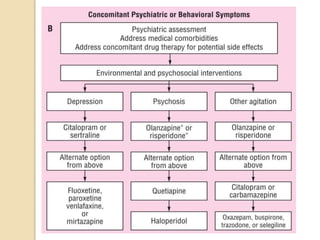
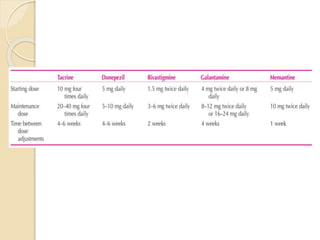
- While the exact causes are unknown, genetic and environmental factors likely contribute. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with cholinesterase inhibitors or memantine, which target acetylcholine and glutamate pathways respectively. Currently there is no cure for AD.