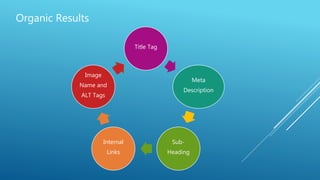
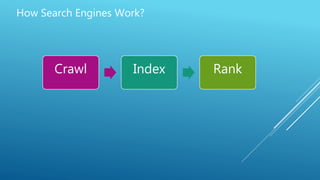
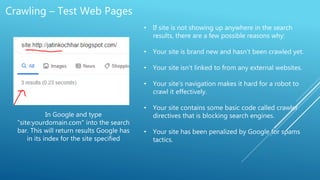
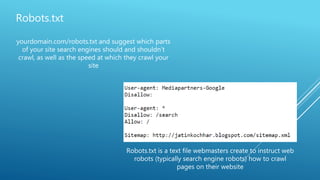
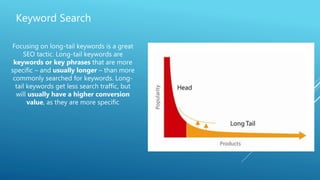
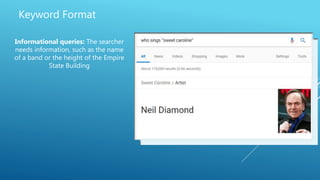
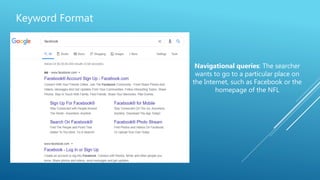
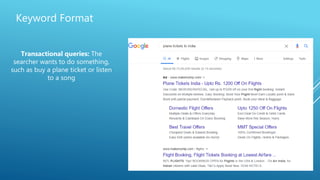
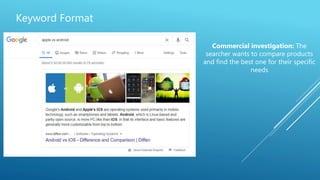
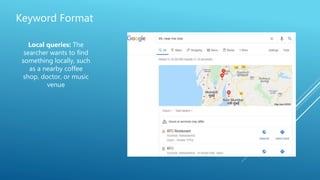
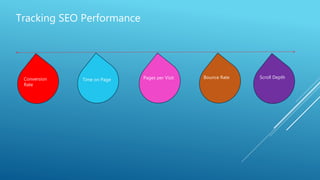
The document discusses the principles of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and its impact on organic search traffic. It explains the processes of crawling, indexing, and ranking by search engines, as well as the difference between white hat and black hat SEO techniques. The document also highlights the importance of keyword strategies and metrics for tracking SEO performance, such as conversion rates and bounce rates.