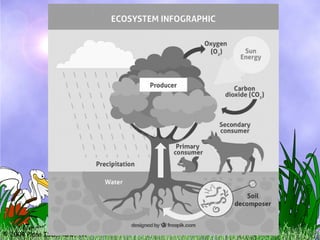
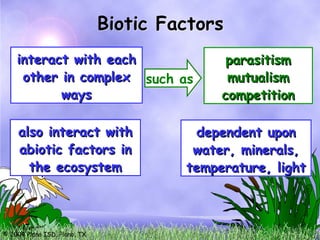
This document discusses the relationships between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors within ecosystems. It outlines the definitions and examples of biotic and abiotic components, as well as the concept of biomes and levels of organization in ecological systems. The text emphasizes the complexity of interactions between these factors and their influence on ecosystem dynamics.