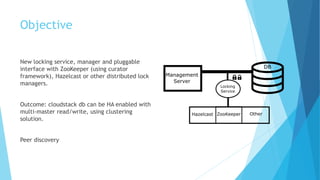
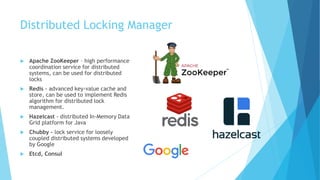
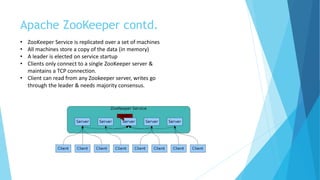
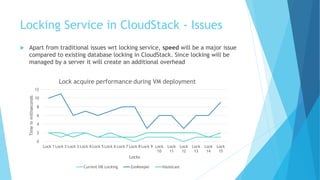
Abhishek Kumar proposes developing a new locking service, manager, and pluggable interface for CloudStack to enable high availability of the CloudStack database. The new service would use distributed lock managers like ZooKeeper or Hazelcast to allow for multi-master database replication. Currently, CloudStack uses MySQL locks that do not support database clustering solutions. A distributed locking approach would allow the database to be clustered for active-active or active-passive configurations. Abhishek then discusses database locking, distributed locking, ZooKeeper, and Hazelcast as potential implementations and demonstrates a proof of concept using ZooKeeper and Hazelcast before considering future work.