This document provides an overview of nephrotic syndrome, including its pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, investigations, and management. Some key points:
- Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia. It is mostly seen in children aged 2-6 years.
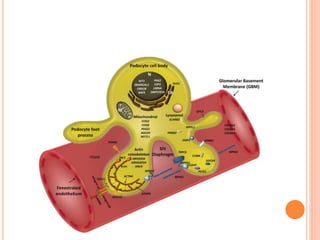
- The podocyte plays a crucial role in the glomerular filtration barrier and podocyte injury can lead to nephrotic syndrome.
- Clinical consequences include edema, hyperlipidemia, increased infection risk, and hypercoagulability.
- Corticosteroids are the main treatment for minimal change nephrotic syndrome, with relapses requiring high-