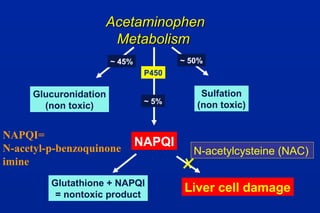
A 17-year-old man was brought to the hospital drunk, depressed, and having taken pills and alcohol after failing exams. He was treated with IV fluids, monitored until sober, and discharged home with psychiatric support. Three days later he returned with jaundice, leading to the diagnosis of paracetamol poisoning.