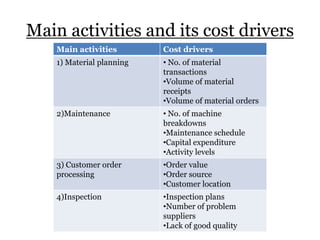
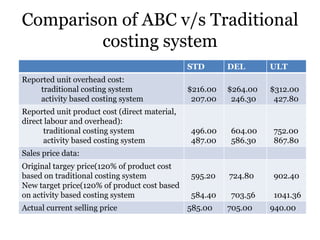
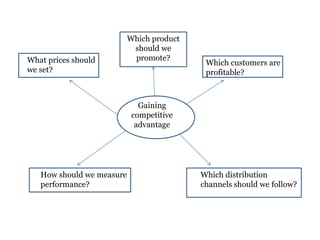
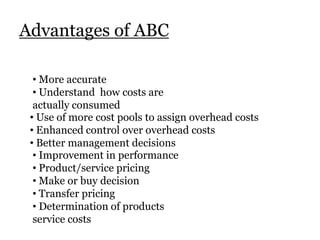
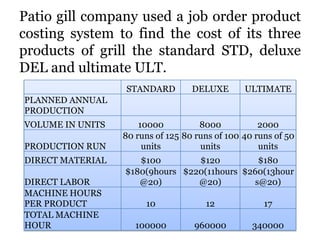
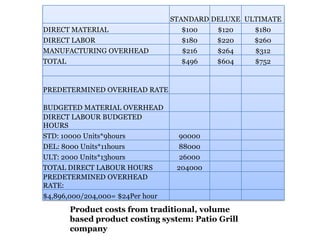
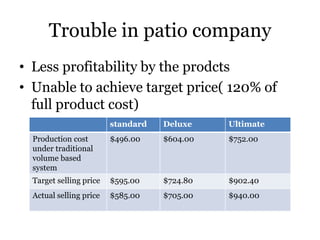
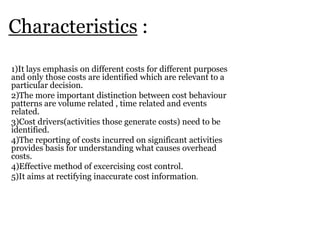
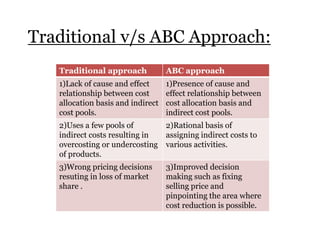
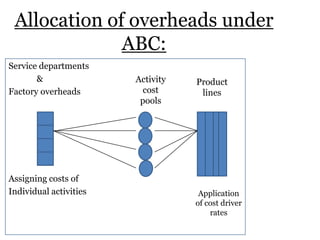
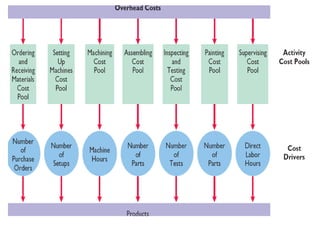
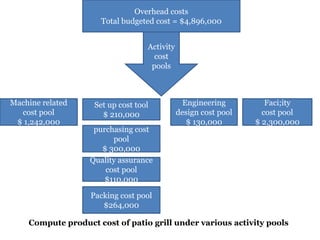
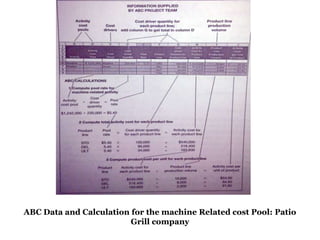
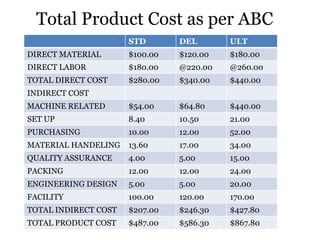
Traditional costing systems allocate overhead costs to products based on direct labor hours or machine hours. This can result in inaccurate product costs. Activity-based costing (ABC) assigns overhead to activities and then to products based on cost drivers like number of set-ups. Patio Grill Company found its traditional system inaccurate. ABC analysis identified machine hours and set-ups as major cost drivers. ABC allocated overhead more precisely, revealing Ultimate grill was underpriced. ABC provides more accurate product costs for pricing, outsourcing, and cost reduction decisions.












![•Product-sustaining level:
It includes activities that are needed to support entire product line .
• Facility level [general operations level]:
These activities are required in order for the entire production process to
occur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abc1-140306133330-phpapp02/85/ABC-ANALYSIS-23-320.jpg)