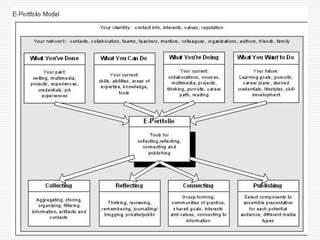
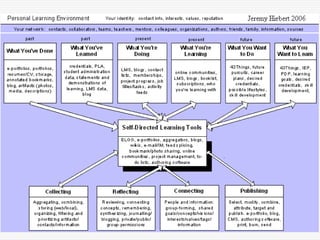
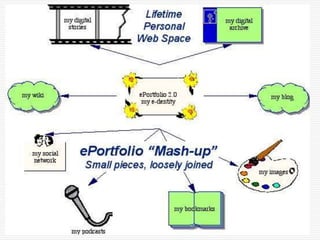
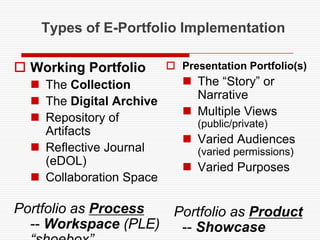
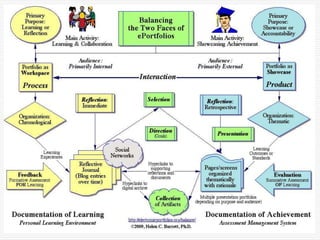
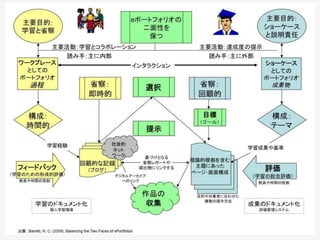
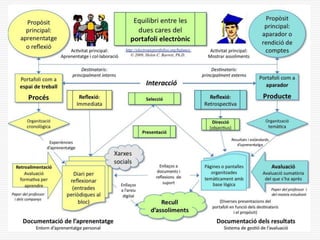
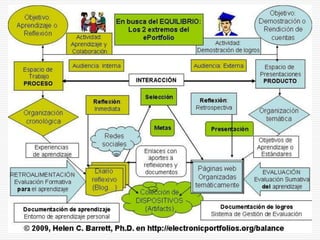
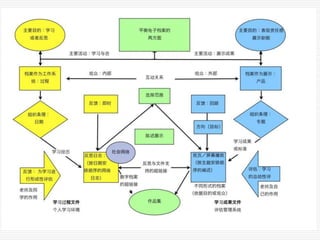
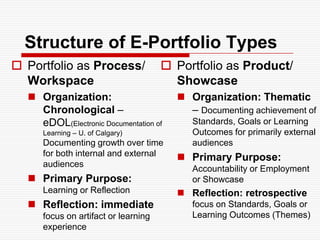
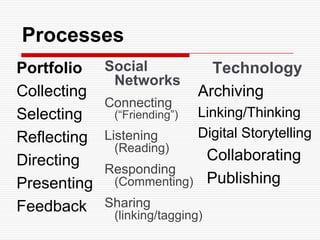
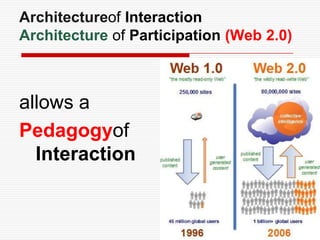
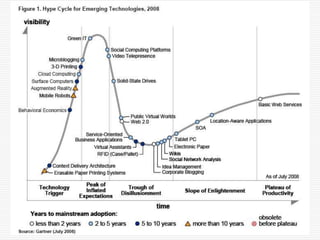
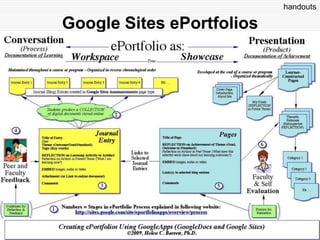
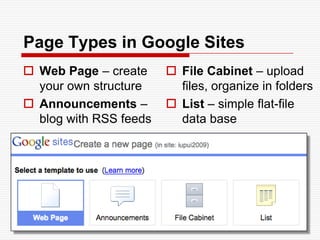
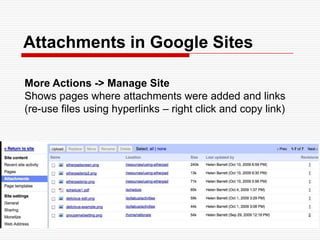
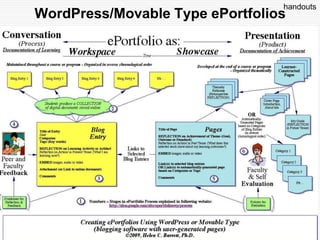
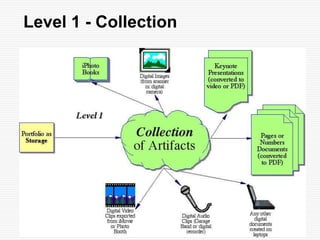
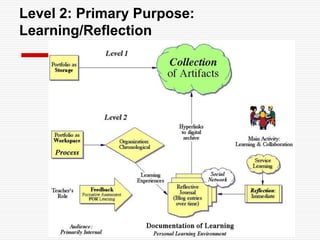
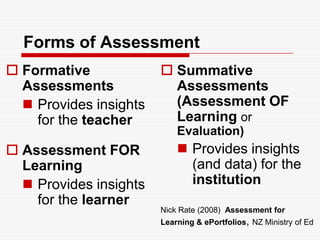
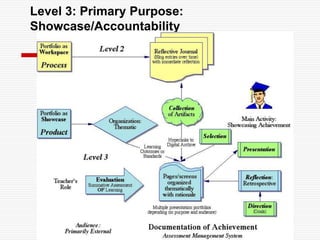
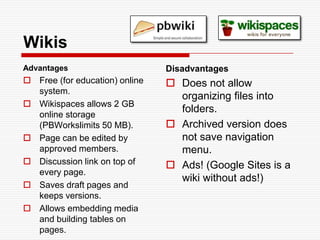
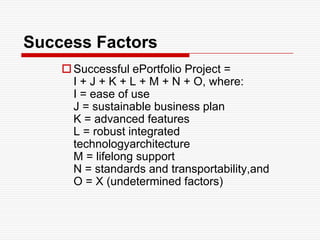
This document discusses using Web 2.0 tools to create personal learning environments and e-portfolios. It defines personal learning environments as being social, lifelong, self-directed, motivating, and online. It describes different types of e-portfolio implementations including working, collection, archive, and presentation portfolios. It also discusses using Web 2.0 tools like blogs, wikis, and Google sites to support reflection, collaboration, and presentation in e-portfolios.