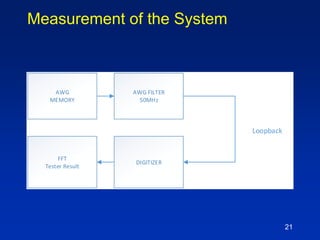
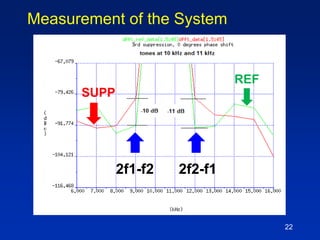
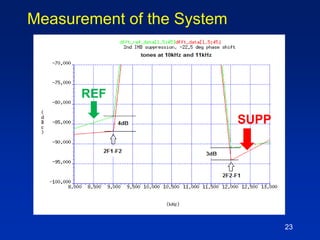
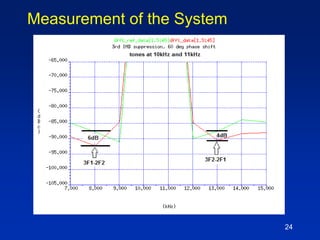
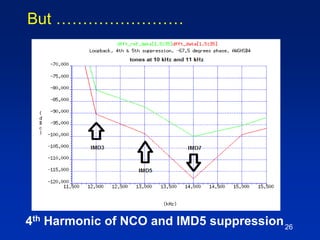
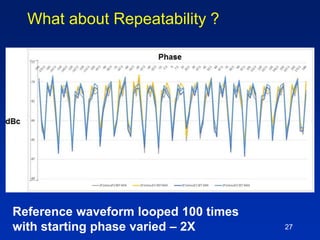
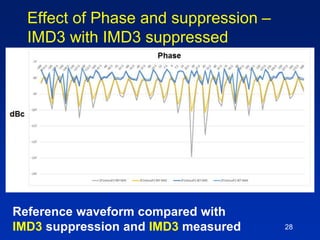
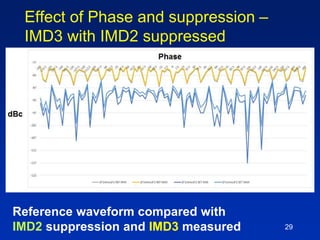
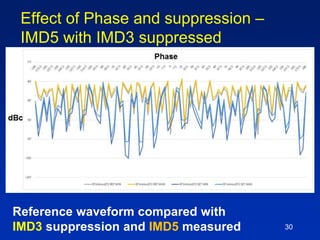
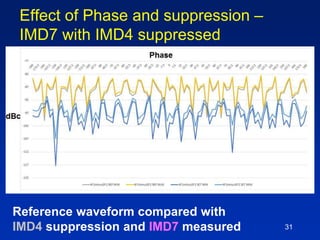
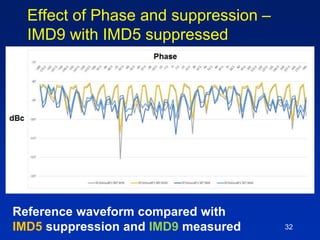
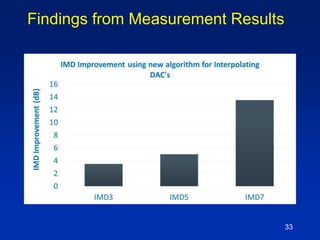
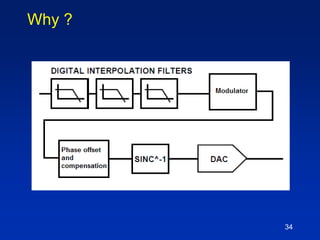
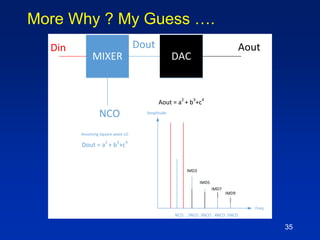
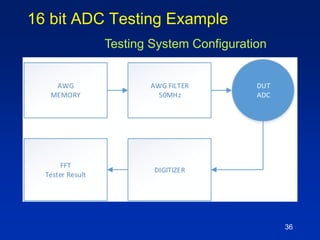
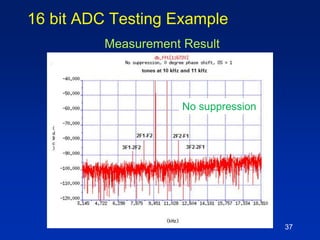
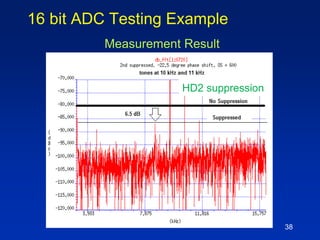
The document presents a technique for improving the dynamic range of intermodulation distortion products in an arbitrary waveform generator using a phase switching algorithm. It discusses the challenges of current test instrumentation limitations and how a simple DSP method can extend performance while driving down testing costs. The findings suggest that this method can yield a significant reduction in IMD levels, which could translate to approximately a 1-bit improvement in ADC performance.

















![Confidential © ams AG
Page 18
AWG
DAC
CLK
DSP
X XXX
Din
Din
AWG sampling frequency: fs(AWG) = 1/Ts
A
𝐗= Acos(2πfinnTs)
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
-300
-200
-100
0
Power[dB]
Normalized frequency f/fs
𝐟𝐢𝐧
𝐇𝐃𝟑
In case
Single-tone generation
DAC has 3rd-order distortion
Conventional Signal Generation with
AWG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session1a-170425081047/85/A-Technique-for-Dynamic-Range-Improvement-of-Intermodulation-Distortion-Products-for-an-Interpolating-DAC-based-Arbitrary-Waveform-Generator-Using-a-Phase-Switching-Algorithm-18-320.jpg)
![Confidential © ams AG
Page 19
Signal Generation with AWG using
Phase Switching
AWG
DAC
CLK
DSP
X0 X1X0X1
Din
Din
AWG sampling frequency: fs(AWG) = 1/Ts(AWG)
𝐗 𝟎= 1.15Acos(2πfinnTs−π/6)
𝐗 𝟏= 1.15Acos(2πfinnTs+𝜋/6)
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
-300
-200
-100
0
𝐟𝐢𝐧
𝐟𝒔/2−𝟑𝐟in
𝐟𝒔/2−𝐟in
Power[dB]
Normalized frequency f/fs
Θ = π/3𝐓𝐬(𝐀𝐖𝐆)
X0
𝐗 𝟏
In case
Single-tone generation
DAC has 3rd-order distortion
HD3 disappears](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session1a-170425081047/85/A-Technique-for-Dynamic-Range-Improvement-of-Intermodulation-Distortion-Products-for-an-Interpolating-DAC-based-Arbitrary-Waveform-Generator-Using-a-Phase-Switching-Algorithm-19-320.jpg)