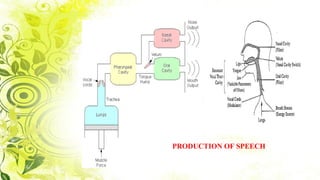
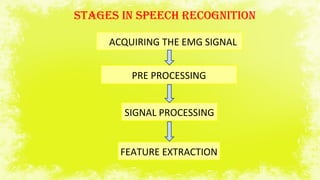
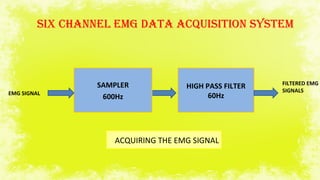
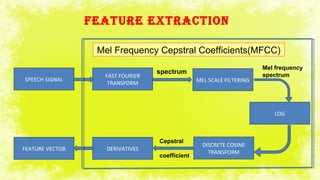
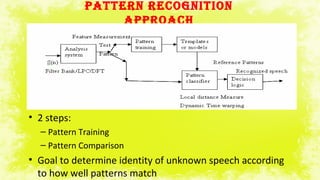
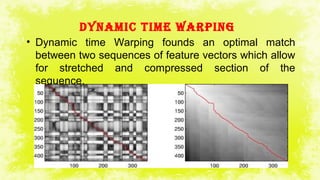
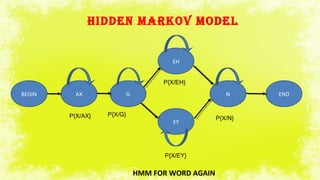
This document summarizes a study on electromyography (EMG)-based speech recognition using silent speech interface (SSI). EMG detects muscle cell electric potentials during activation. The study examines techniques for each stage of speech recognition and compares matching techniques. SSI uses EMG sensors on the face to record muscle signals during speech, which are converted to electric pulses and translated to speech without sound. Future prospects include incorporating EMG electrodes directly into systems and adding lip reading and translation to more languages.