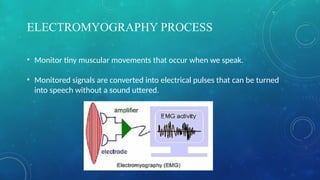
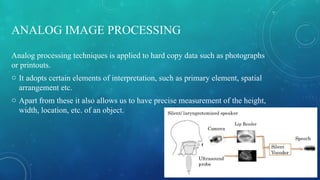
Silent sound technology allows information transmission without vocal cords, utilizing lip movements and electromyography to generate sound. It presents advantages like communication in noisy areas and support for individuals with speech disabilities, but faces challenges including language translation issues and practicality concerns. The technology has applications in military and space communication, and future developments may lead to more integrated devices.