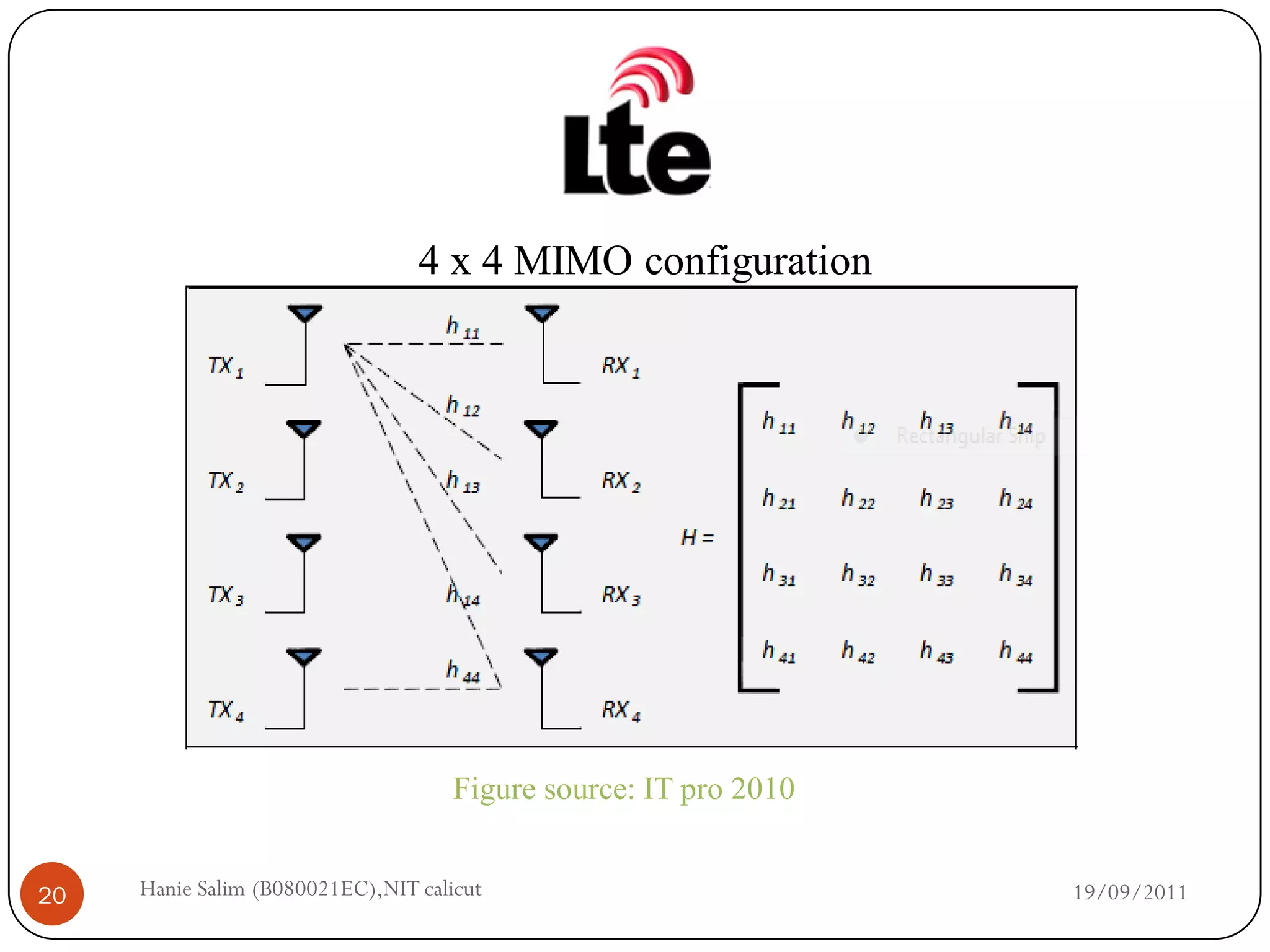
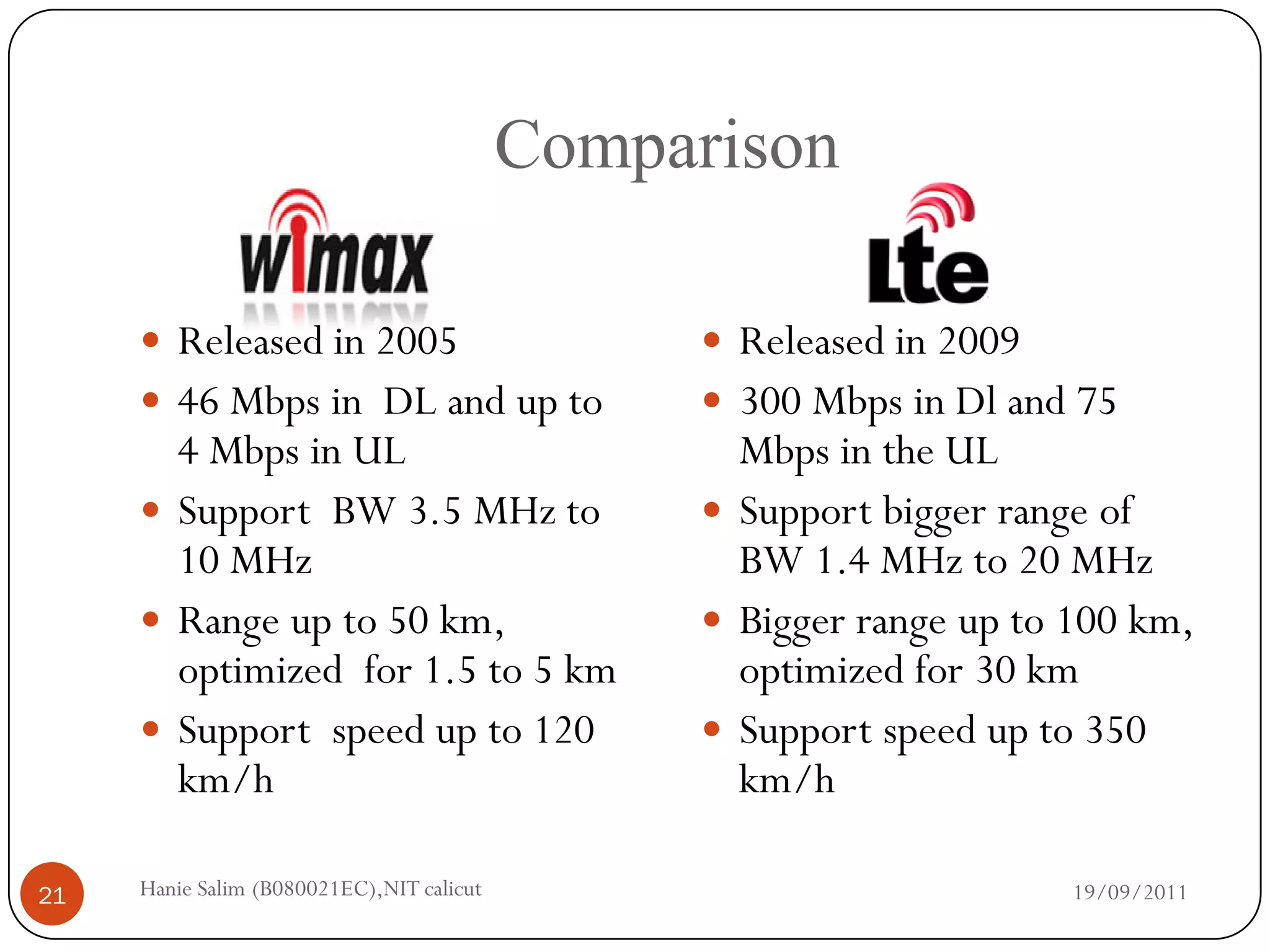
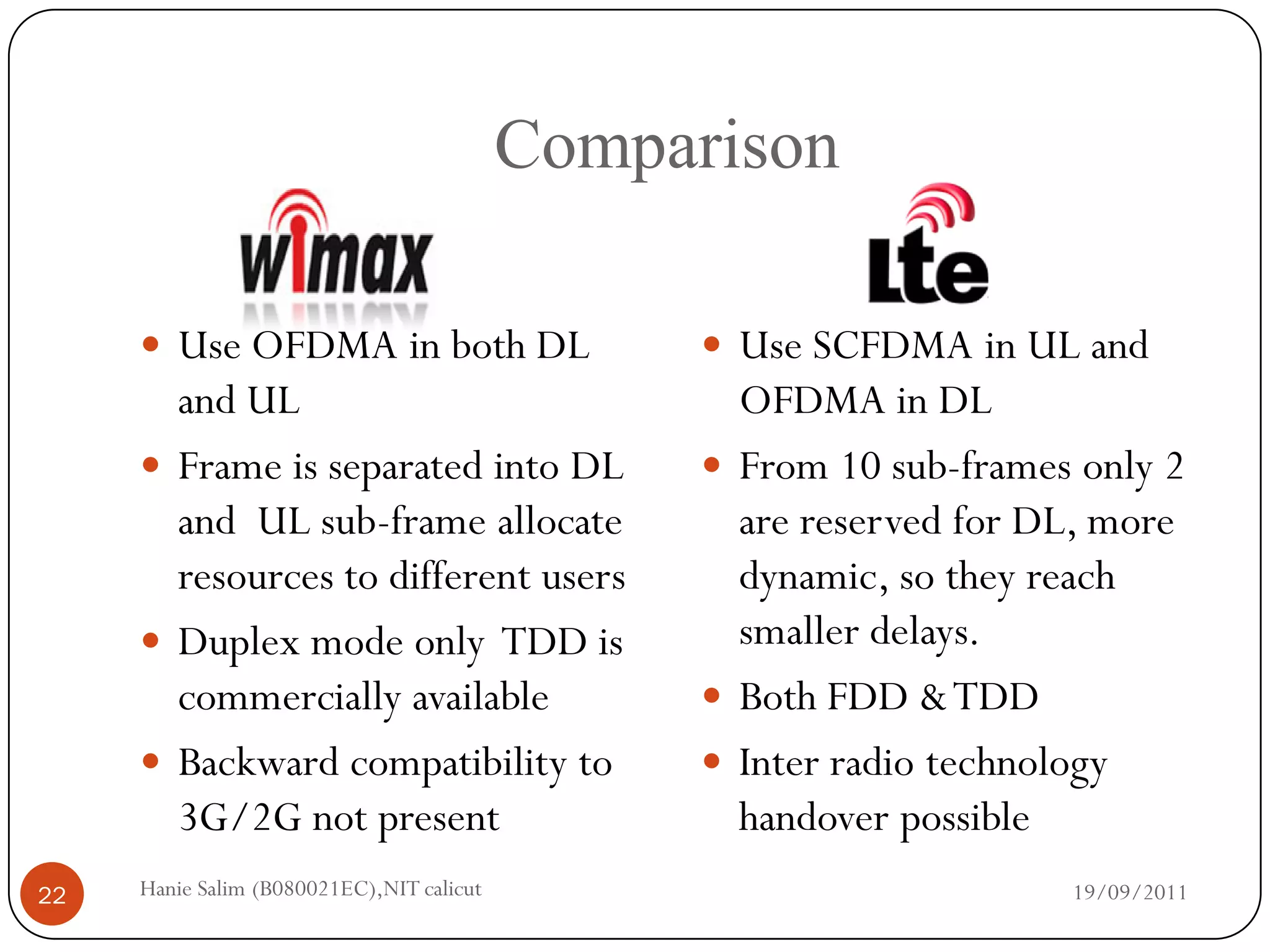
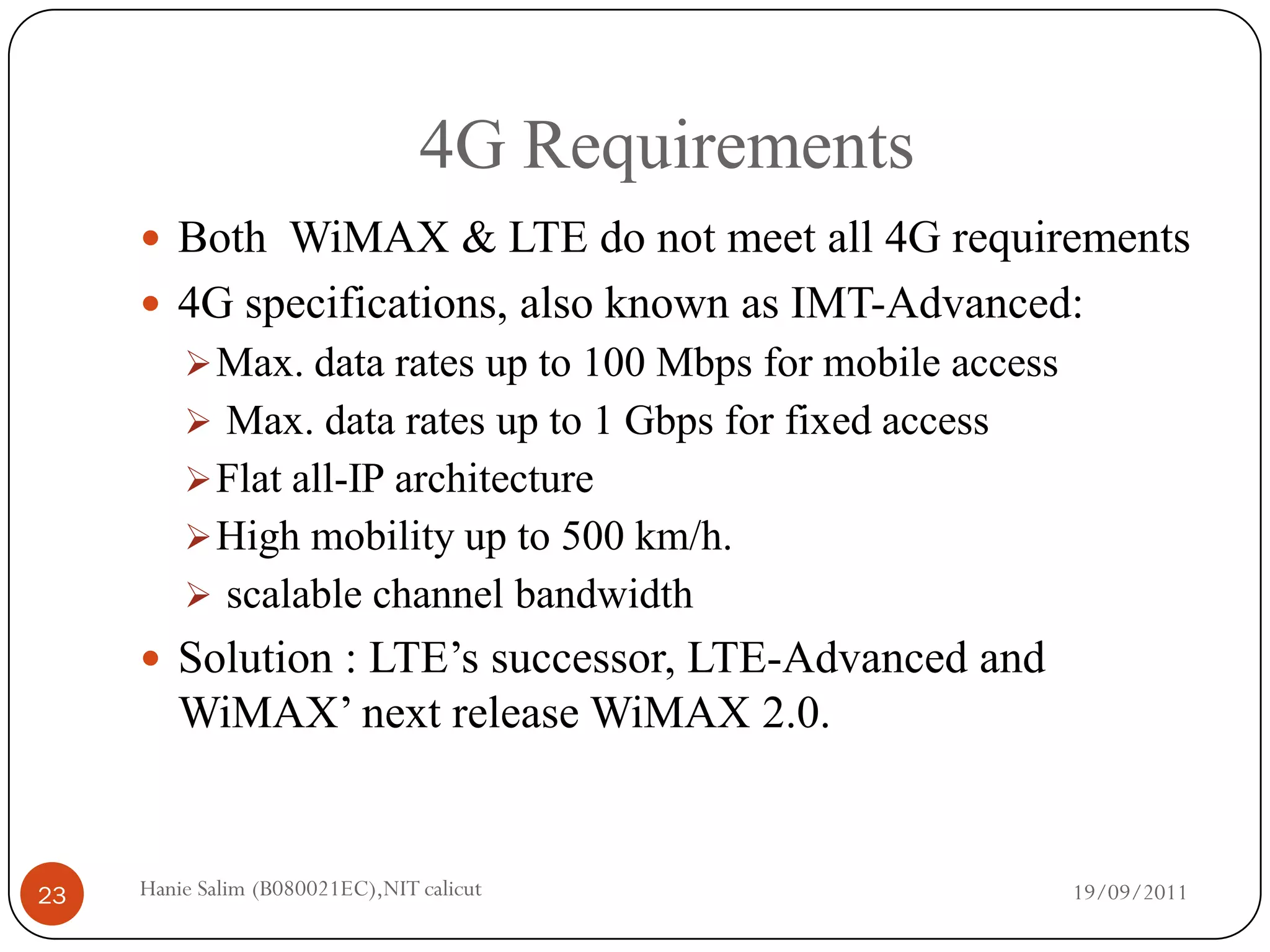
This document provides a comparative study of WiMAX and LTE networks. It summarizes key aspects of each network, including supported data rates and bandwidth, range, supported speeds, modulation techniques, frame structure, quality of service mechanisms, and security features. The document concludes with a comparison table highlighting that LTE supports higher data rates but shorter range compared to WiMAX, and different duplexing and frame allocation approaches between the two technologies.




![References
[1] M.Chang, Z. Abichar, and Chau –Yun Hsu, “Wimax vs. lte:
Who will lead the broadband mobile internet?,” IT Professional, vol.
12, no. 3, pp. 26 - 32, 2010.
[2] Ozgur Oyman , Jeffrey Foerster ,Yong-joo Tcha and Seong-
Choon Lee , “Toward Enhanced Mobile Video Services over
WiMAX and LTE,” IEEE Communications Magazine ,vol. 48,no.8,pp.
68 – 76,2010
[3] J. Conti, “Lte vs wimax: the battle continues,” Engineering
Technology, 2010.
[4] Leo Yi ,Kai Miao ,Adrian Liu,” A comparative study of WiMAX
and LTE as the next generation mobile enterprise network,”
Advanced Communication Technology(ICACT),pp. 654-658,feb 2011.
27 Hanie Salim (B080021EC),NIT calicut 19/09/2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acomparativestudyofwimaxandlte-110924083018-phpapp02/75/A-comparative-study-of-wimax-and-lte-27-2048.jpg)