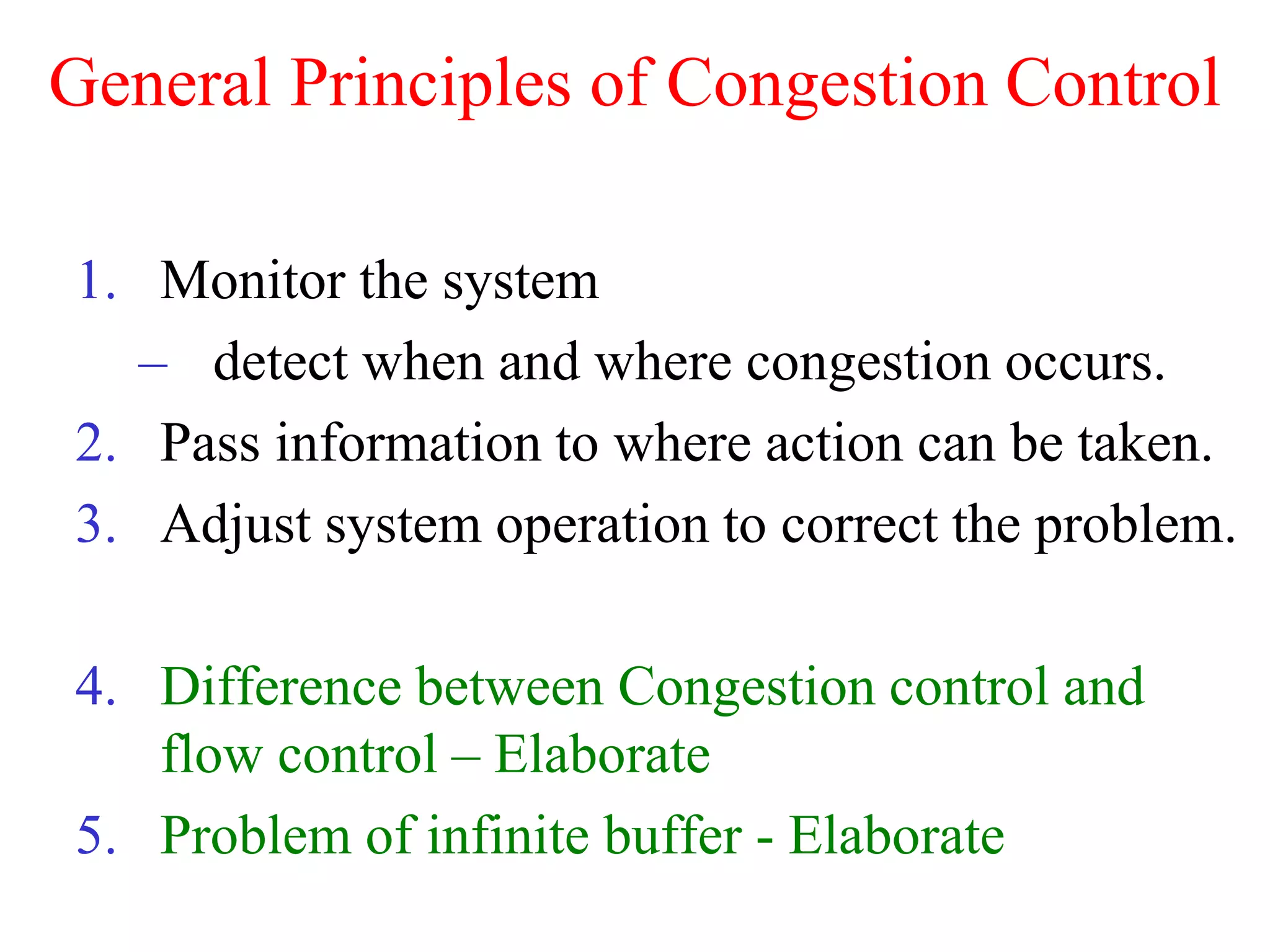
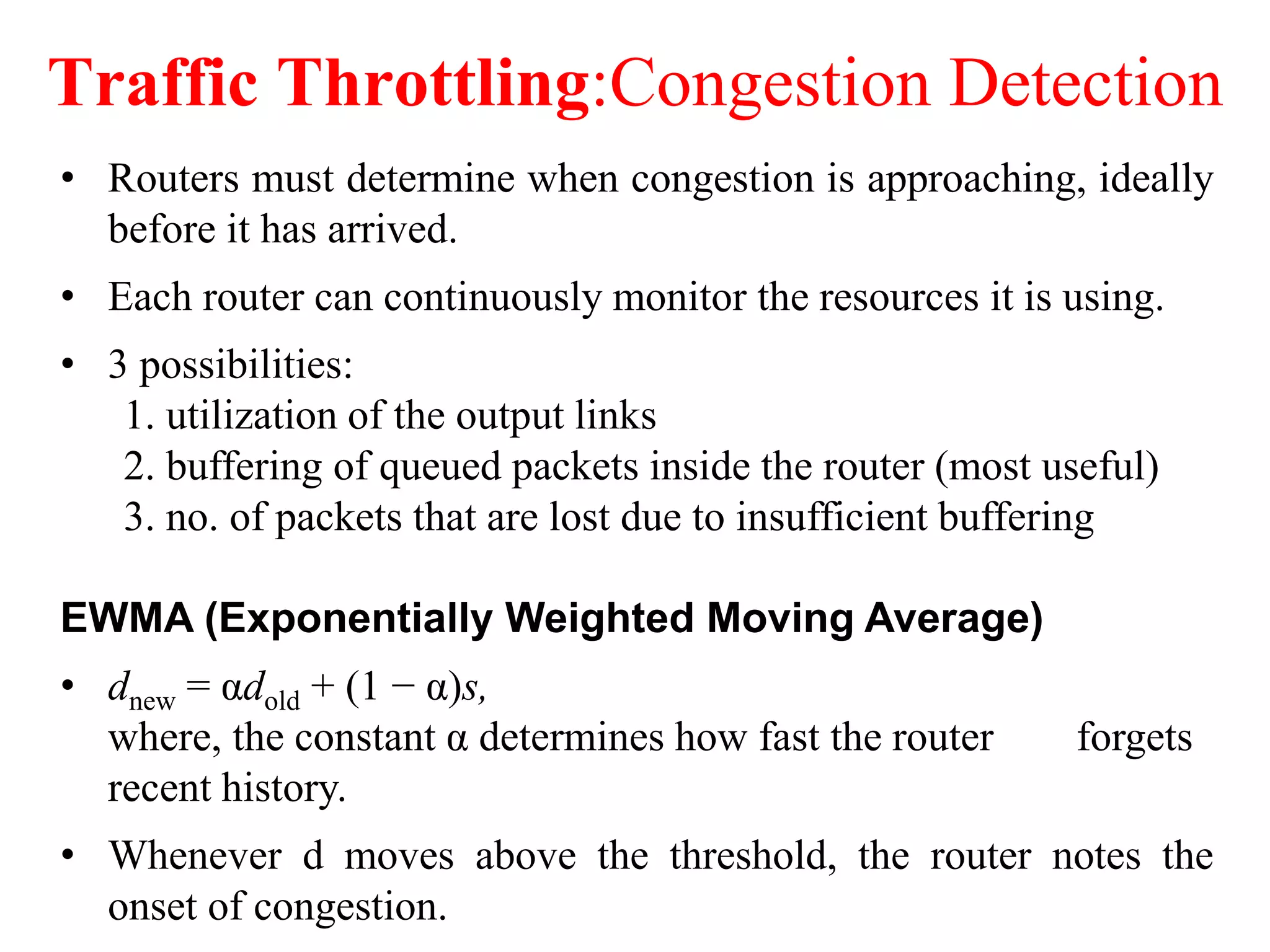
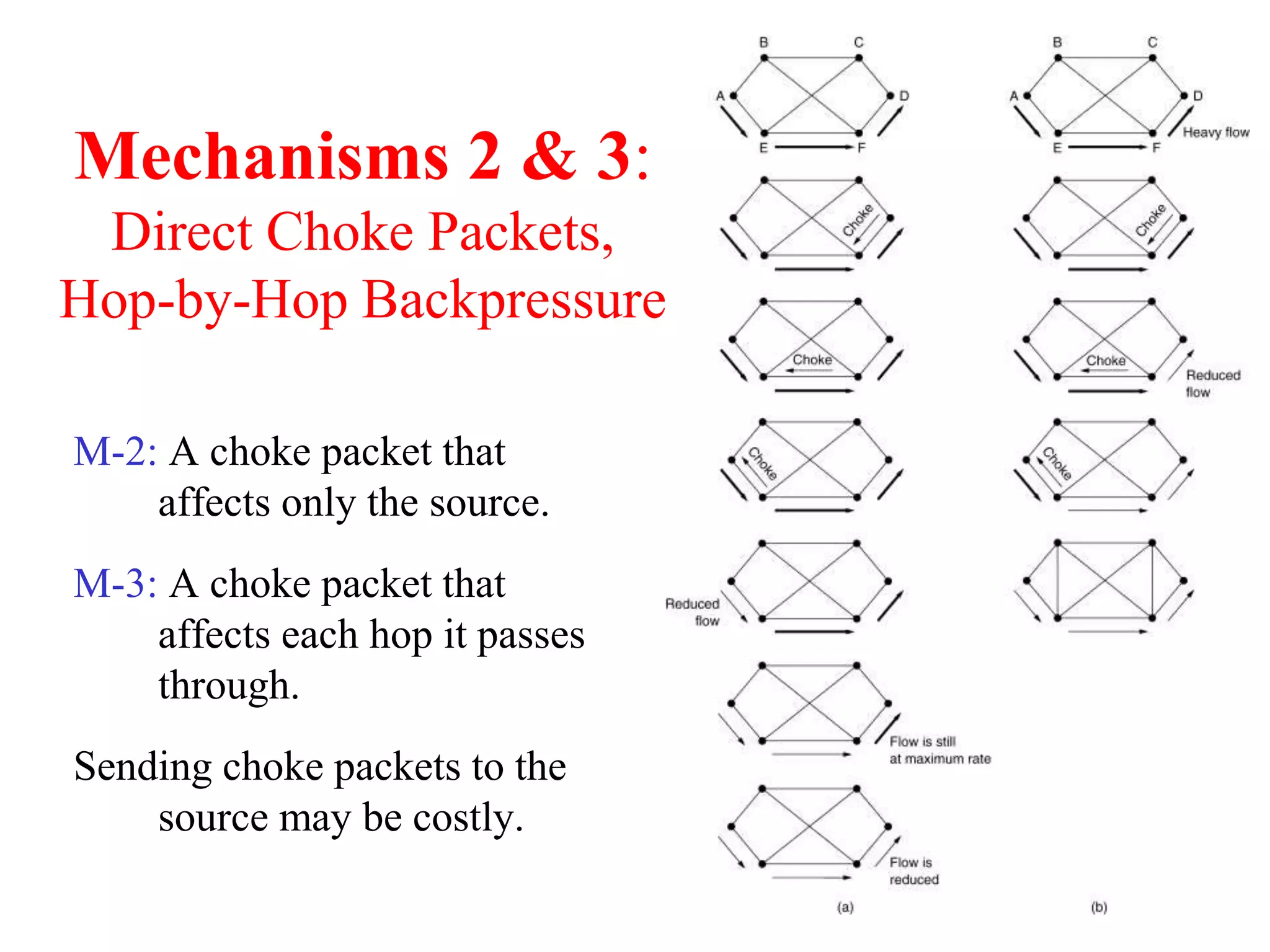
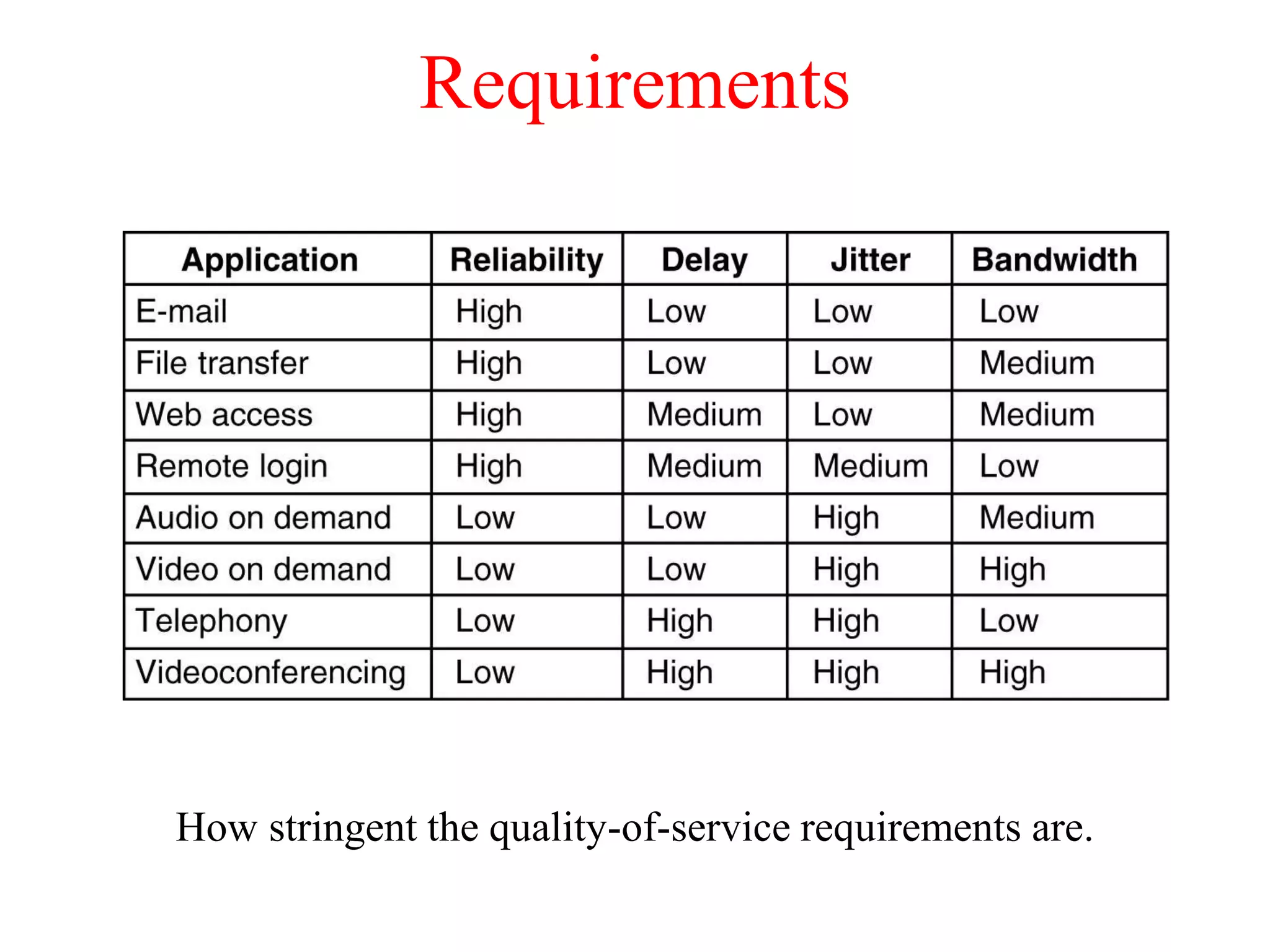
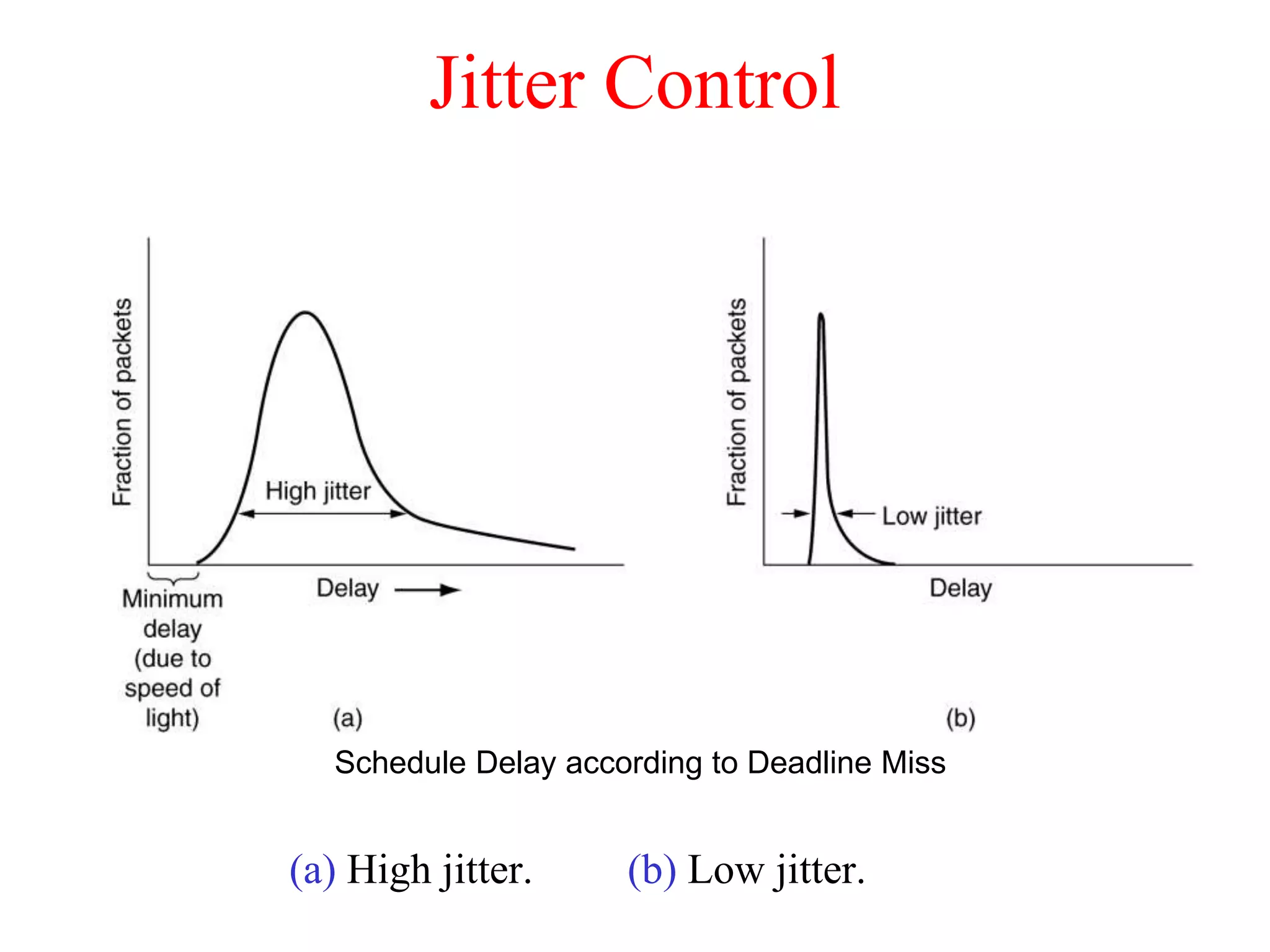
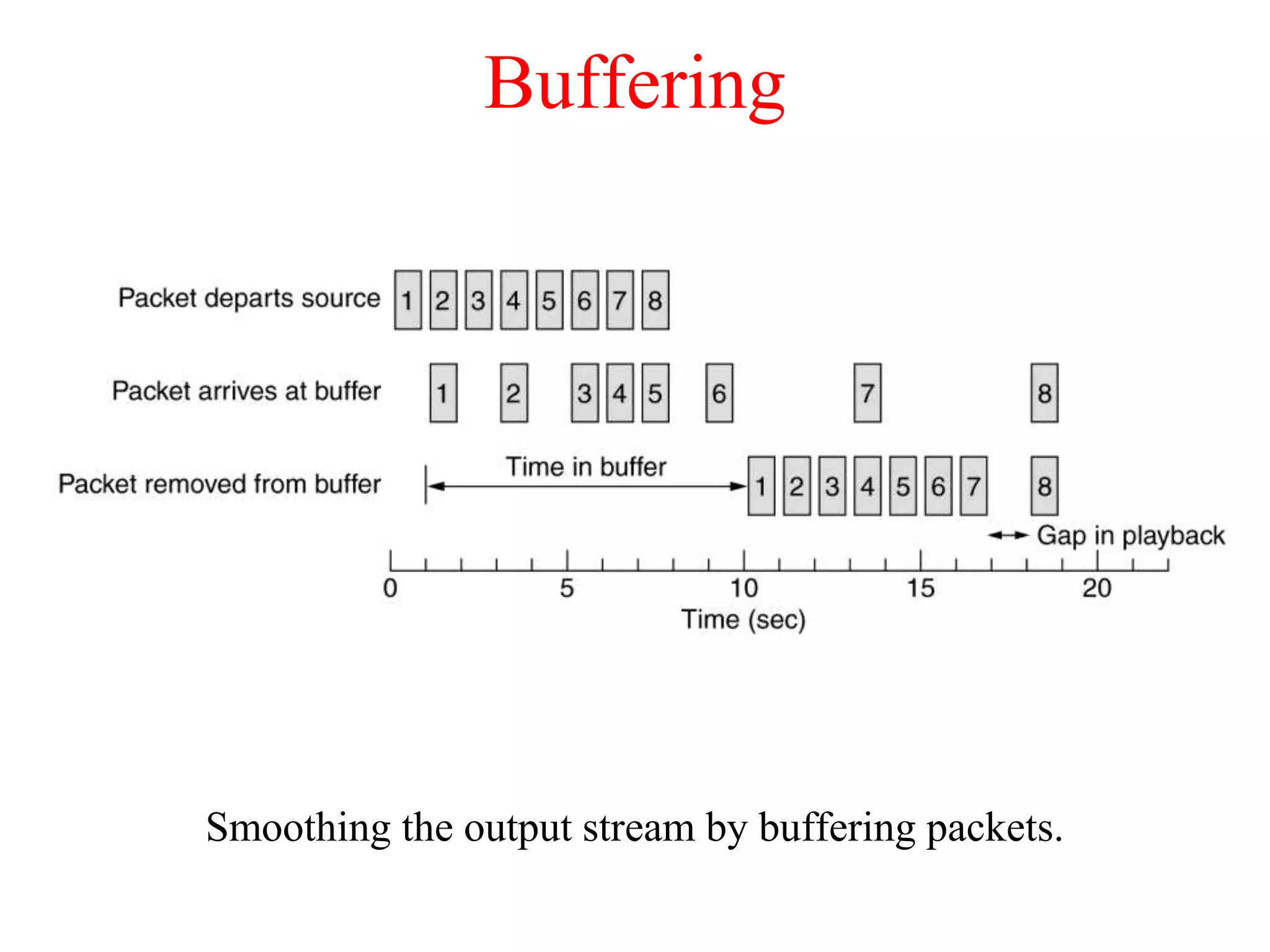
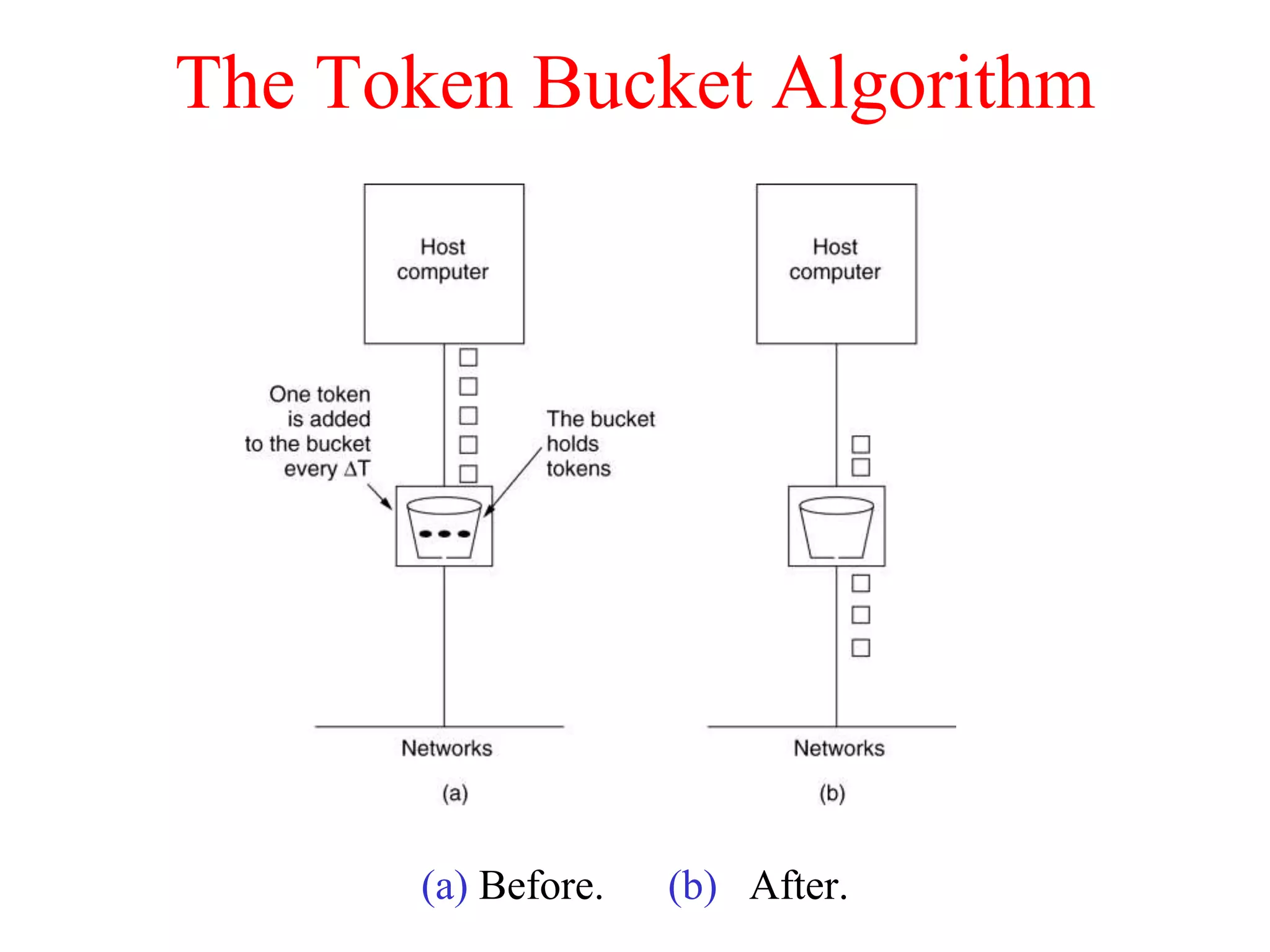
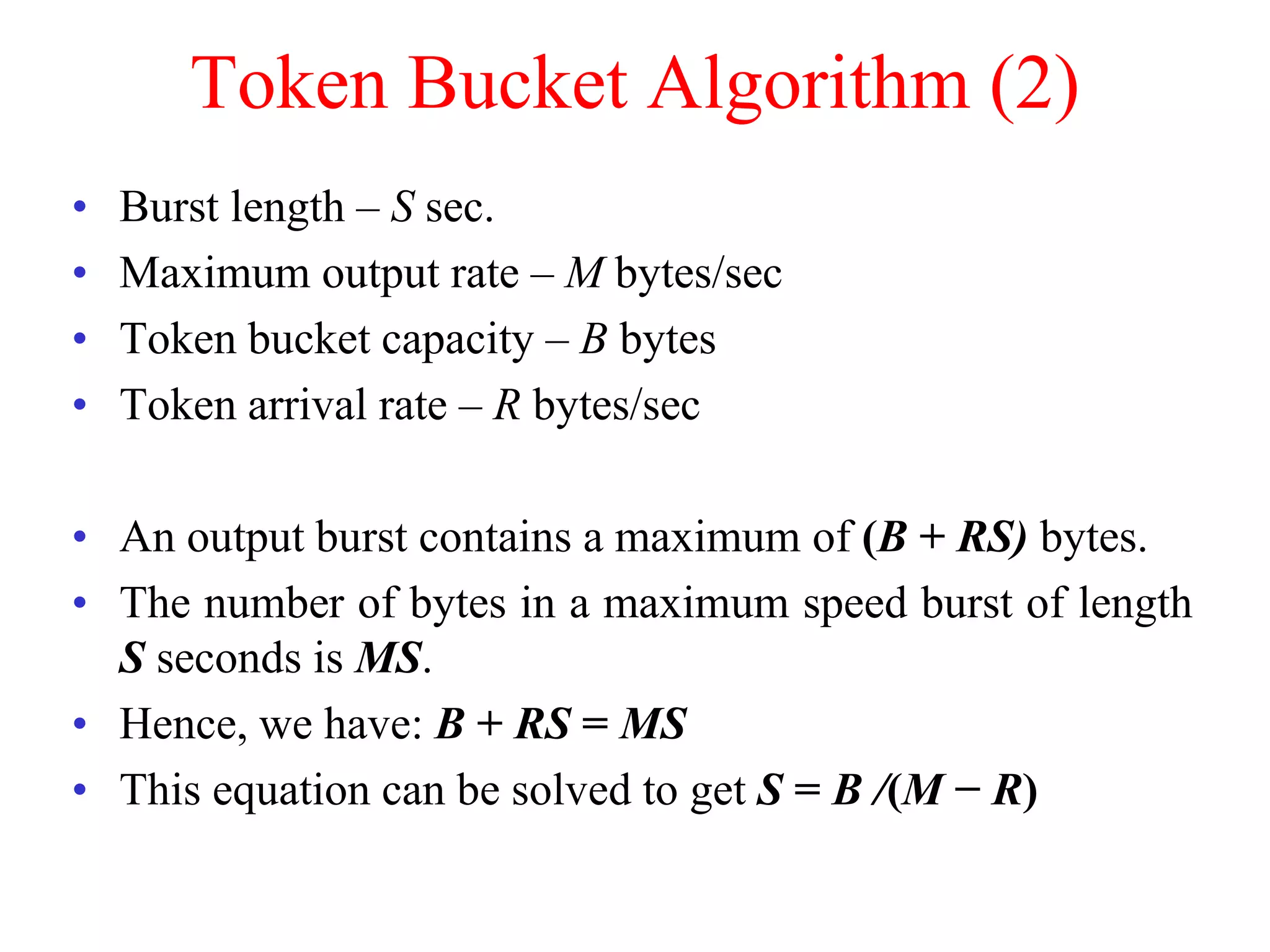
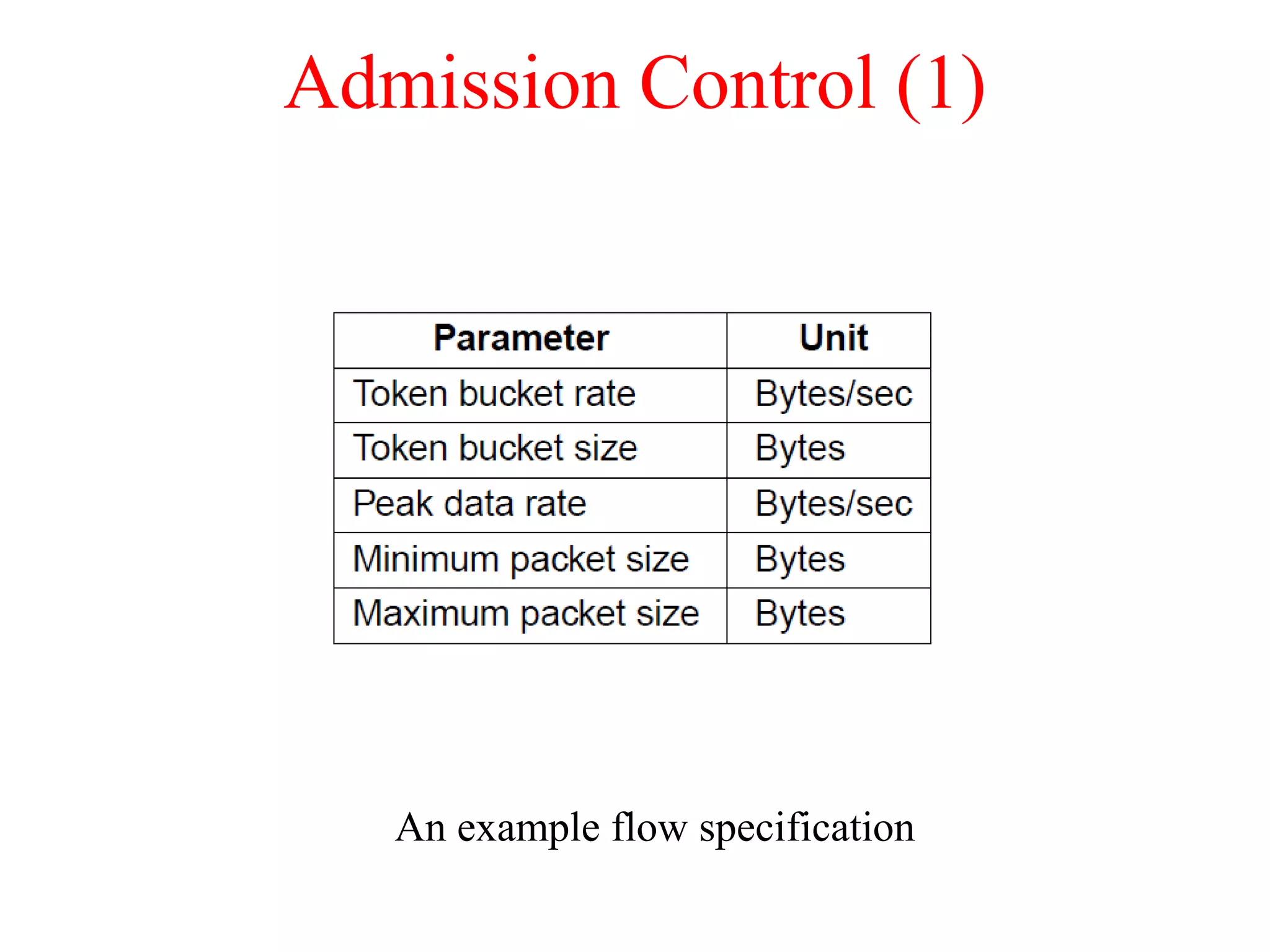
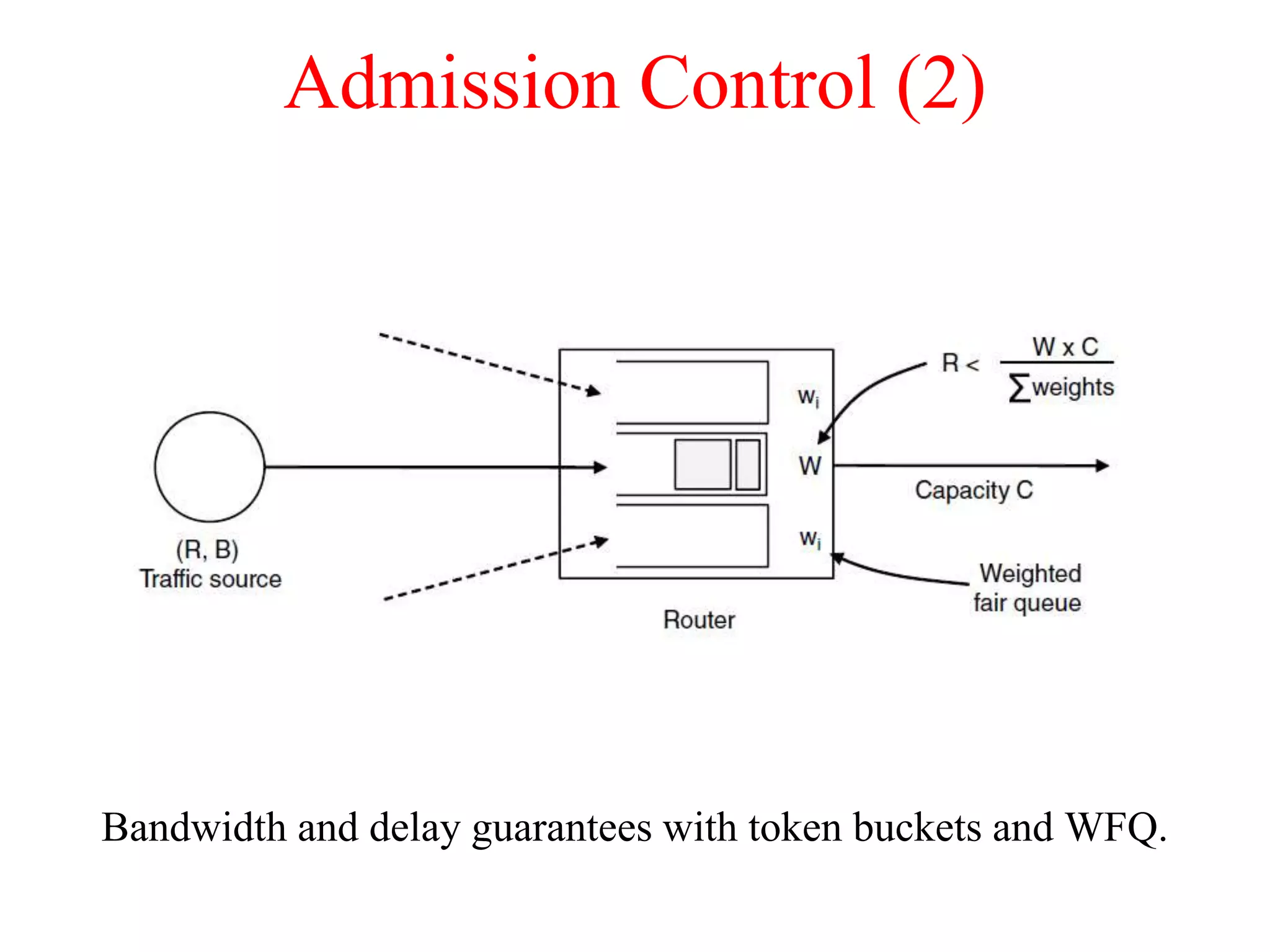
The document discusses various congestion control algorithms and quality of service techniques used in computer networks. It describes approaches like traffic-aware routing, admission control, traffic throttling, and load shedding to control congestion. It also explains how quality of service is achieved through integrated services, differentiated services, and techniques like traffic shaping, packet scheduling, buffering, and jitter control.