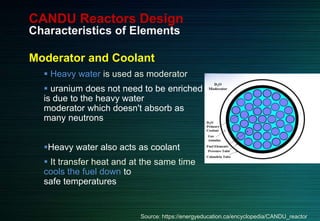
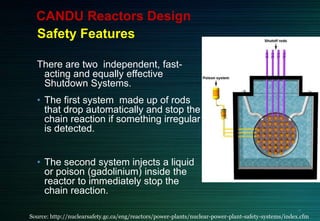
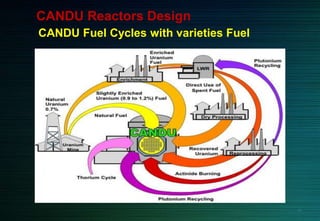
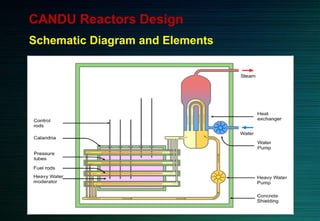
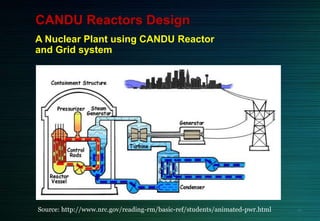
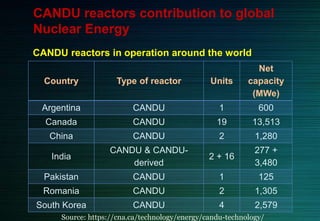
The document discusses the CANDU nuclear reactor, a pressurized heavy water reactor designed in Canada. It provides details on the design of CANDU reactors, including their use of natural uranium fuel and heavy water as both moderator and coolant. CANDU reactors allow for online refueling without shutdown and have safety features like shutdown rods and poison injection. The document also outlines the pros and cons of CANDU reactors and their contribution to nuclear energy globally, with over 20 reactors operating or under construction in 7 countries.





![Understanding of a Nuclear Reactor…
Current Technologies of Nuclear Reactor
1. Pressurized water reactors (PWR)- [moderator: high-
pressure water; coolant: high-pressure water]
2. Boiling water reactors (BWR)- [moderator: low-
pressure water; coolant: low-pressure water]
3. Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR)-
[moderator: high-pressure heavy water; coolant: high-
pressure heavy water]
4. Reaktor Bolshoy Moschnosti Kanalniy (High Power
Channel Reactor) (RBMK)- [moderator: graphite;
coolant: high-pressure water]
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_reactor#Reactor_types
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/candureactor-190323152518/85/Candu-reactor-6-320.jpg)
![Understanding of a Nuclear Reactor…
Current Technologies of Nuclear Reactor
5. Gas-cooled reactor (GCR) and advanced gas-cooled
reactor (AGR)- [moderator: graphite; coolant: carbon
dioxide]
6. Liquid-metal fast-breeder reactor (LMFBR)- [moderator:
none; coolant: liquid metal]
7. Pebble-bed reactors (PBR)- [moderator: graphite;
coolant: helium]
8. Molten salt reactors (MSR)- [moderator: graphite;
coolant: molten salt mixture]
9. Aqueous Homogeneous Reactor (AHR)- [moderator:
high-pressure light or heavy water; coolant: high-
pressure light or heavy water]
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_reactor#Reactor_types
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/candureactor-190323152518/85/Candu-reactor-7-320.jpg)