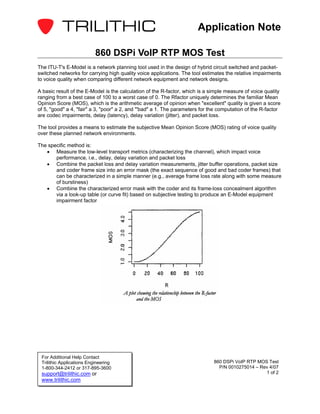
The ITU-T's E-Model is a network planning tool used to estimate voice quality over circuit switched and packet switched networks. It calculates the R-factor based on codec impairments, delay, jitter, and packet loss, which determines the Mean Opinion Score (MOS) rating of voice quality. The specific method measures transport metrics that impact voice quality, characterizes the error mask of packet loss and jitter, and combines it with the codec to estimate a MOS score.