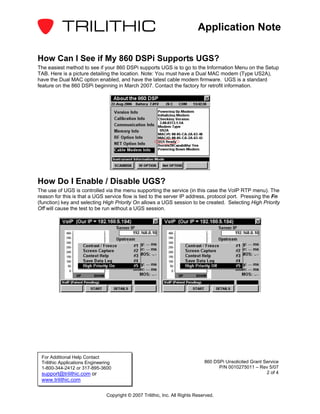
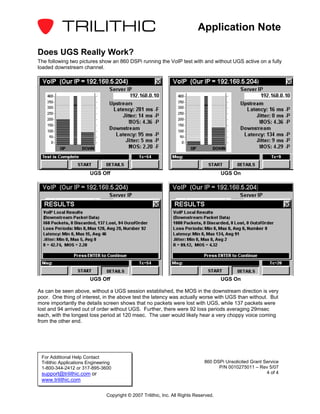
The Unsolicited Grant Service (UGS) provides periodic grants for upstream bandwidth without bandwidth requests. UGS guarantees throughput and latency for applications like VoIP that generate fixed size frames at regular intervals. UGS was created for VoIP because it requires guarantees for latency, jitter, and throughput that best effort scheduling does not provide. Testing on the 860 DSPi showed that using UGS for VoIP eliminated packet loss and improved call quality compared to not using UGS.