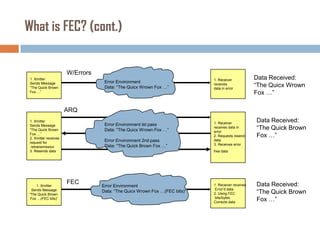
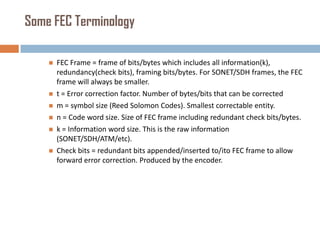
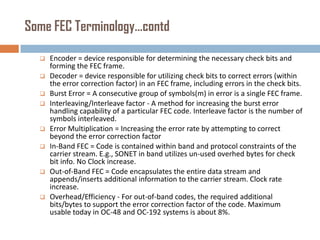
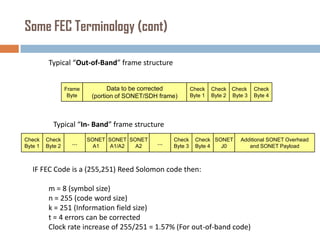
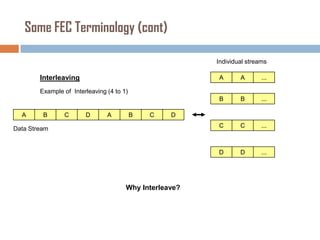
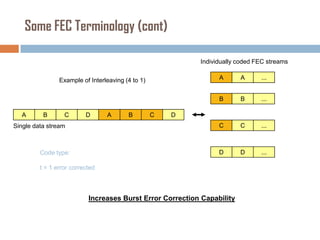
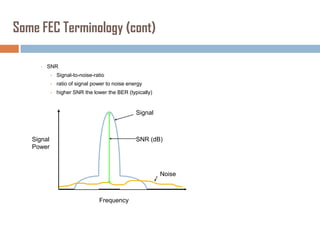
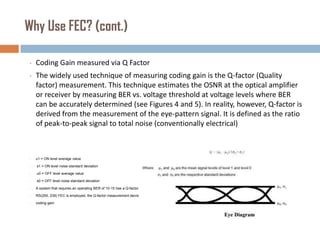
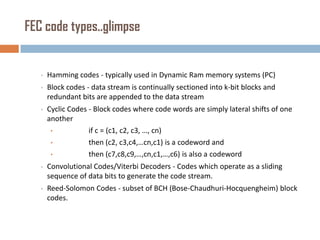
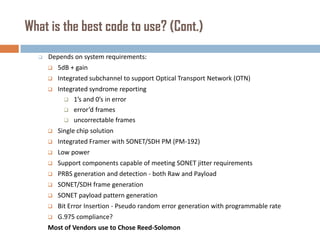
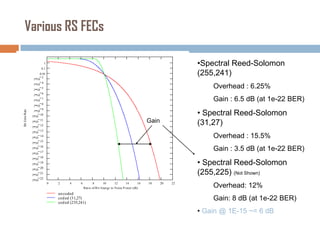
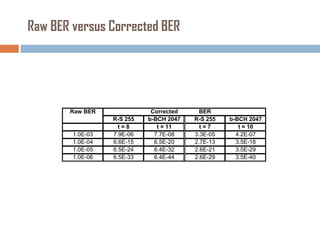
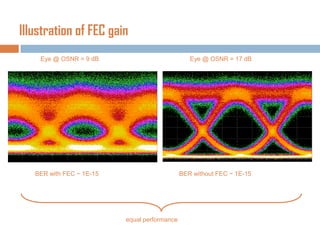
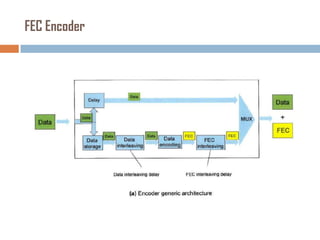
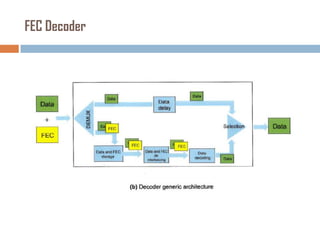
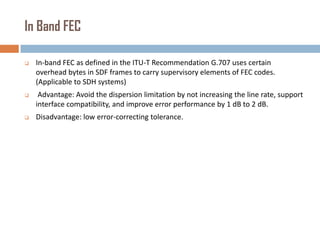
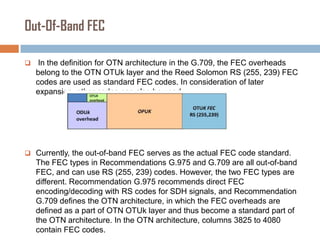
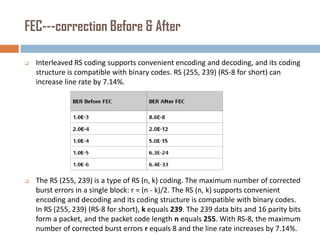
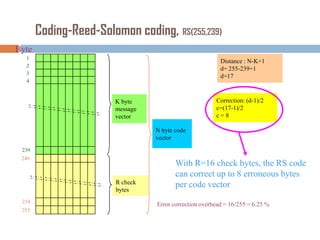
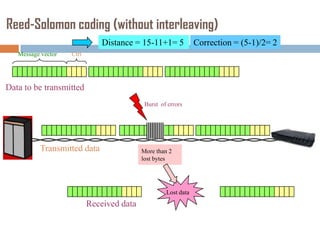
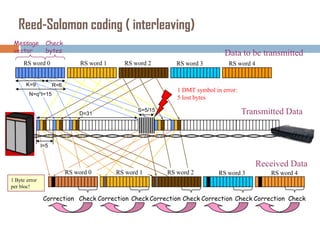
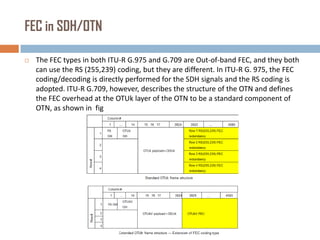
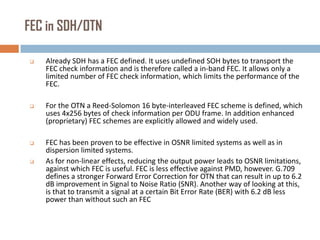
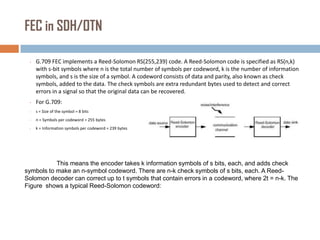
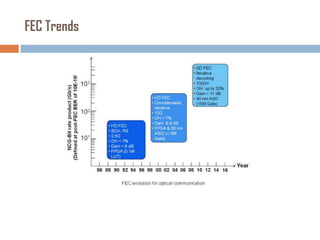
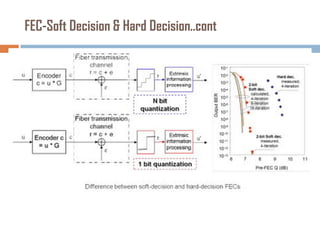
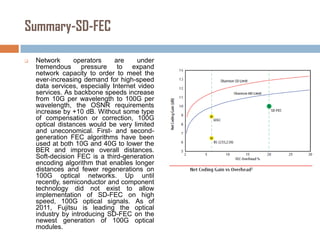
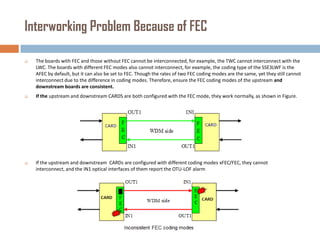
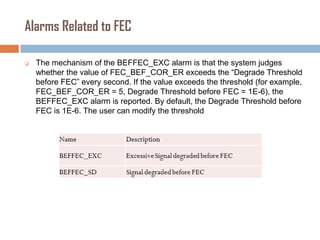
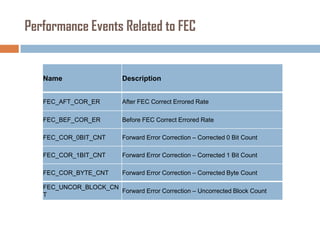
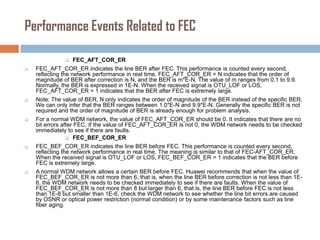
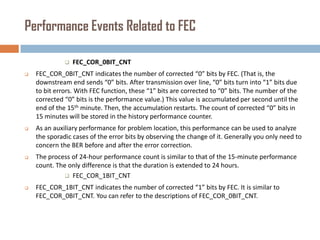
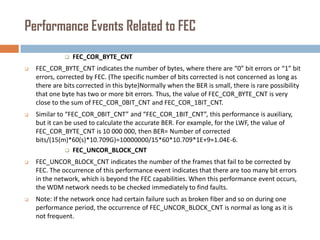
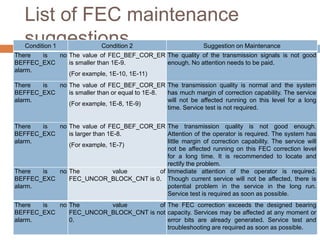
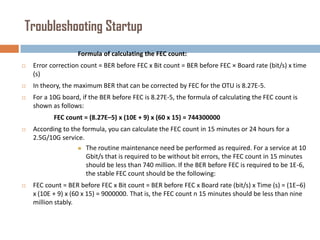
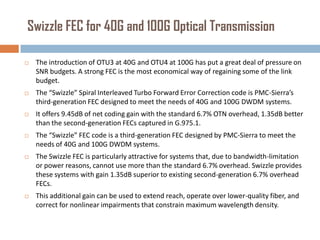
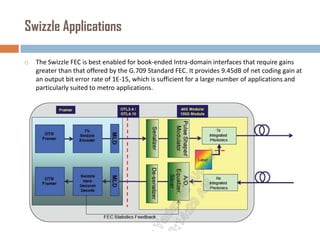
Forward error correction (FEC) adds redundancy to transmitted data to allow errors to be detected and corrected without retransmission. It works by encoding data at the transmitter and decoding it at the receiver. FEC provides increased transmission distance and reliability by improving the bit error rate. Reed-Solomon codes are commonly used for FEC as they can efficiently correct multiple errors within a code block. The amount of redundancy added depends on the code's error correction capability, with higher correction requiring more overhead bits.