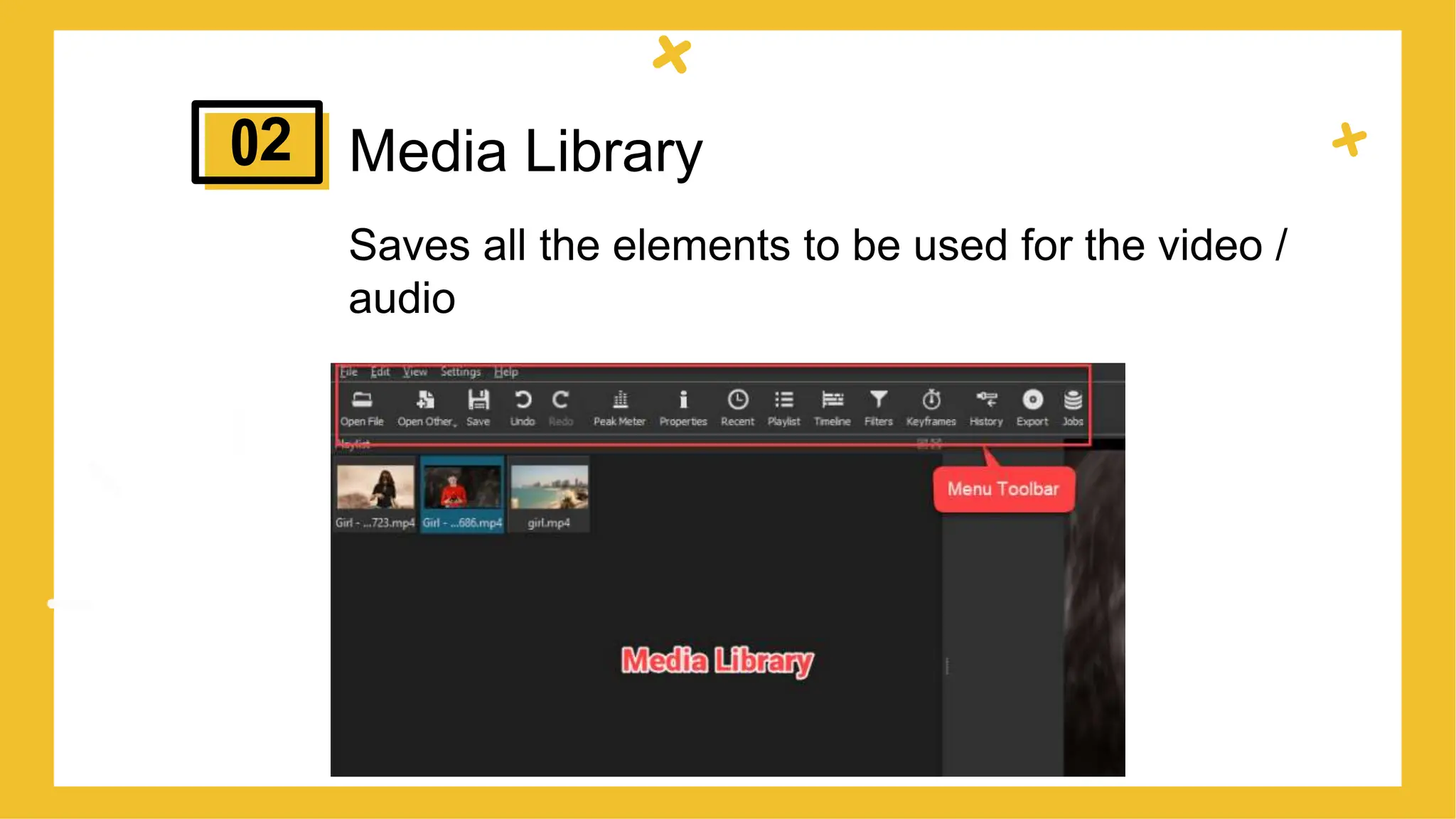
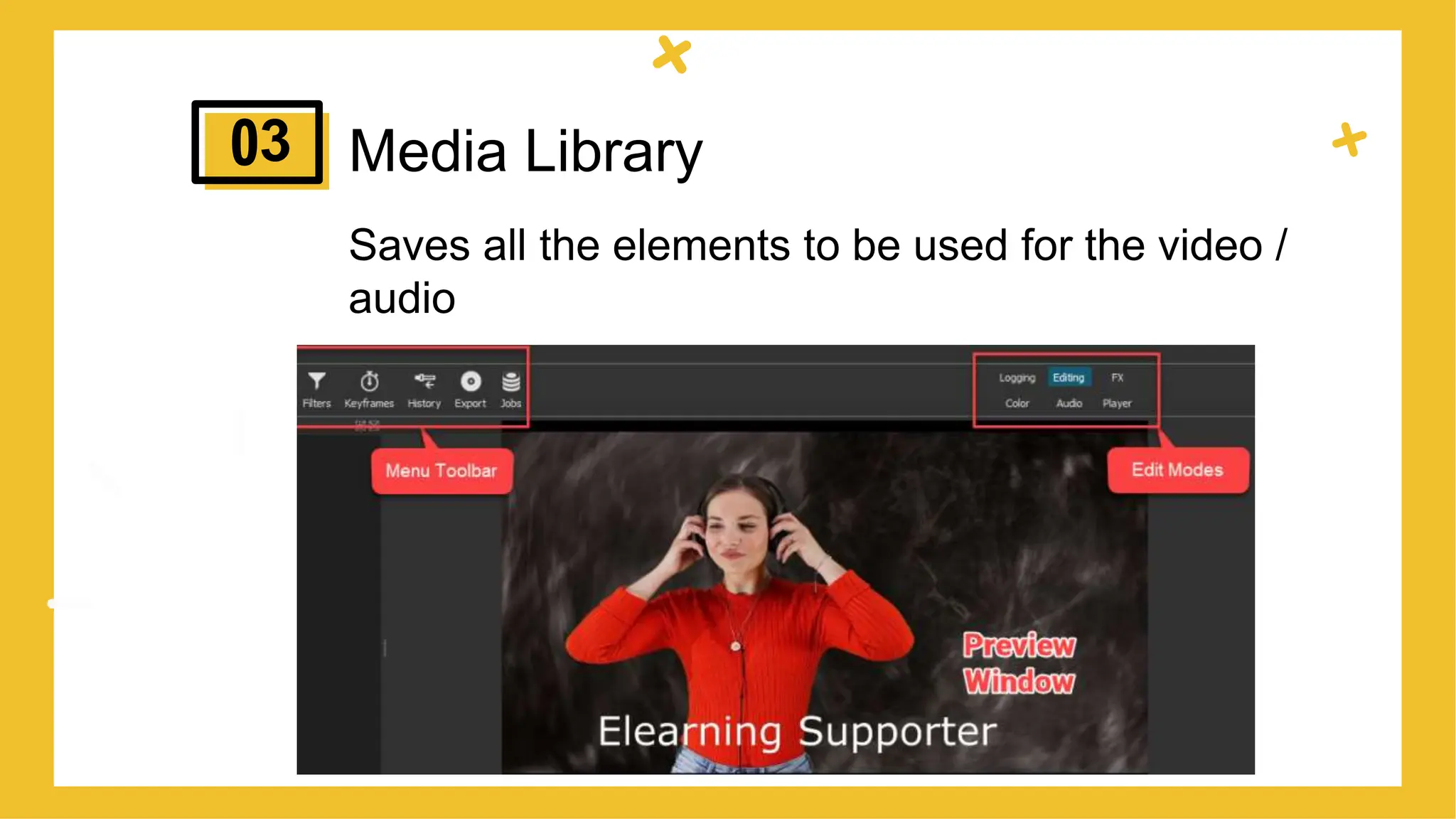
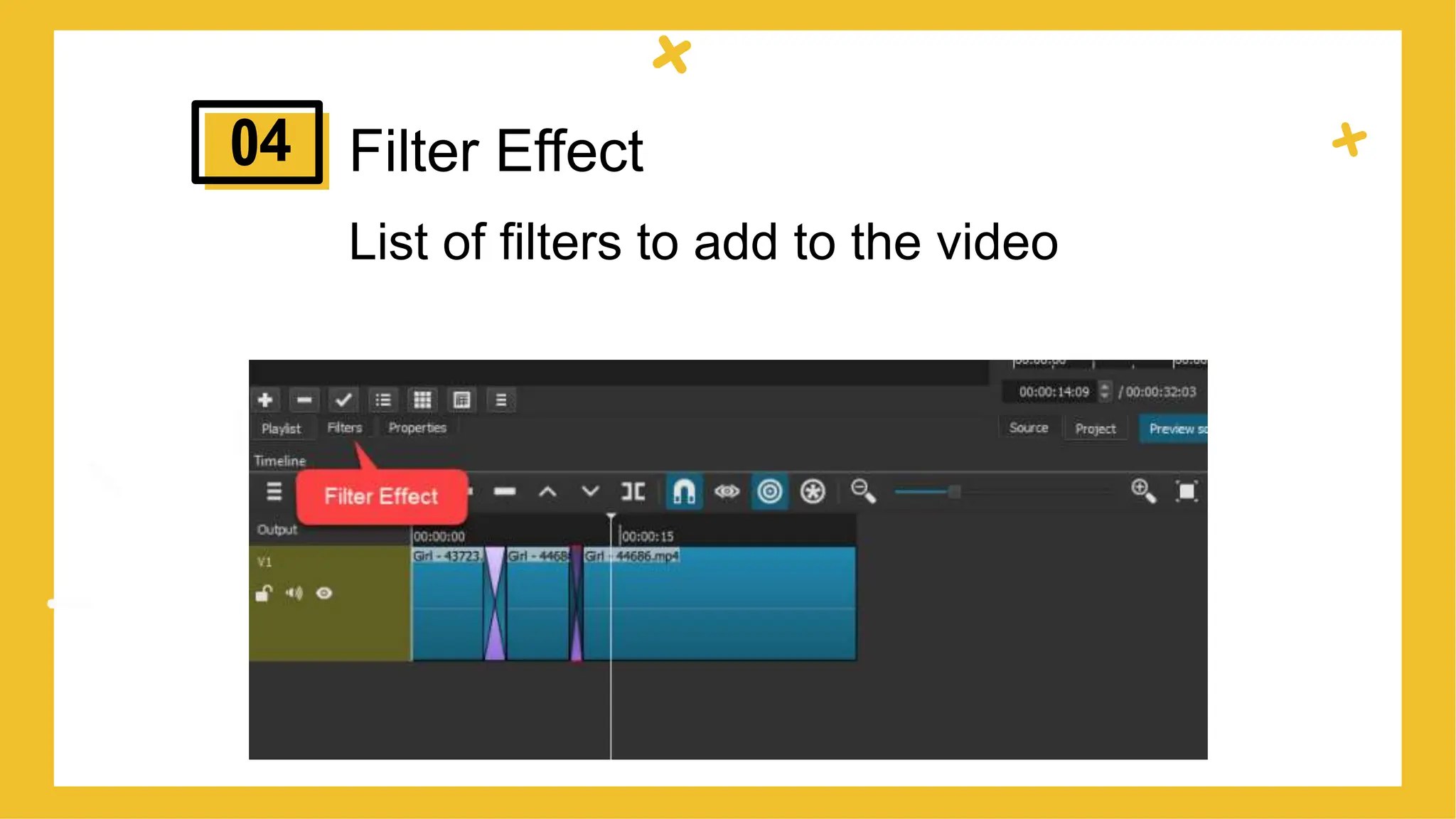
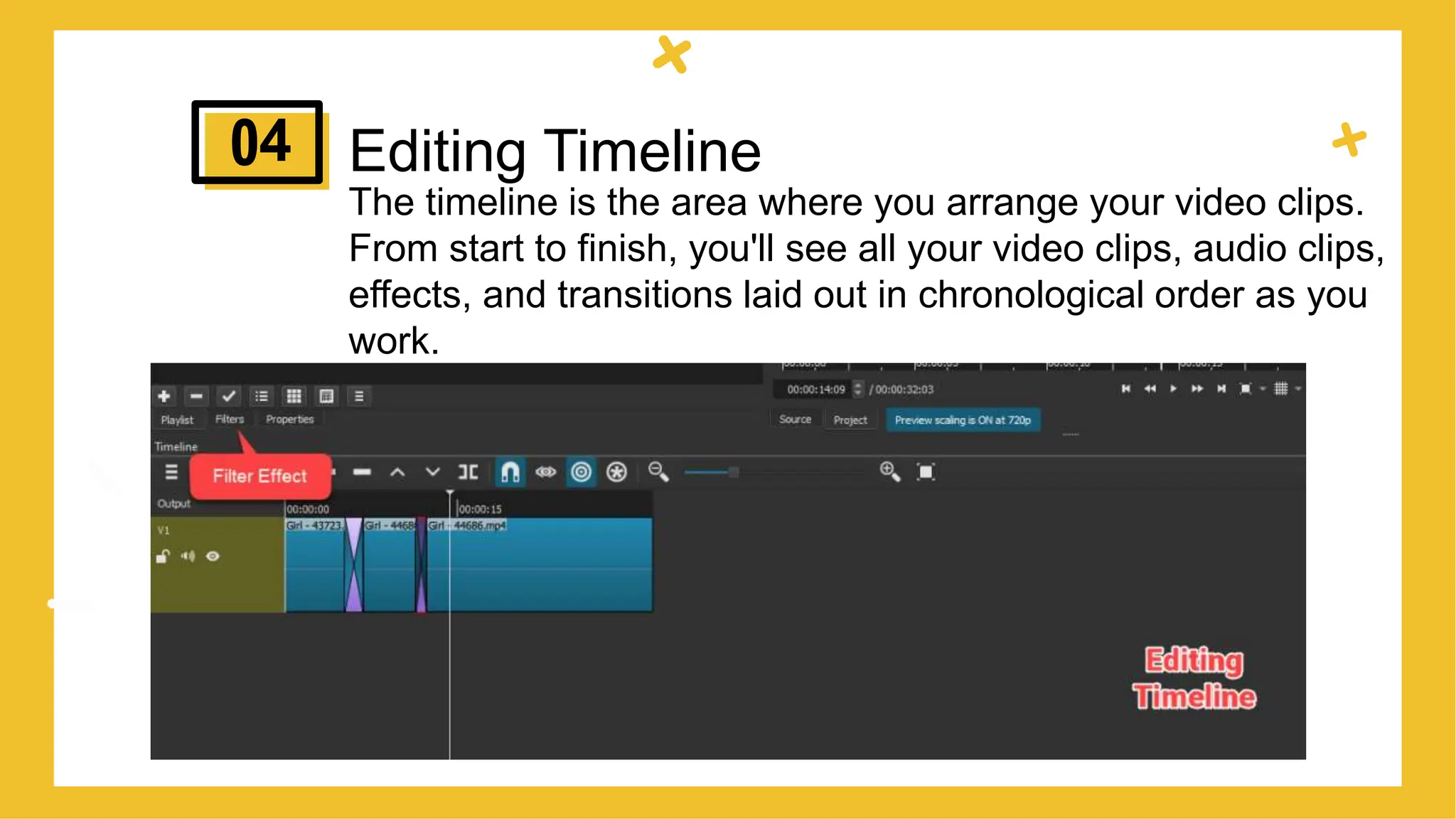
This document provides an overview of different types of educational videos and their uses. It discusses talking head videos, dialogue videos, demonstration videos, screencast videos, web lecture videos, and podcast videos. For each type, it provides examples and discusses when each type would be appropriate to use based on the goal of the video and content being covered. The document aims to help educators choose the right video format based on their learning objectives and what they want to achieve with their video content.