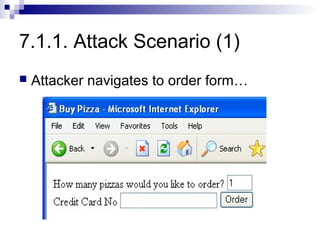
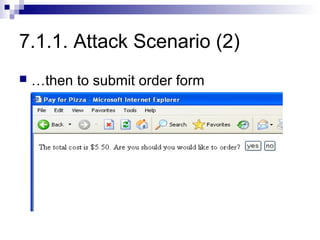
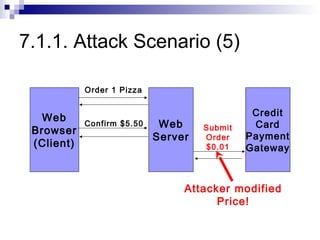
The document discusses client-state manipulation attacks on web applications. It provides an example of a pizza ordering website that is vulnerable because it stores the price in a hidden form field that can be manipulated by an attacker. Several solutions are presented, including storing state on the server, signing state parameters sent to the client, using POST requests instead of GET, and storing state in cookies. The document cautions that user input cannot be trusted and that computations done in JavaScript are not secure.