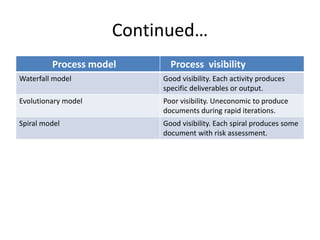
Risk management involves identifying and managing risks associated with software projects. It aims to avoid disasters or heavy losses. There are three categories of risk: project risks that affect schedule or resources, product risks that affect quality or performance, and business risks that affect the developing or purchasing organization. The risk management process involves identifying risks, analyzing their probability and impact, planning risk avoidance or minimization, monitoring risks, and documenting outcomes. Process visibility is important and can be achieved through documentation, diagrams, training, and tools that make processes accessible. It helps ensure competency and collaboration.