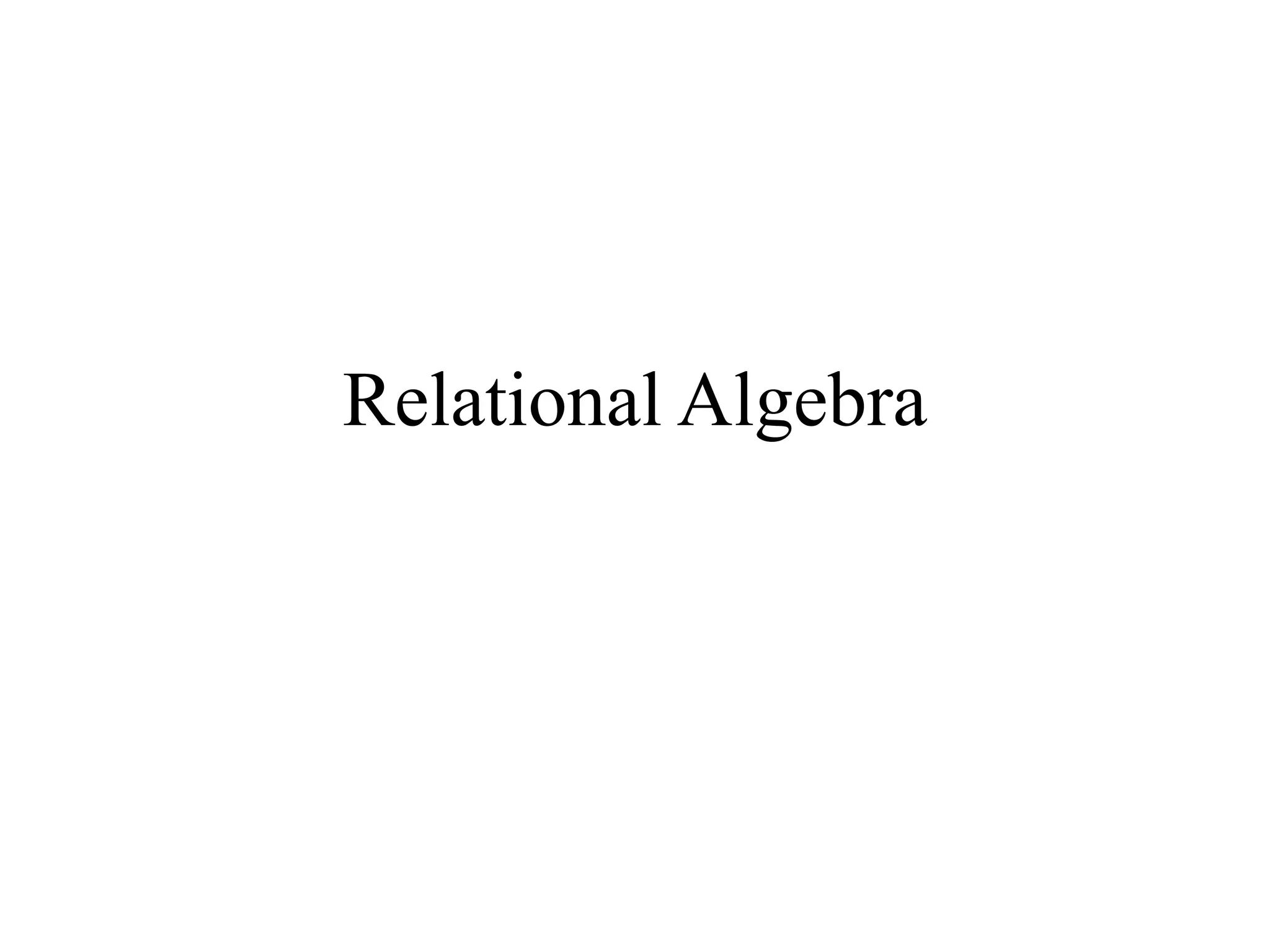
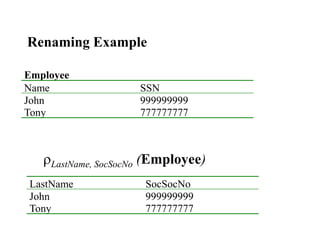
Relational algebra consists of operators that allow deriving new relations from old ones. The five main operators are:
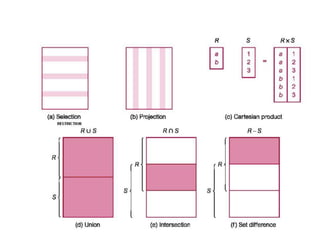
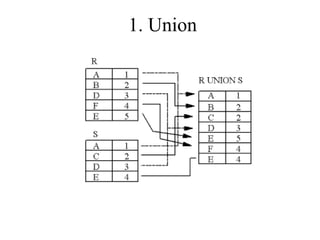
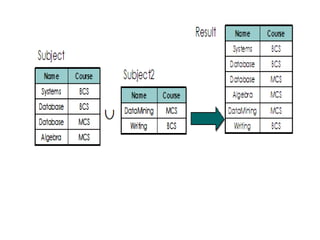
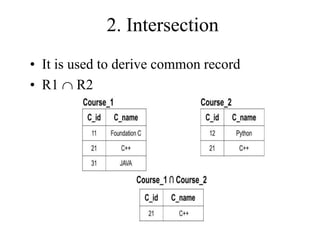
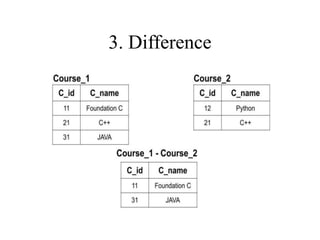
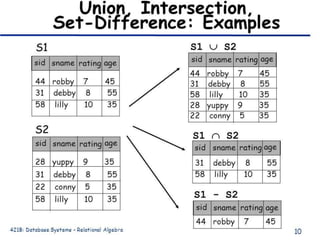
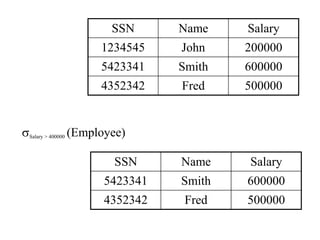
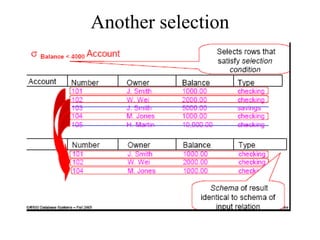
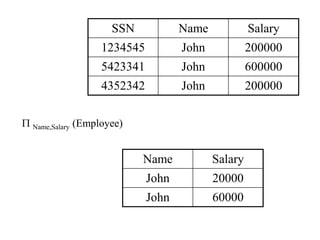
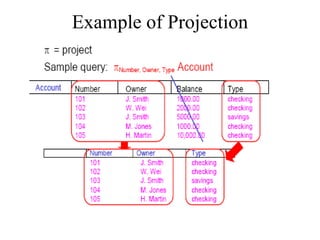
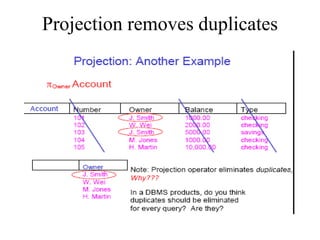
1) Union combines relations, 2) Intersection returns common tuples between relations, 3) Difference returns tuples in one relation not in another, 4) Selection returns tuples satisfying a condition, and 5) Projection eliminates columns and removes duplicates. Other operators include Cartesian Product, which pairs all tuples between relations, and Rename, which changes the schema but not instances.