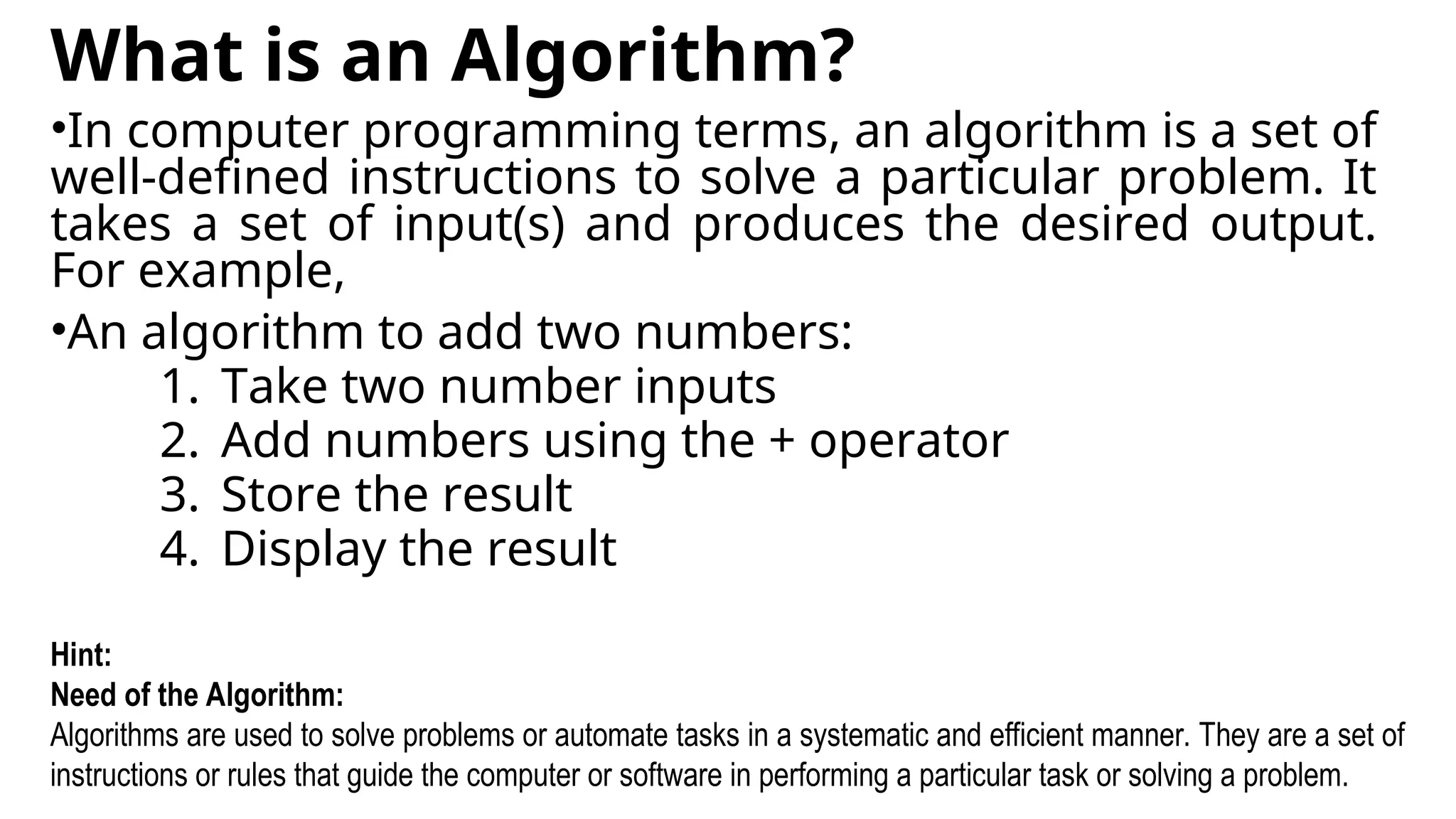
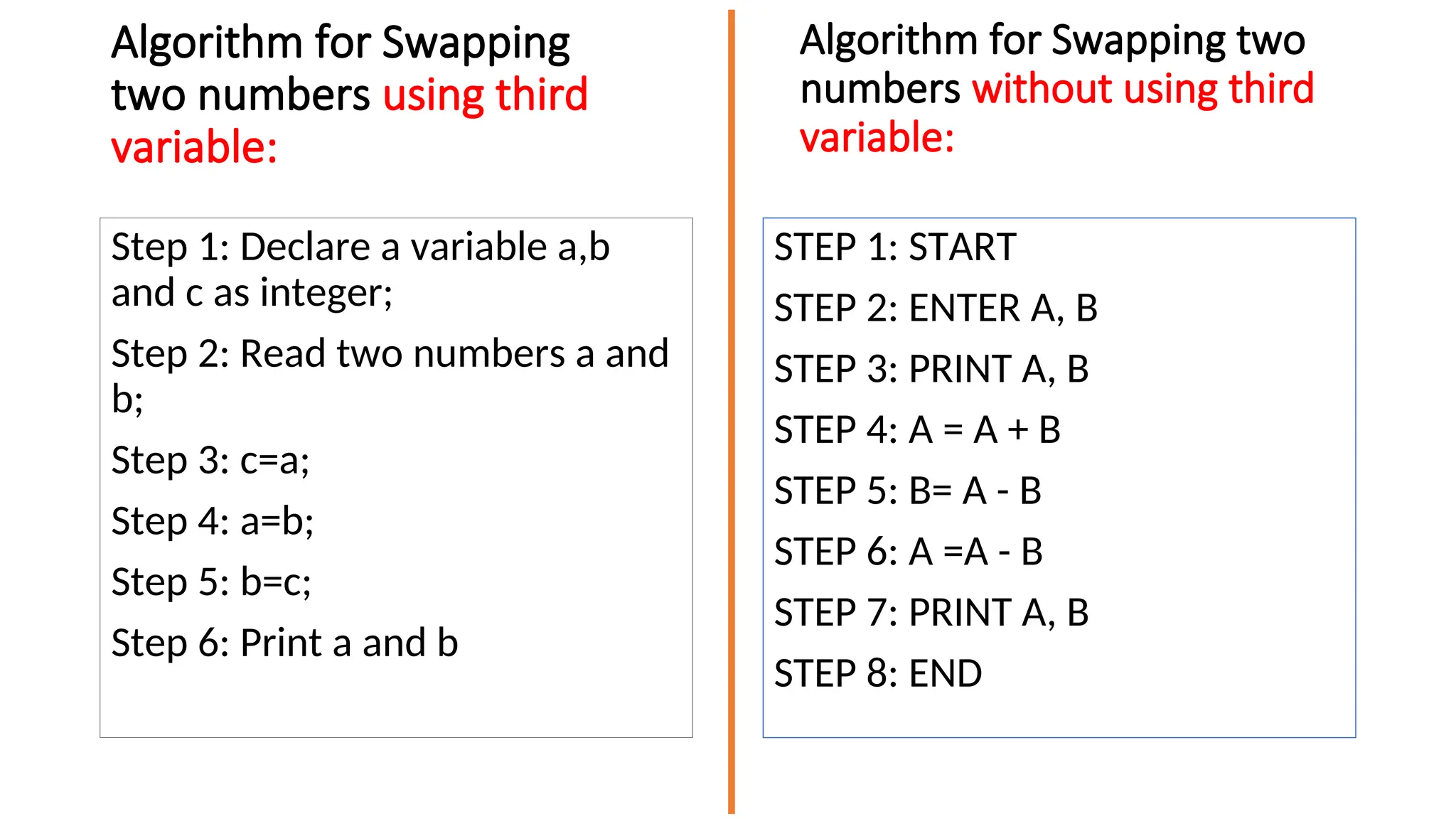
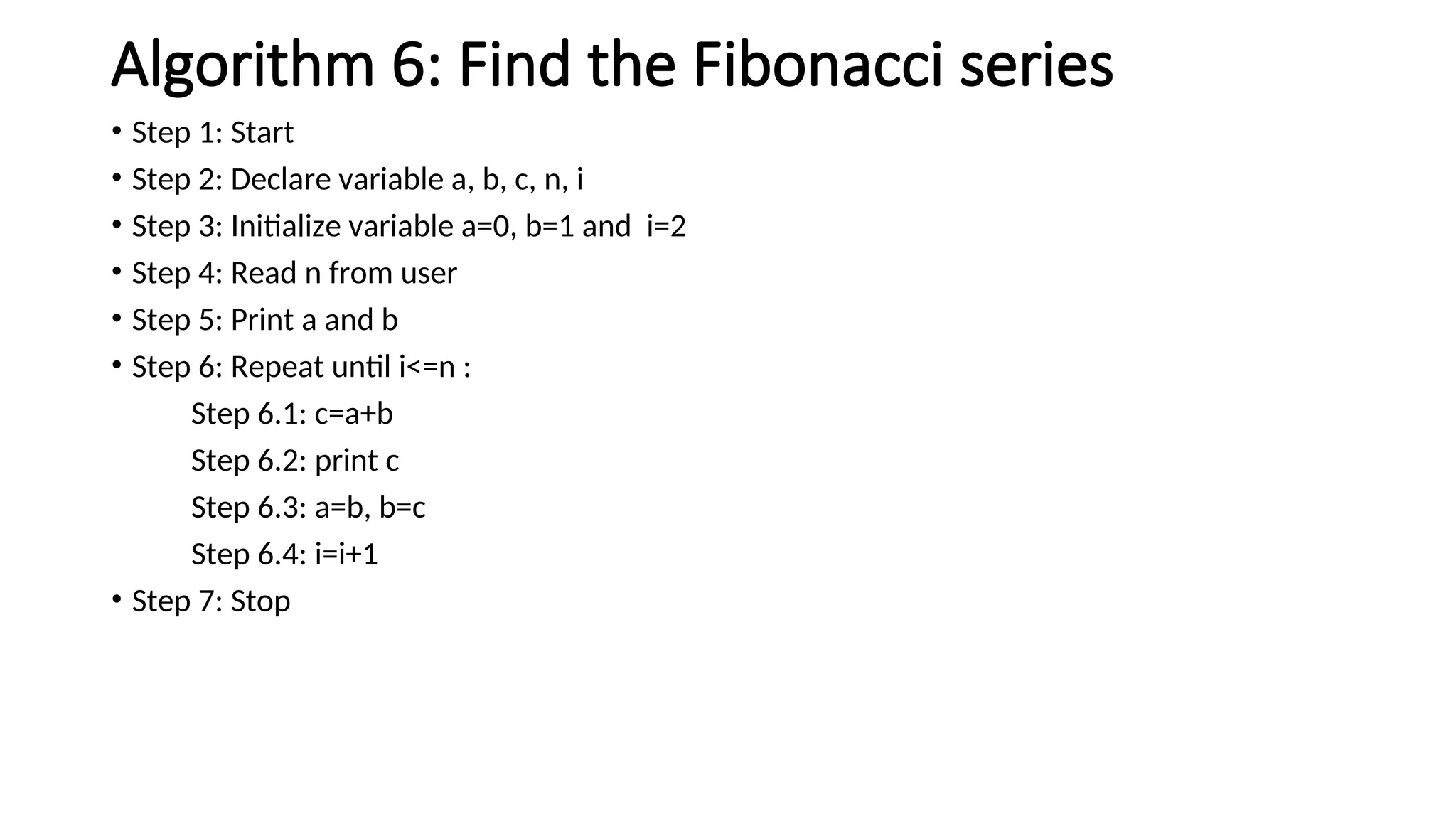
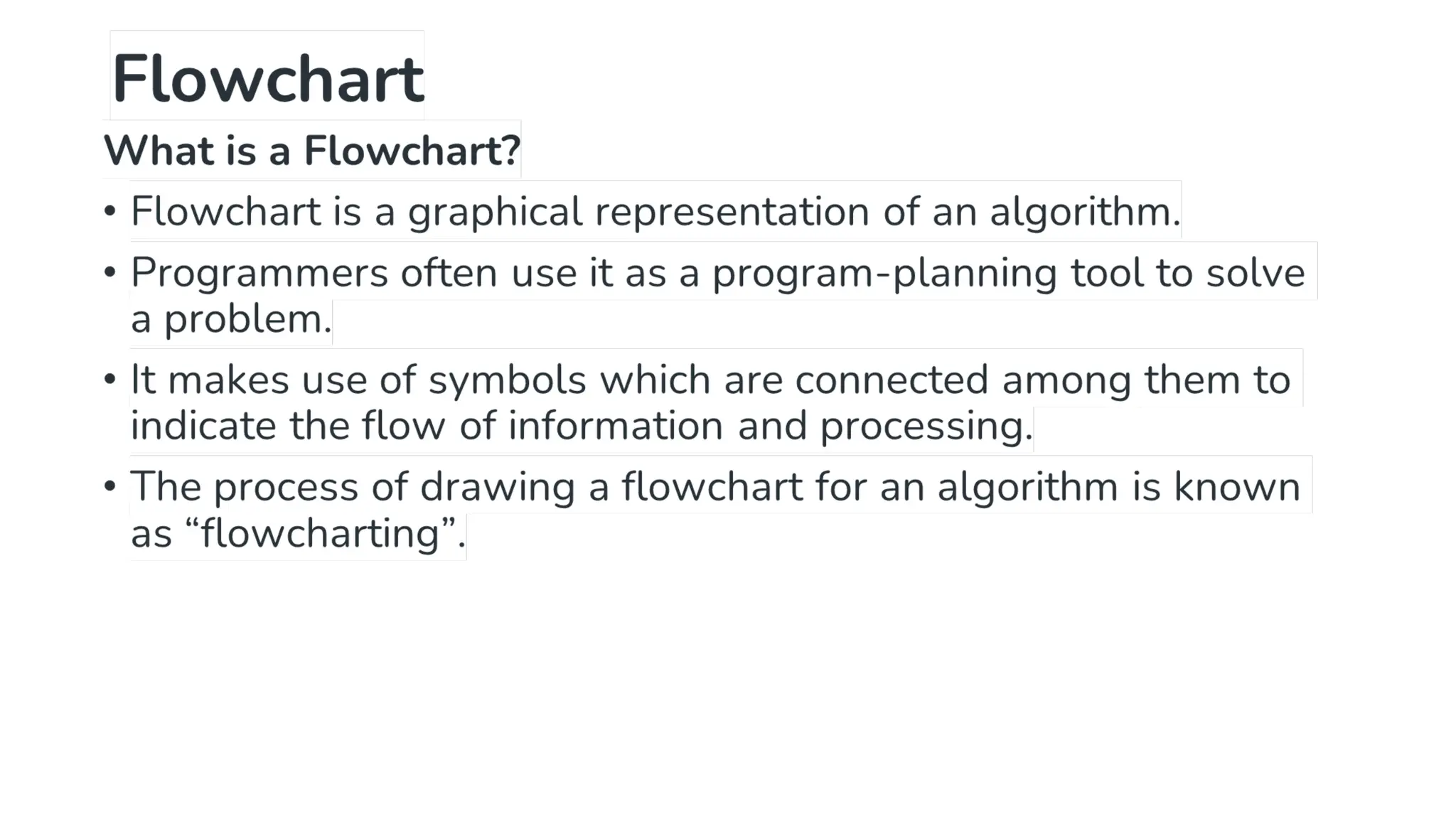
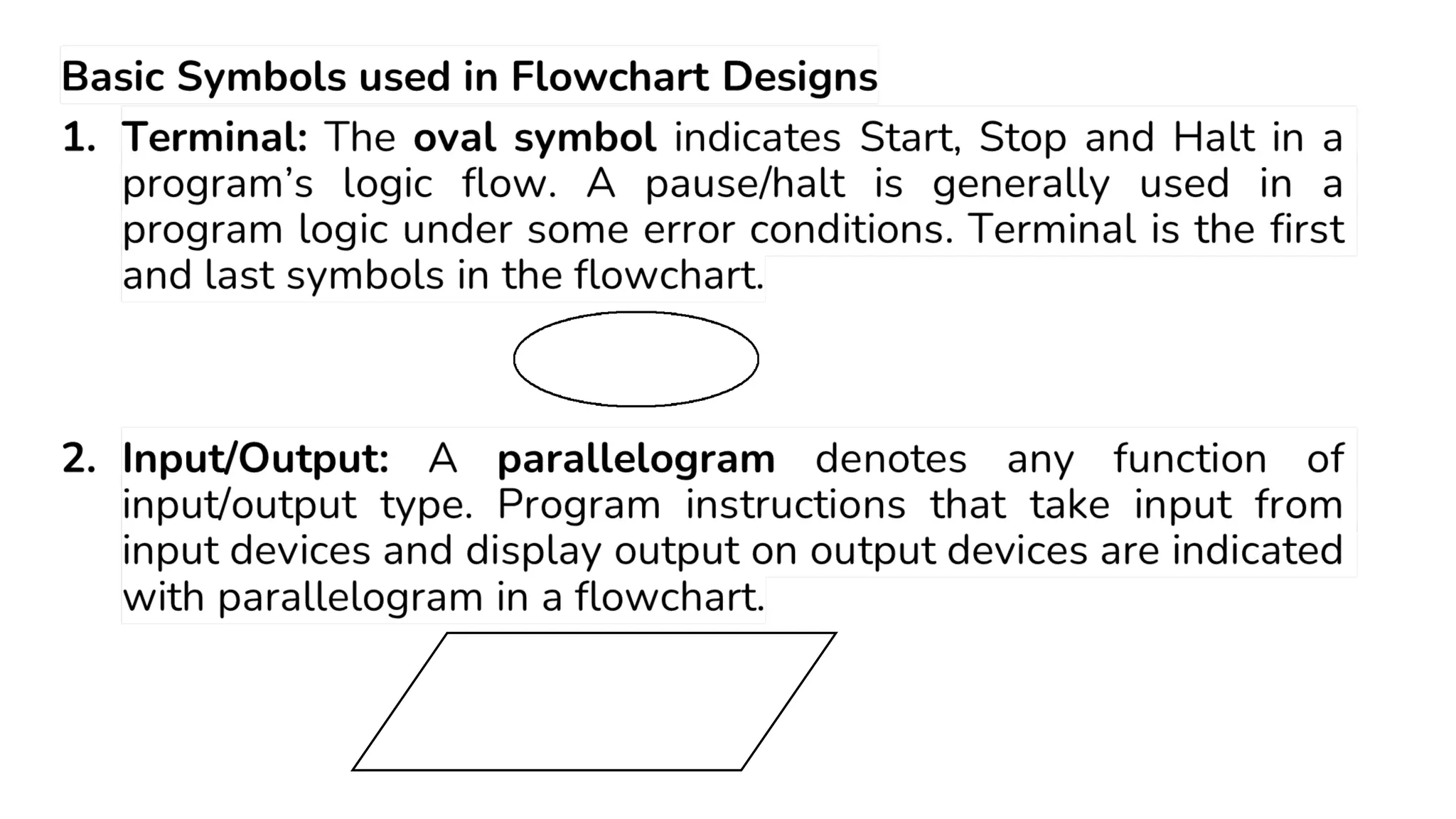
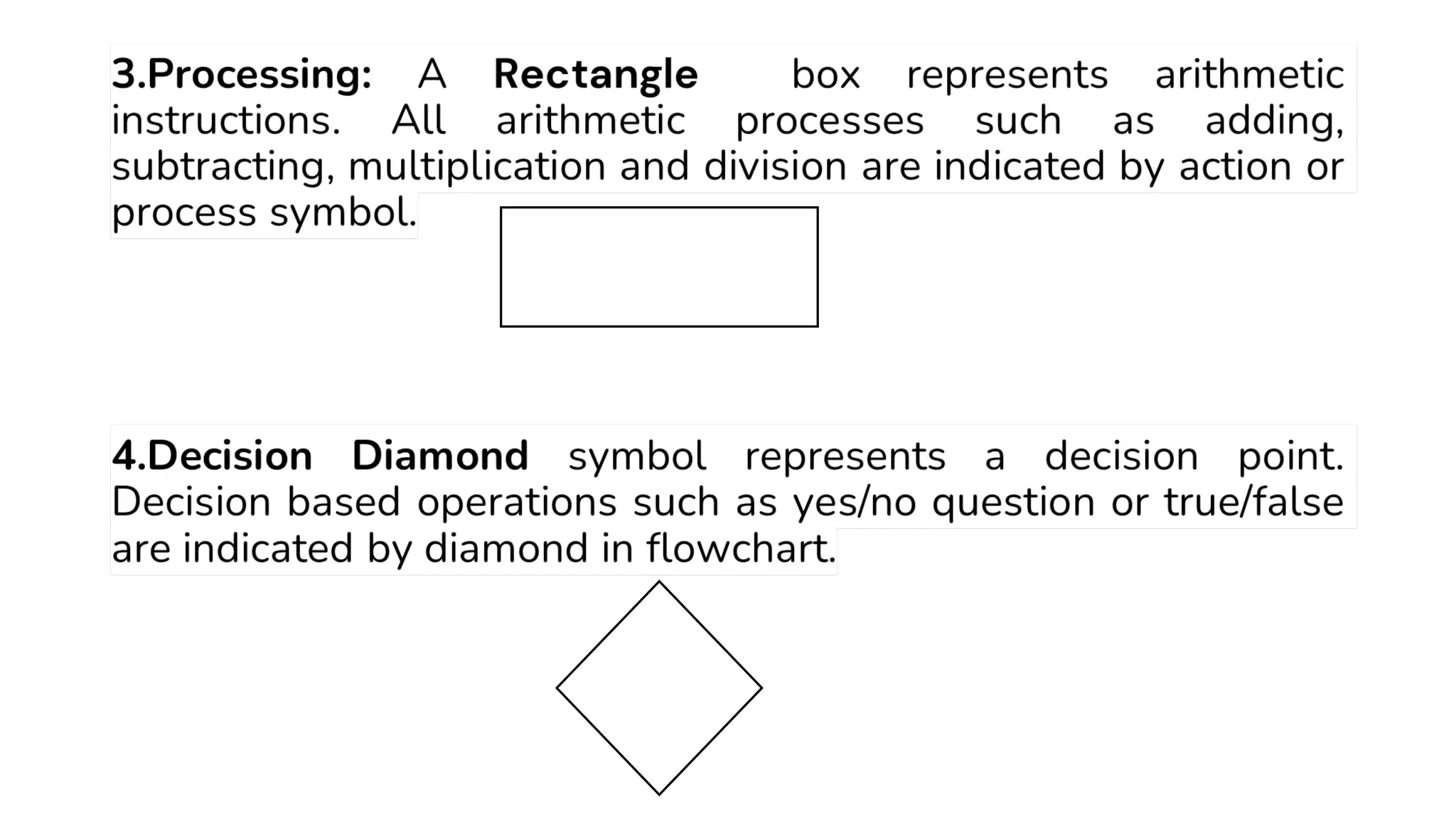
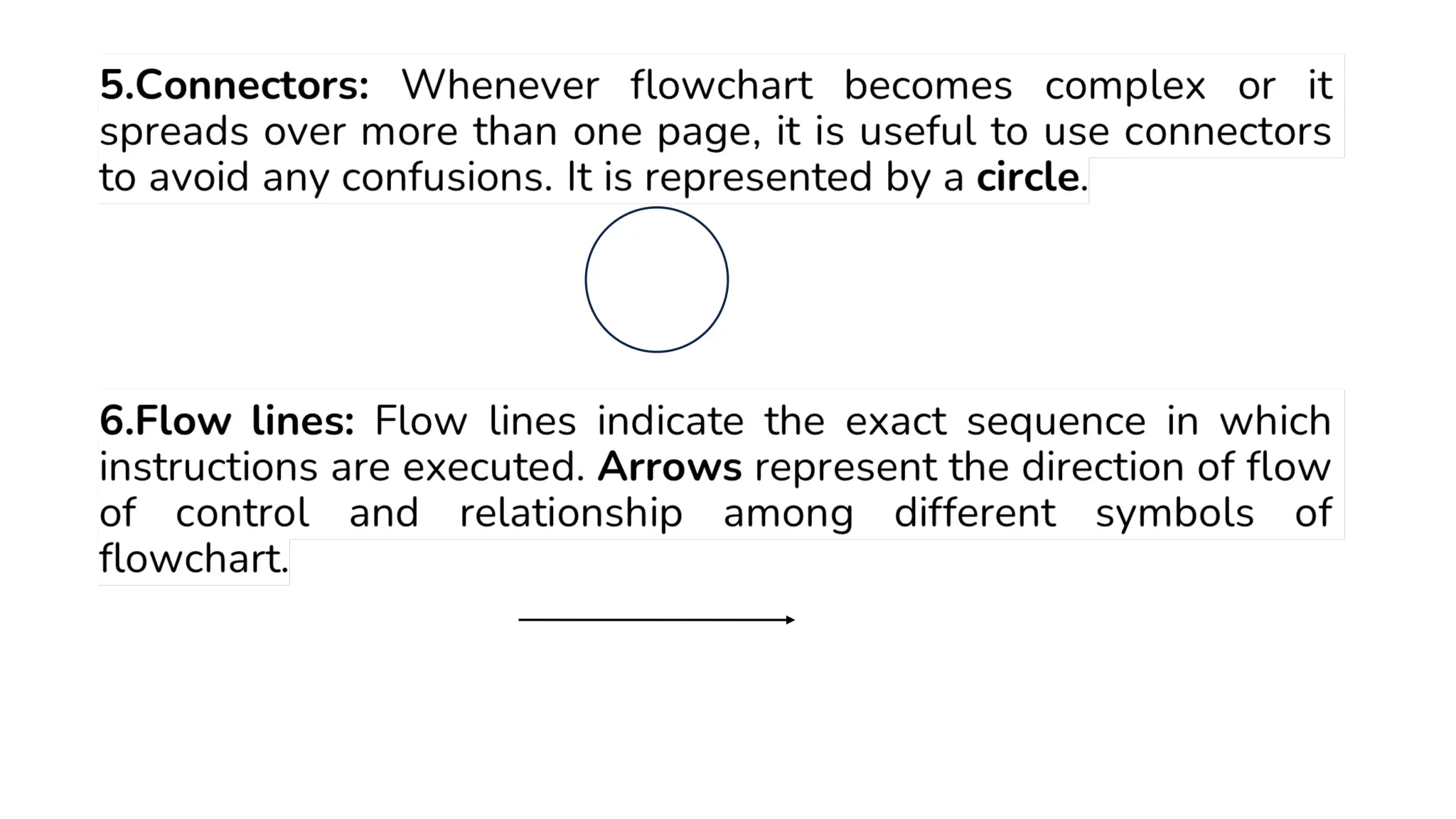
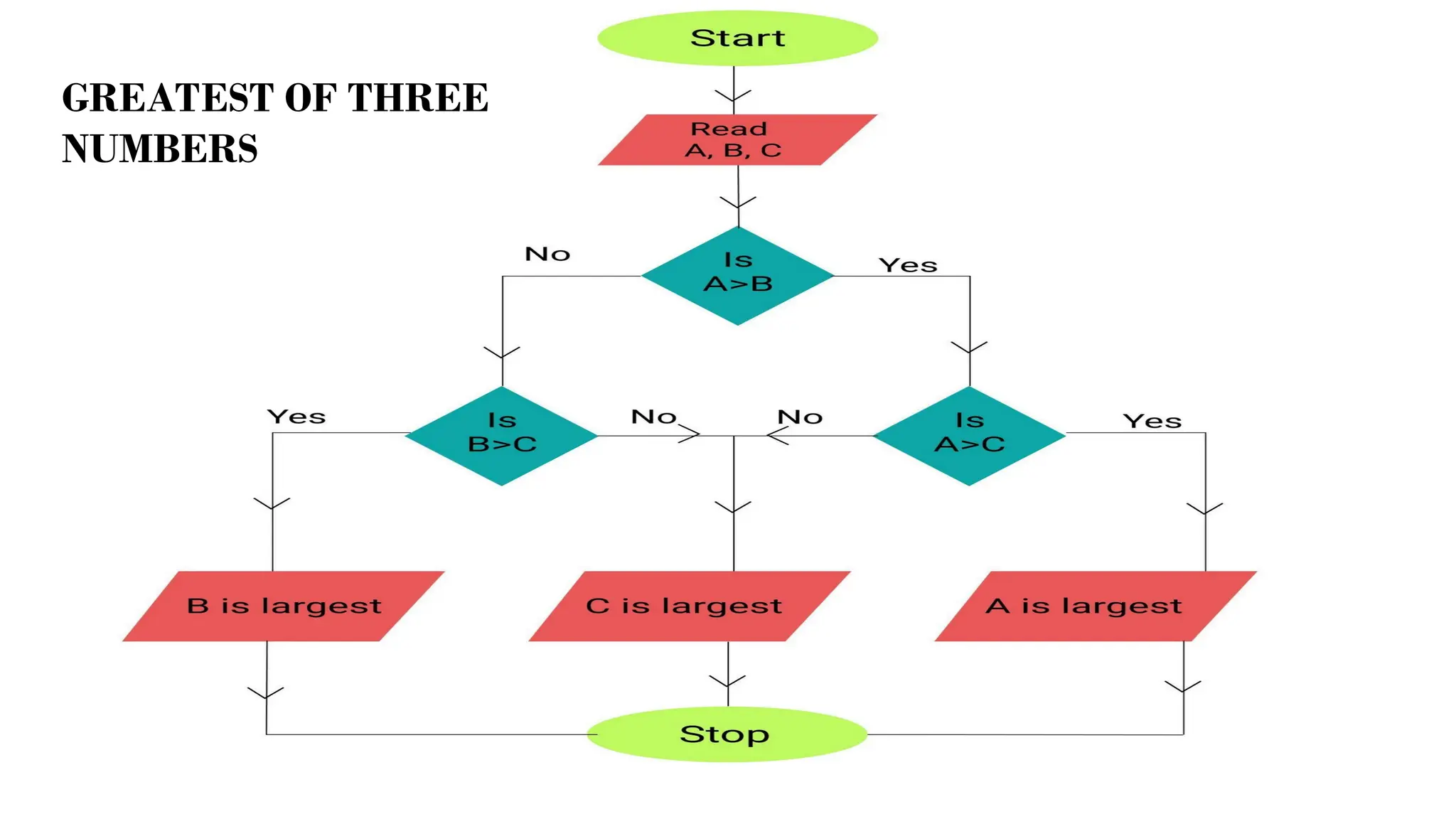
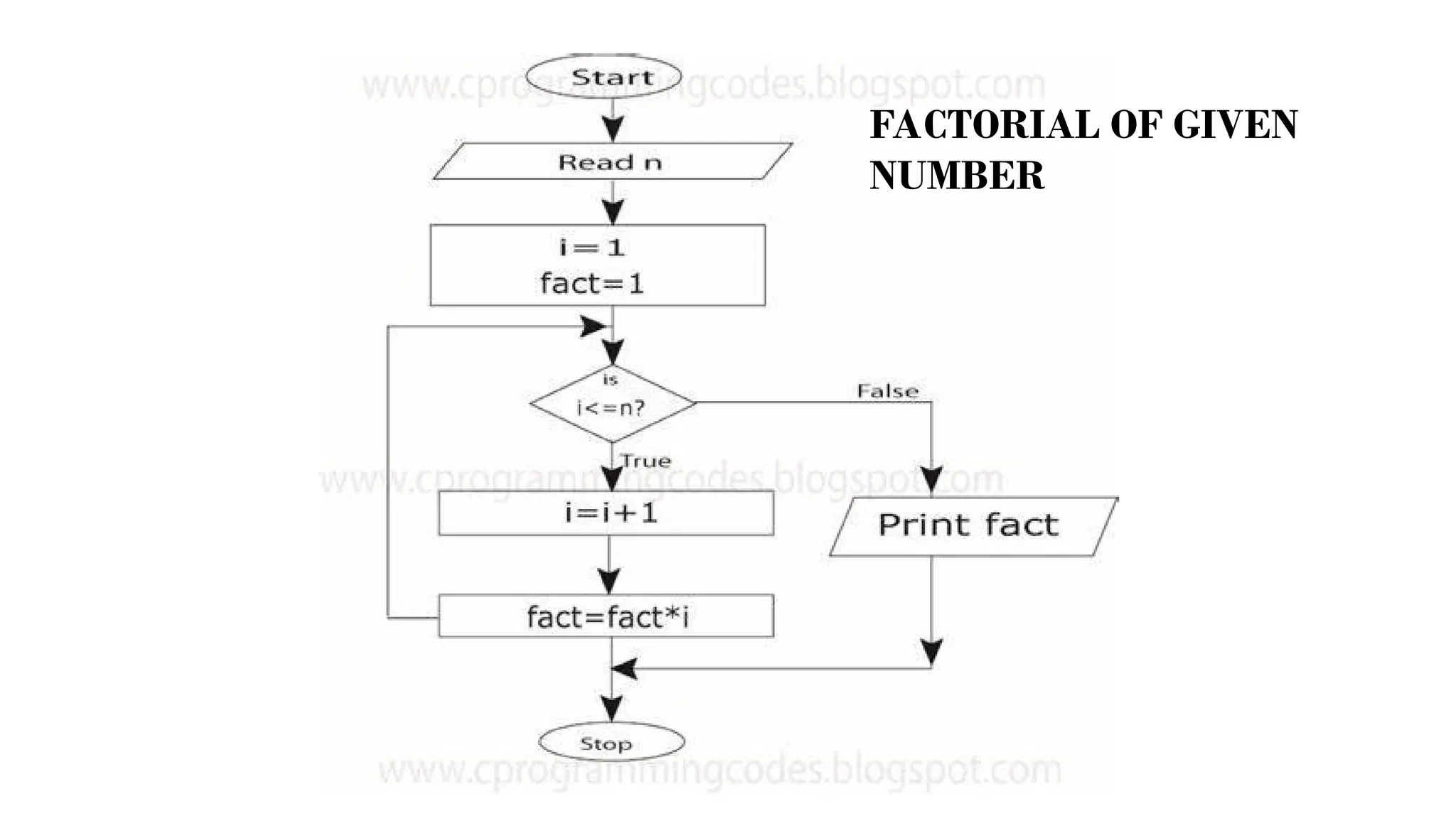
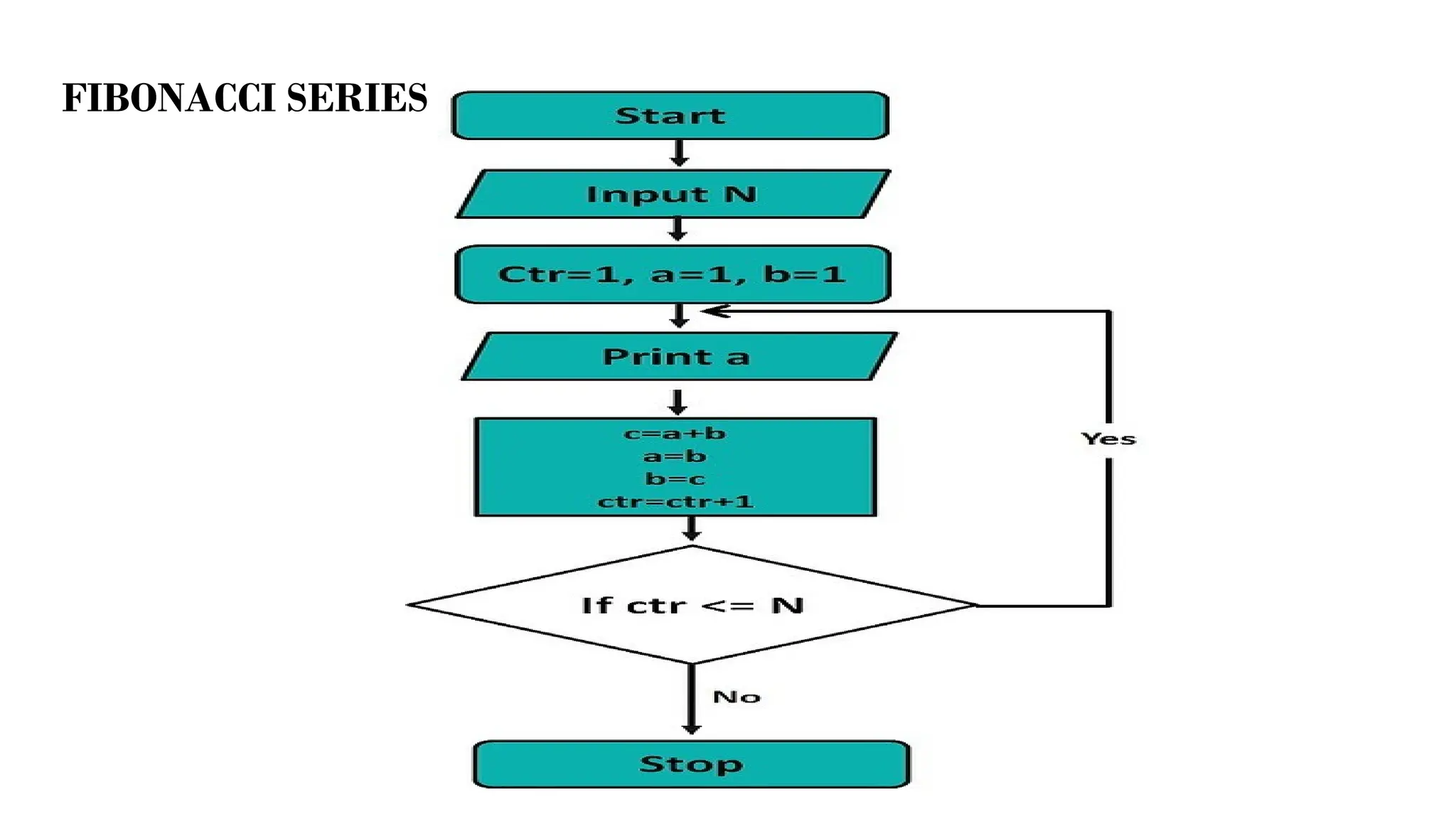
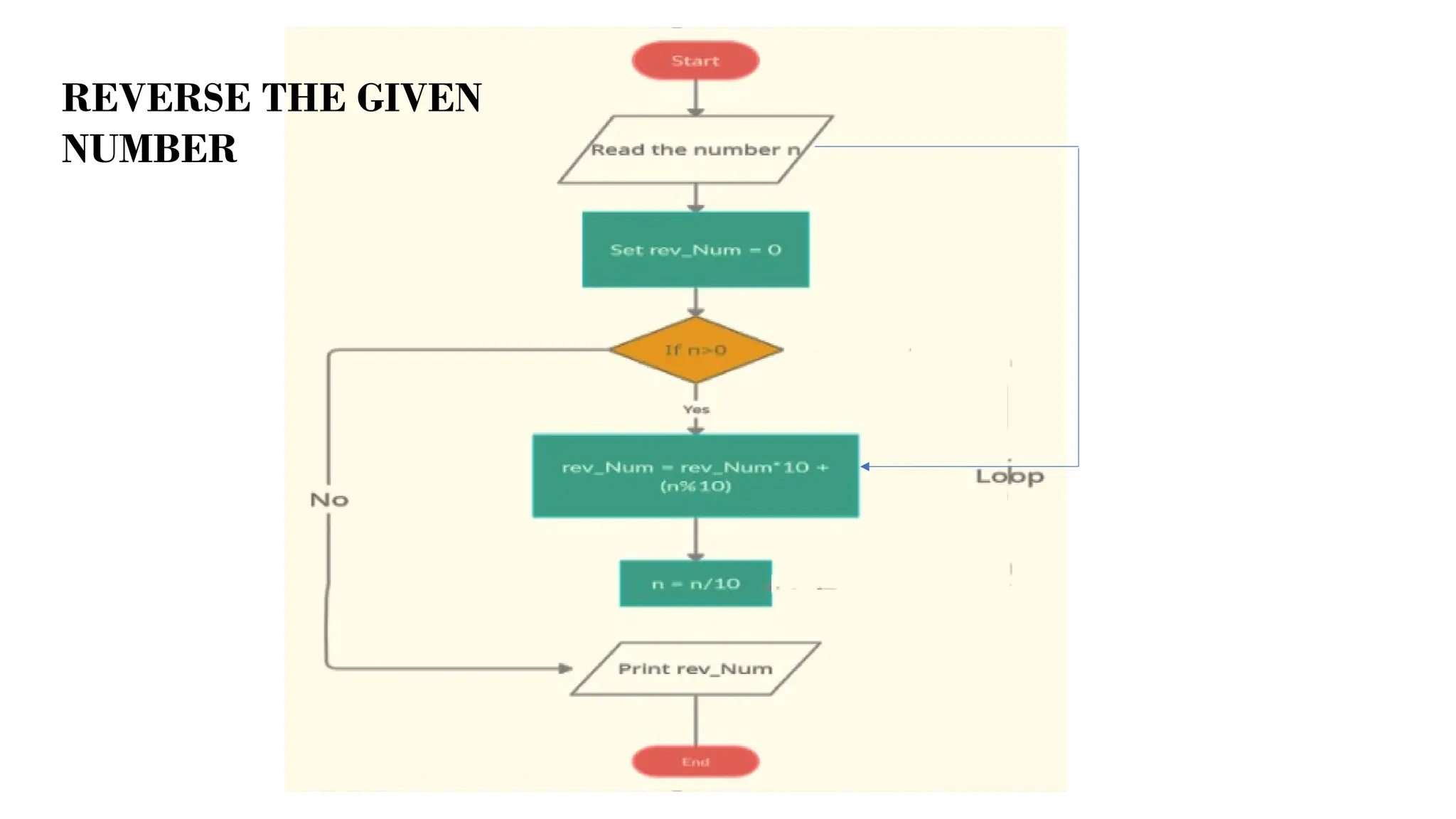
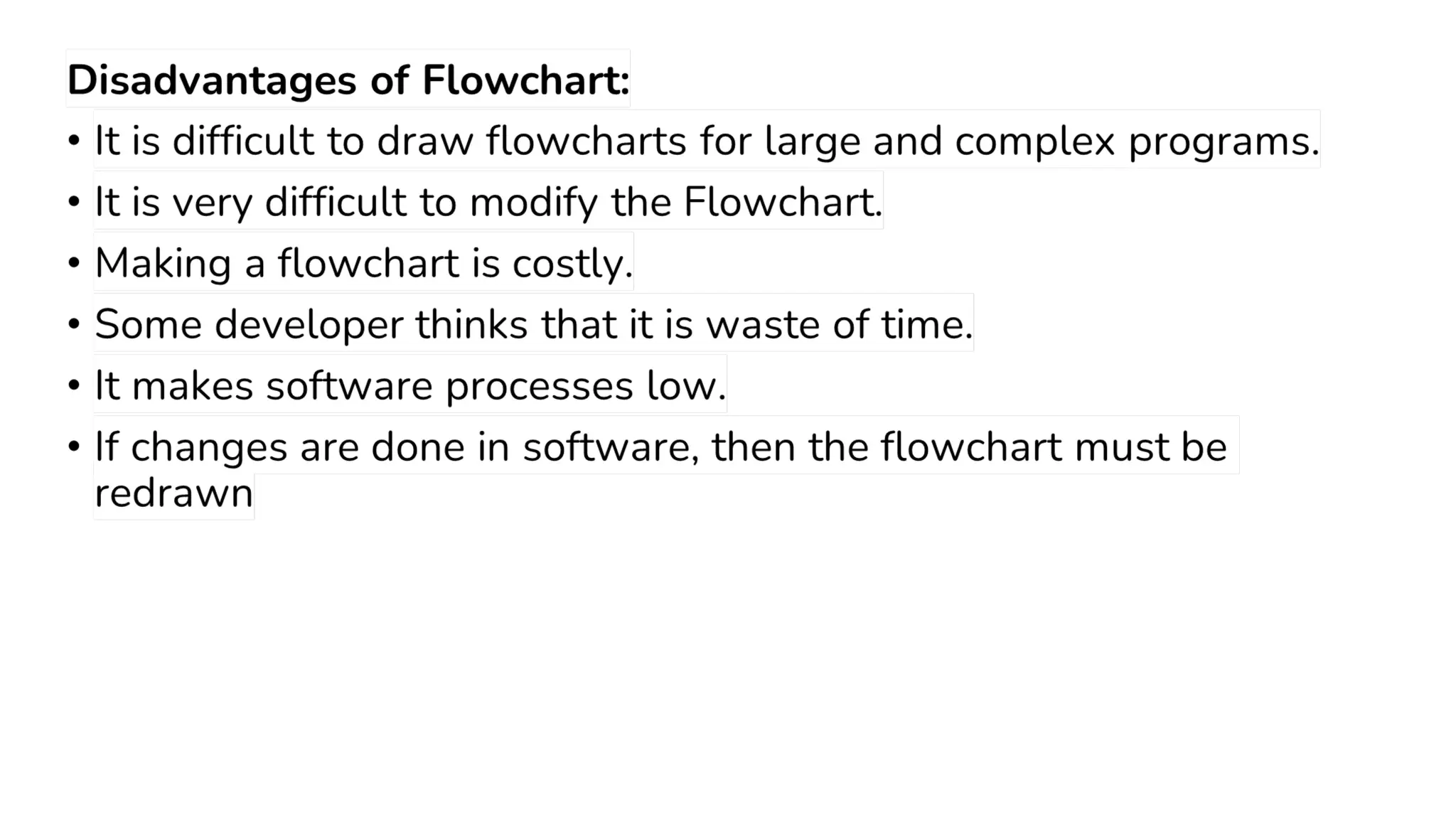
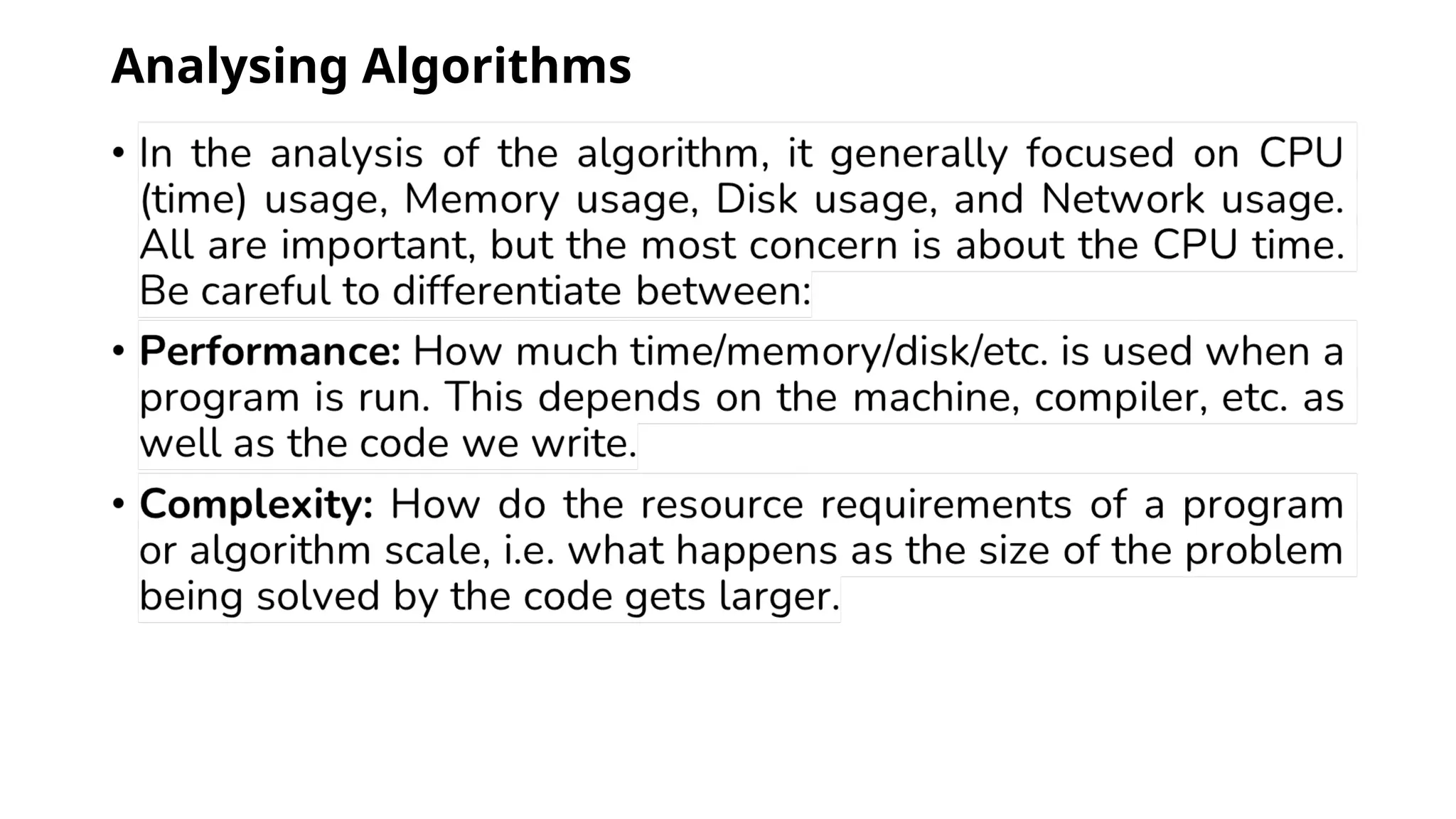
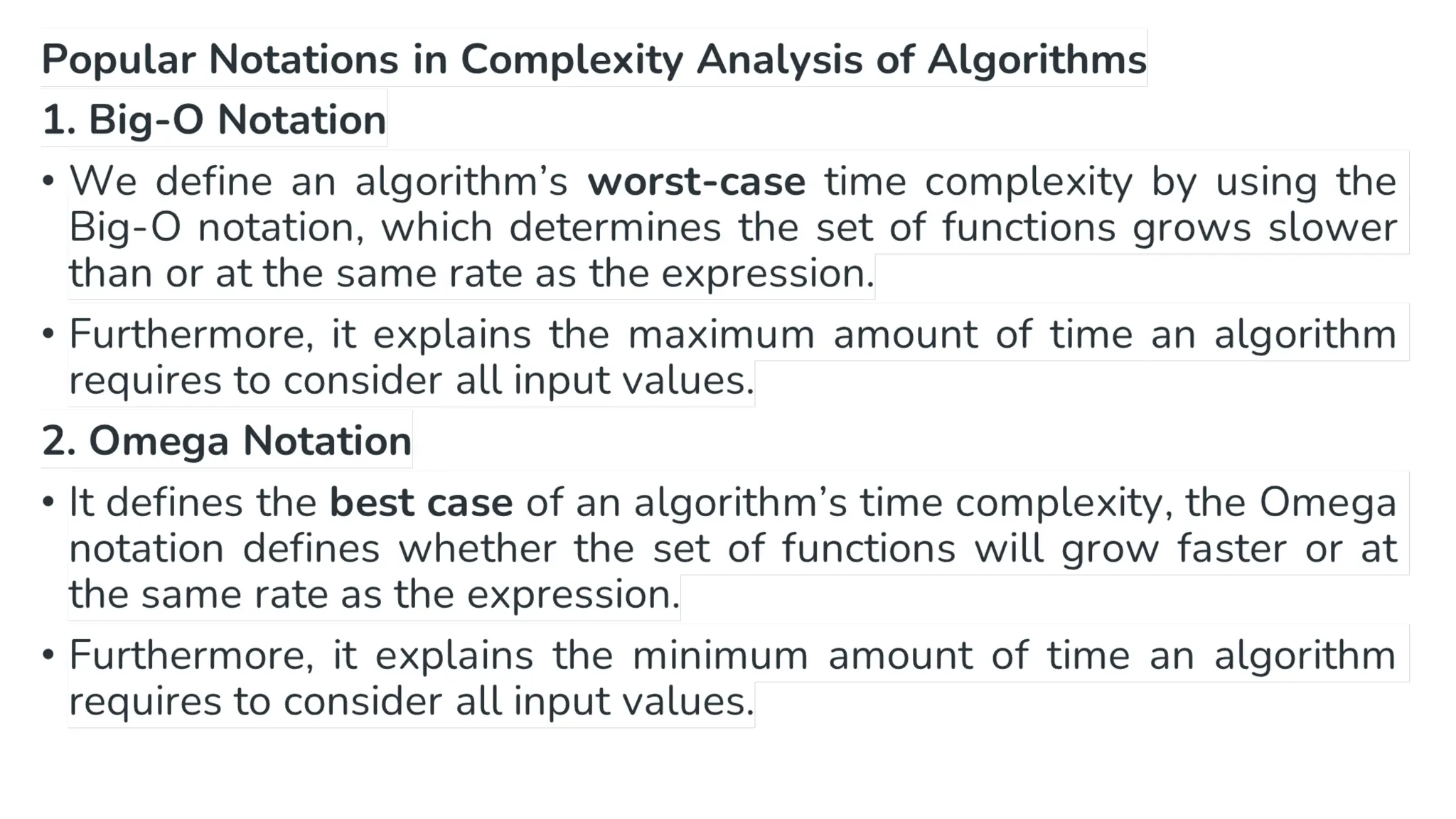
This document provides a comprehensive overview of algorithms in computing, explaining their role, design, and fundamental operations such as exchanging values, counting, and computing factorials. It outlines the steps involved in problem solving, including definition, analysis, design, coding, testing, and maintenance. Additionally, it defines algorithms, highlights their characteristics and advantages, and provides examples of algorithms for common tasks.