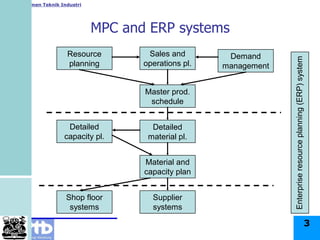
This document discusses Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. It provides an overview of ERP, including its evolution from earlier MRP and MRP II systems, its scope across various business functions, and key characteristics. ERP systems integrate data and processes throughout a company. The document outlines the components and implementation of SAP, a popular ERP software package, and discusses critical success factors, examples of successful and failed ERP implementations, and reasons why ERP projects may fail.