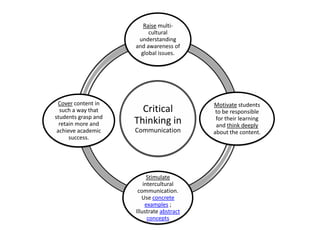
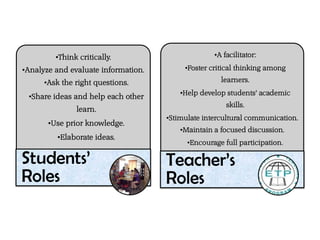
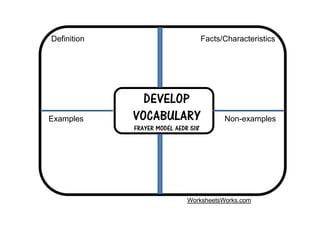
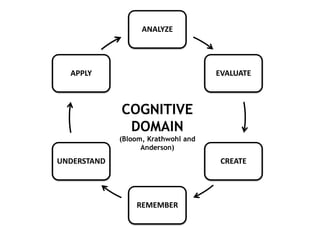
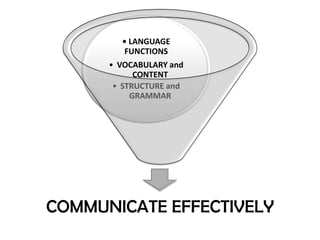
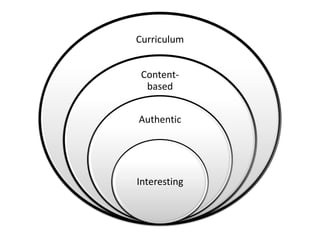
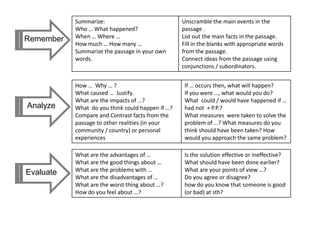
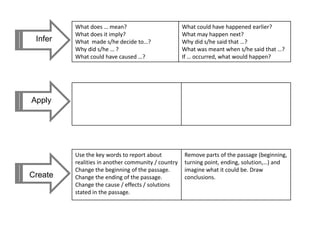
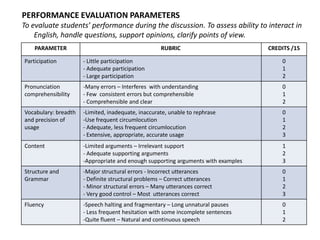
This document outlines strategies for promoting critical thinking in communication. It discusses having students and teachers take active roles, developing vocabulary, using critical thinking skills like analyzing and evaluating, focusing on academic skills like effective communication, and choosing engaging materials. A variety of in-class communication activities are provided to help students summarize, analyze, evaluate, infer, apply, and create. Student performance is evaluated based on participation, pronunciation, vocabulary, content, structure, grammar, and fluency. References for additional information are also included.