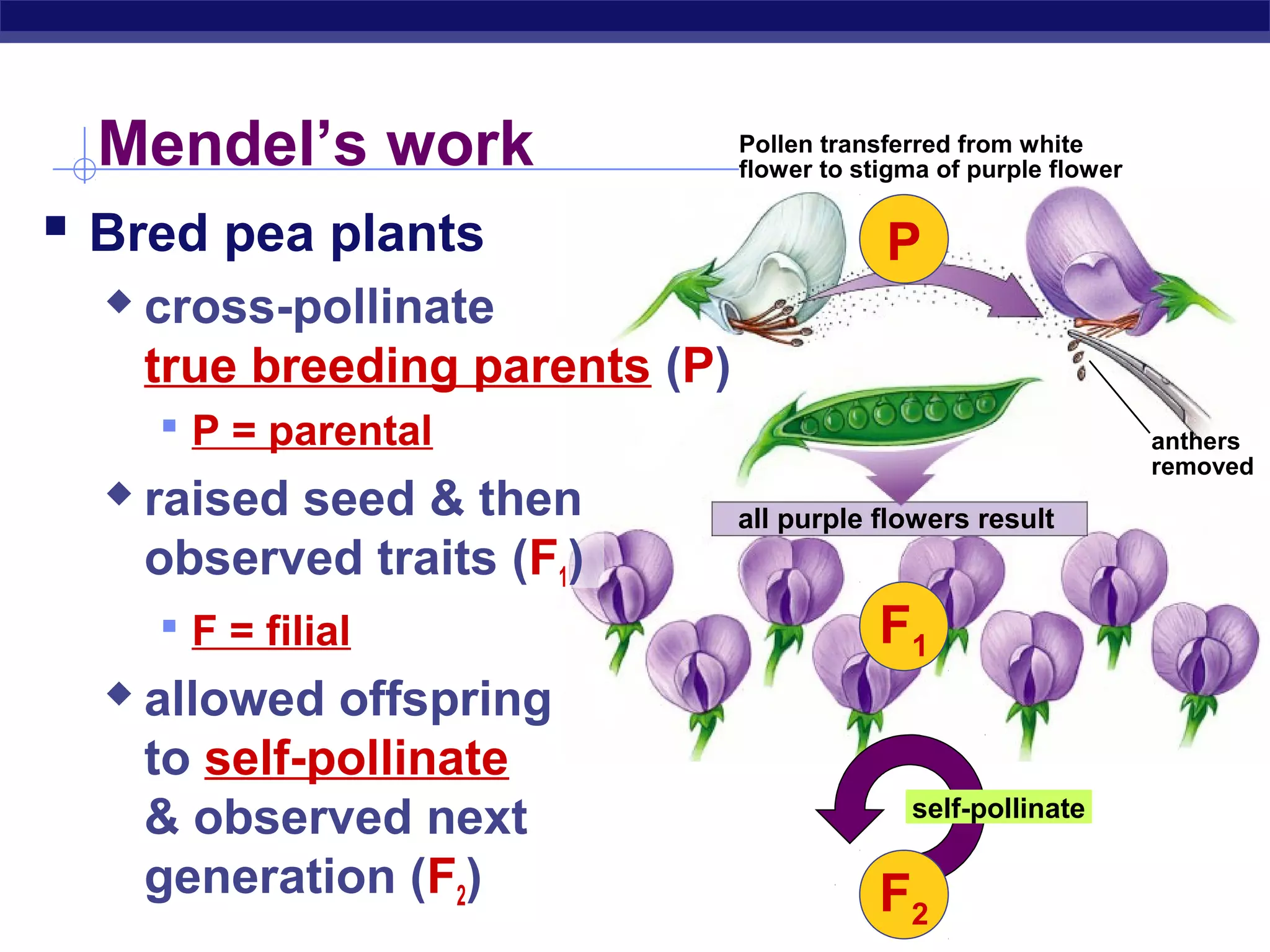
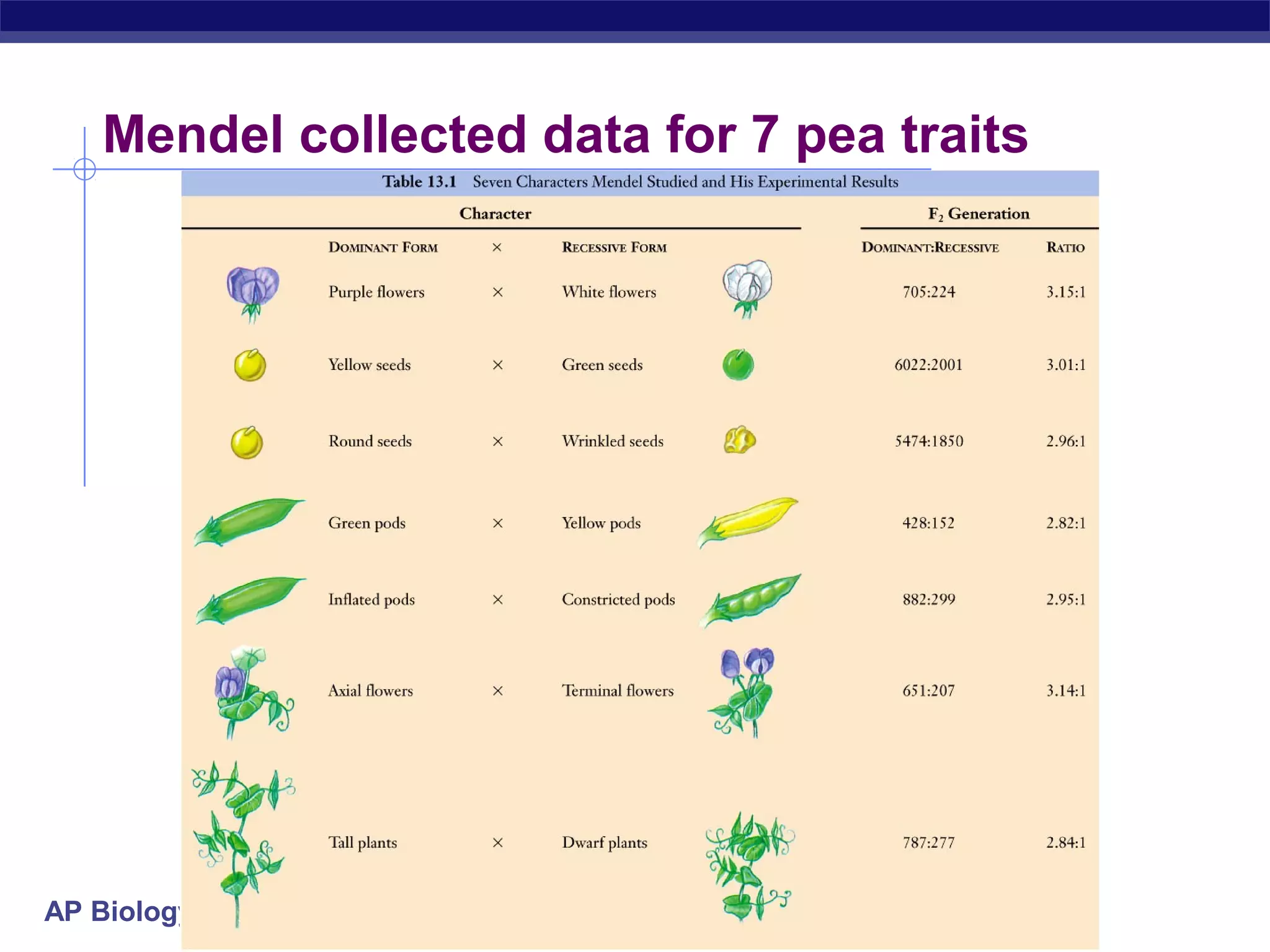
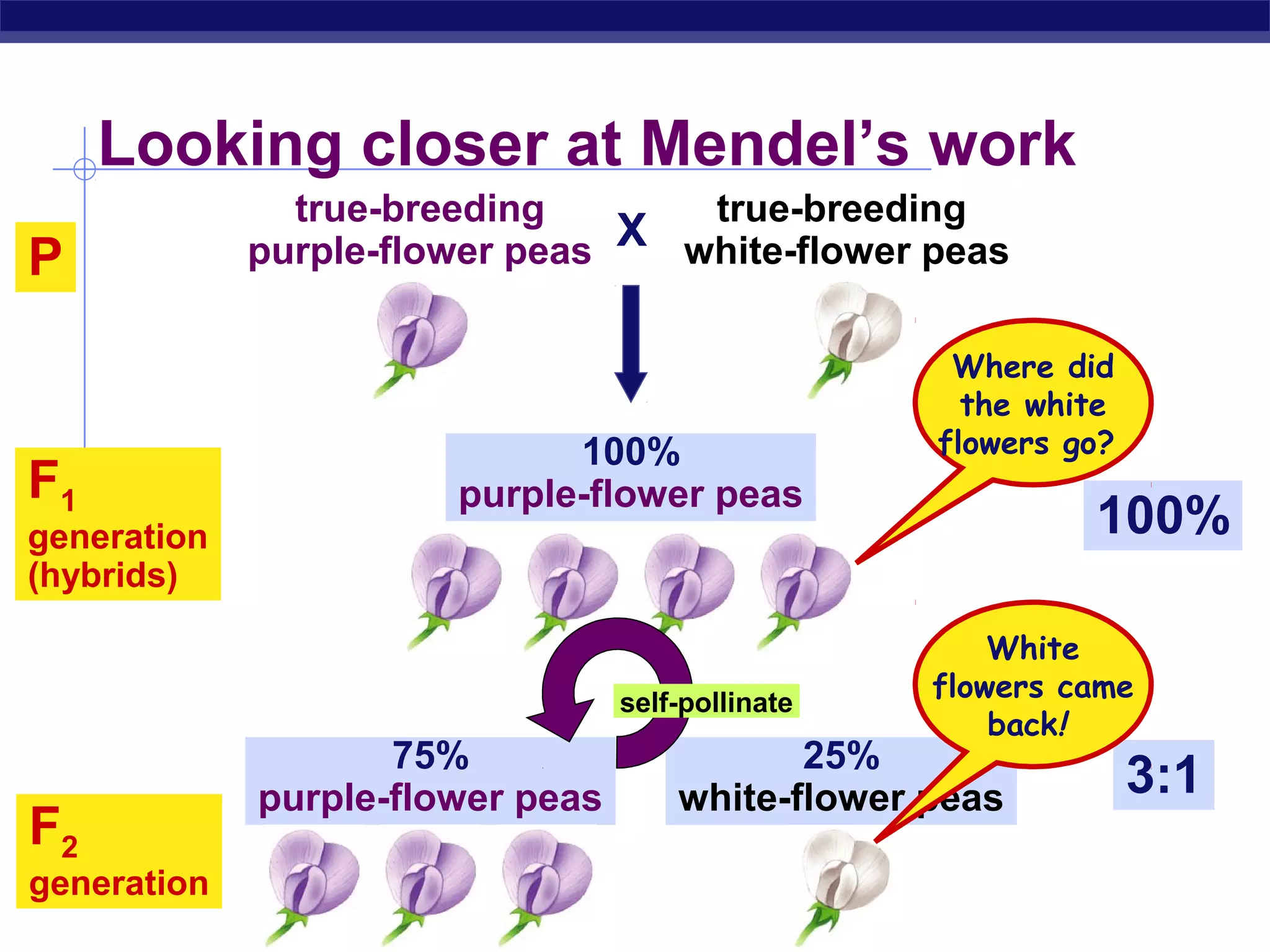
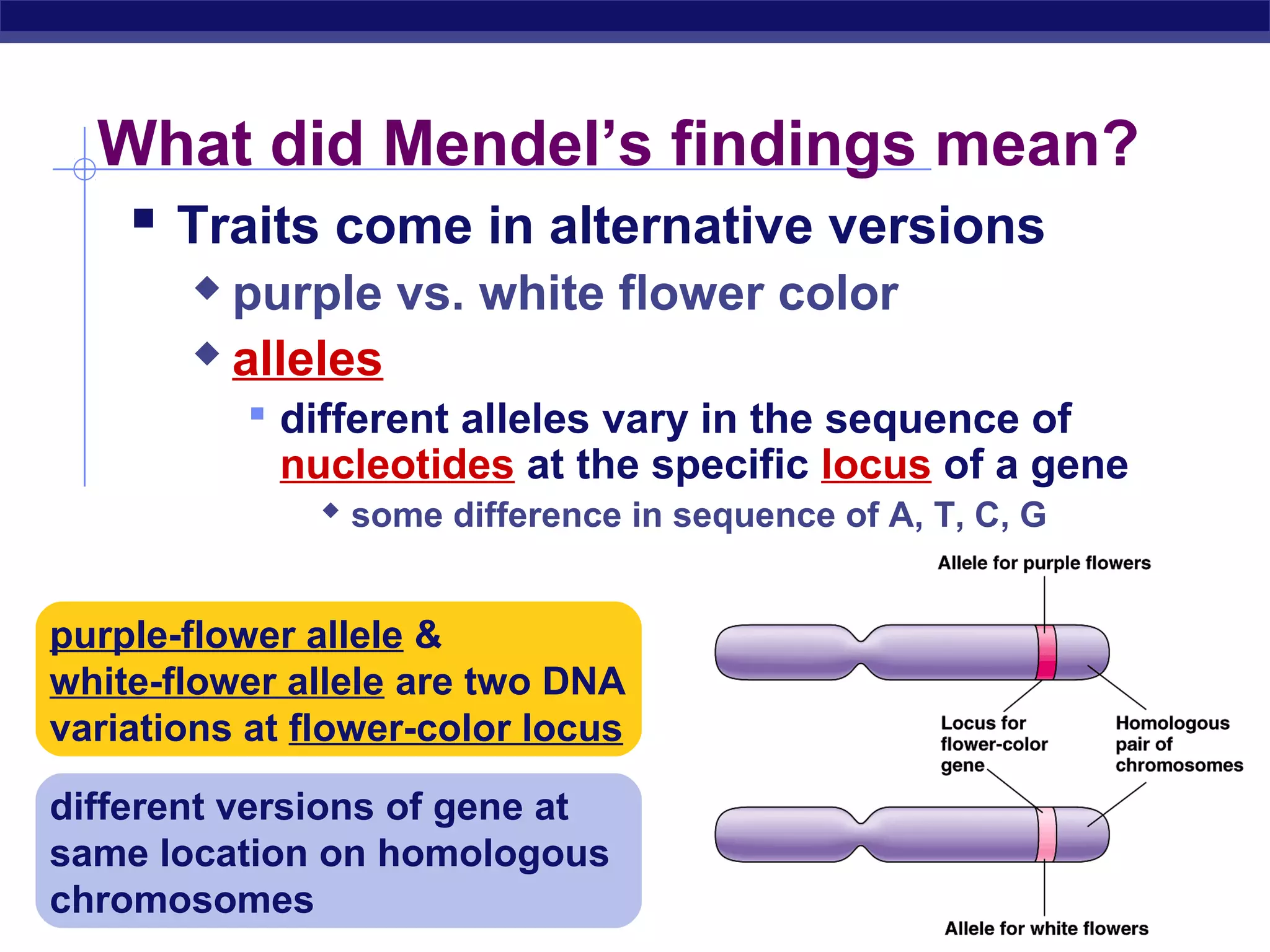
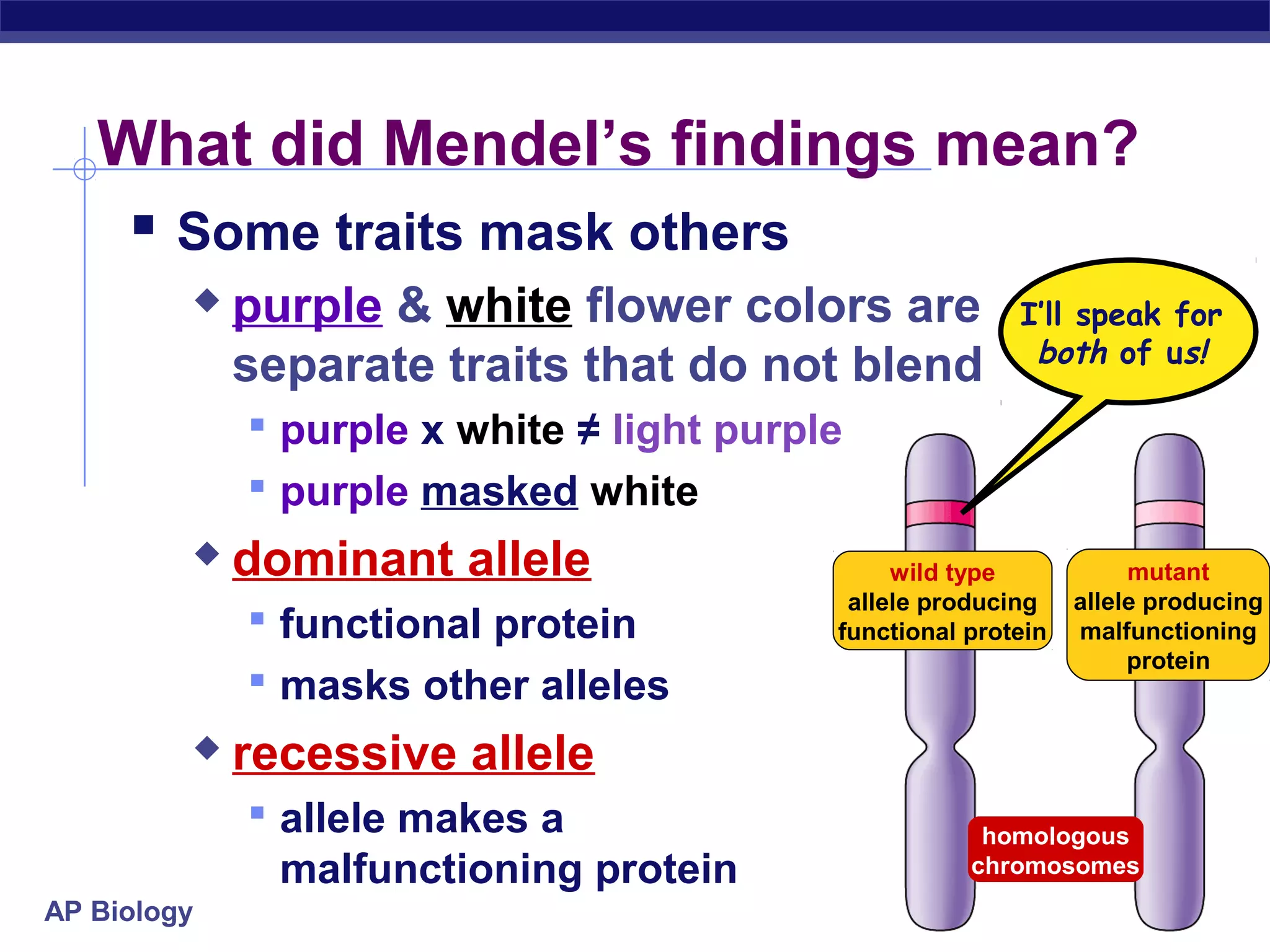
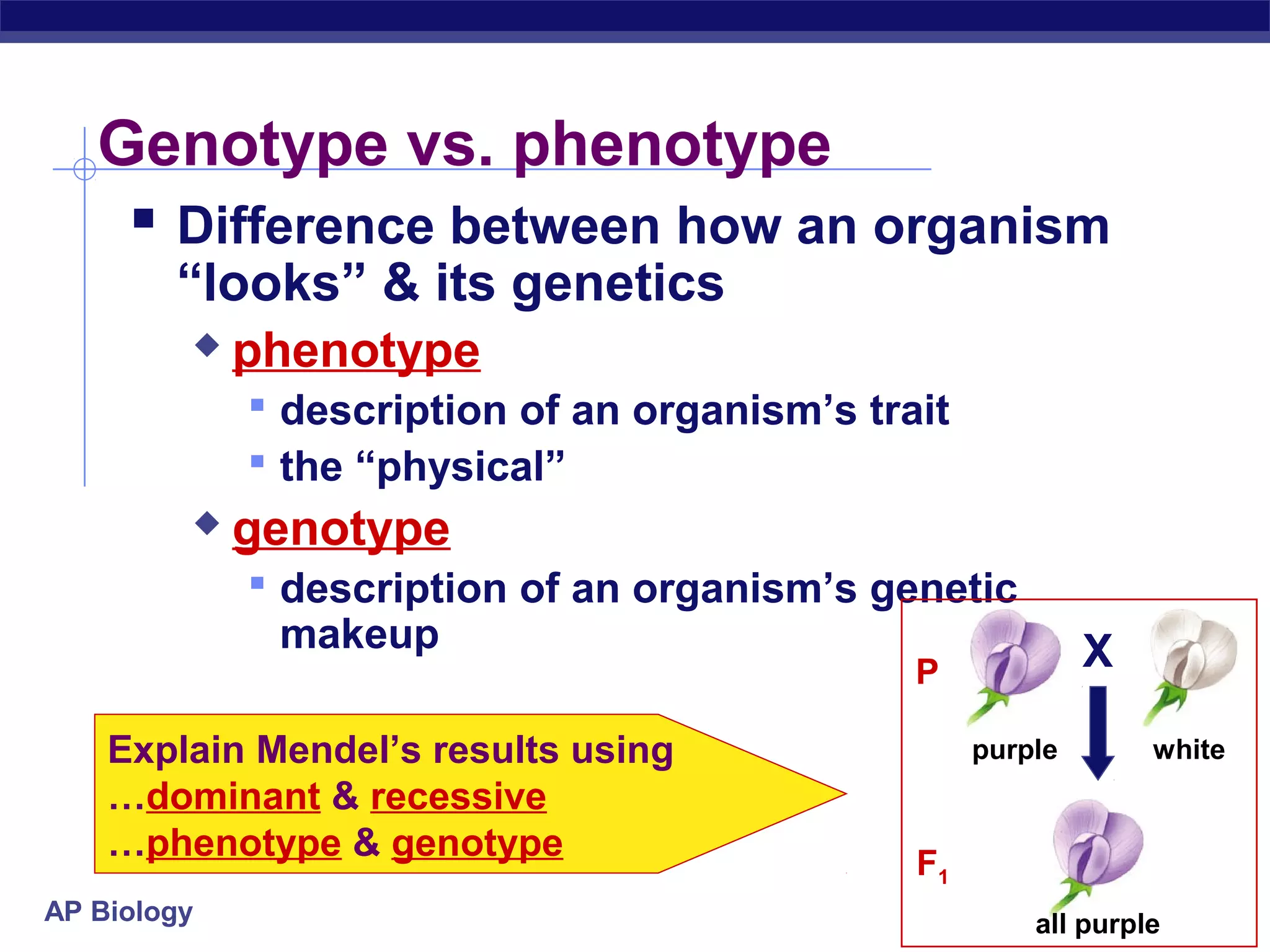
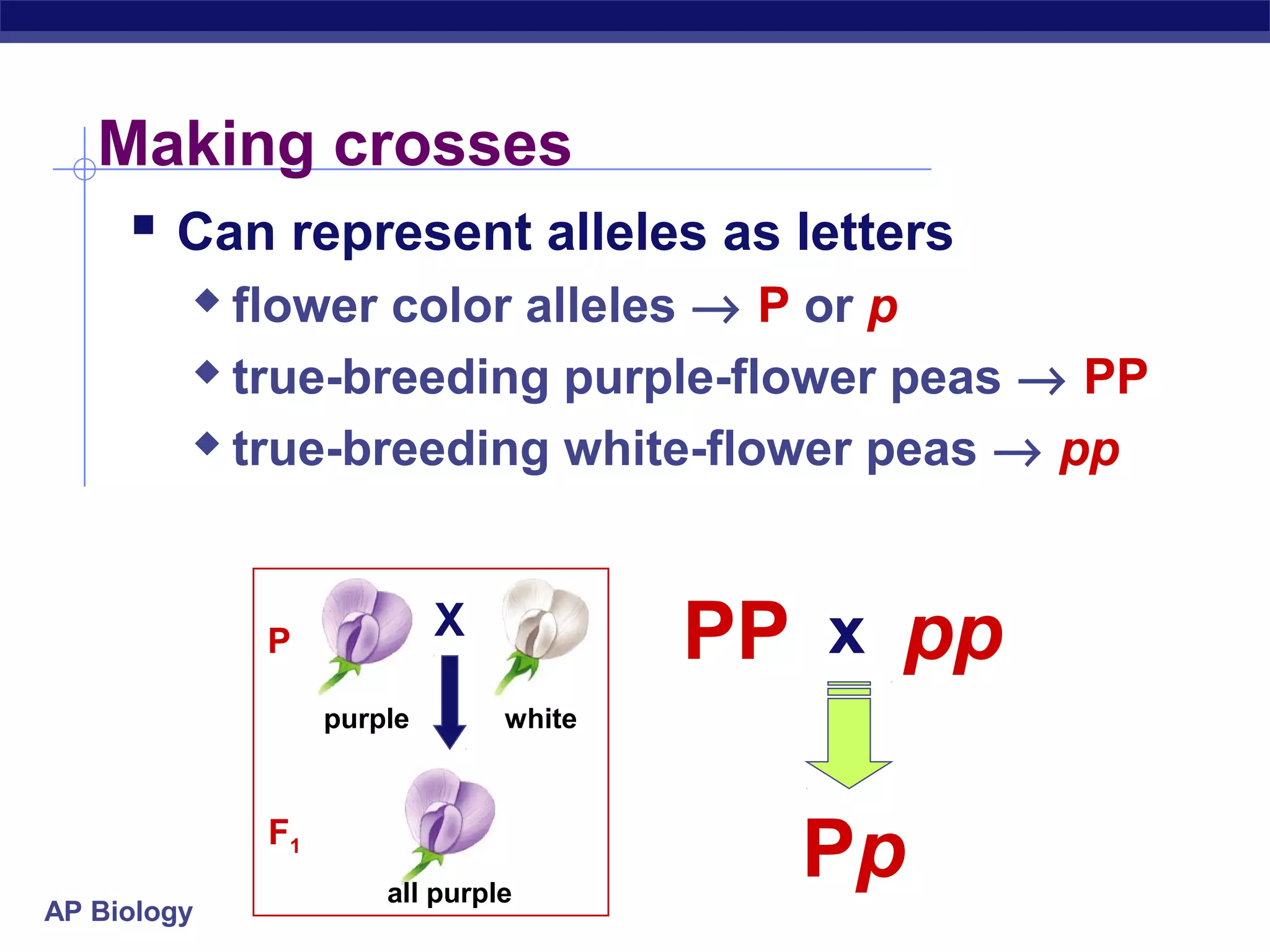
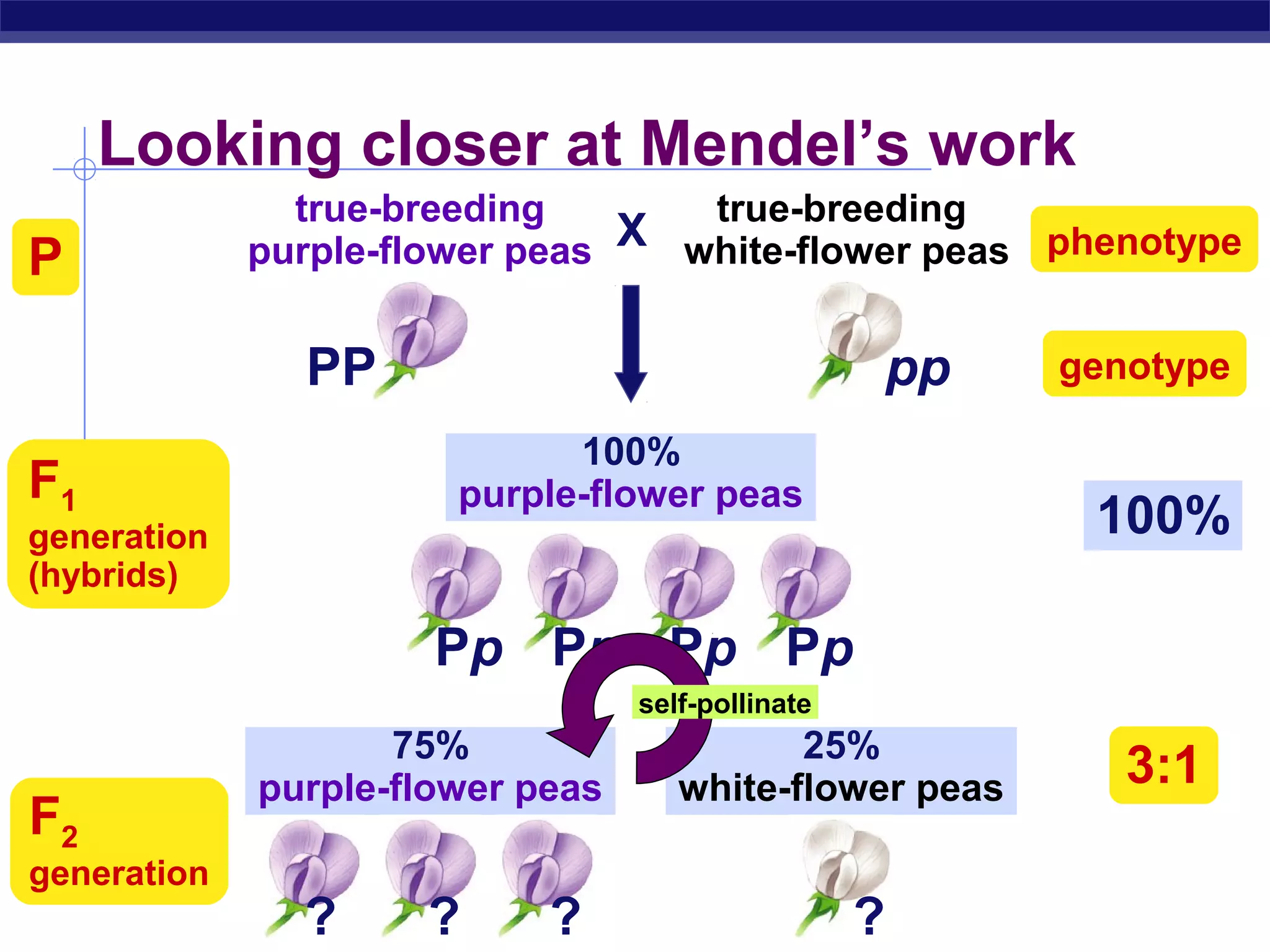
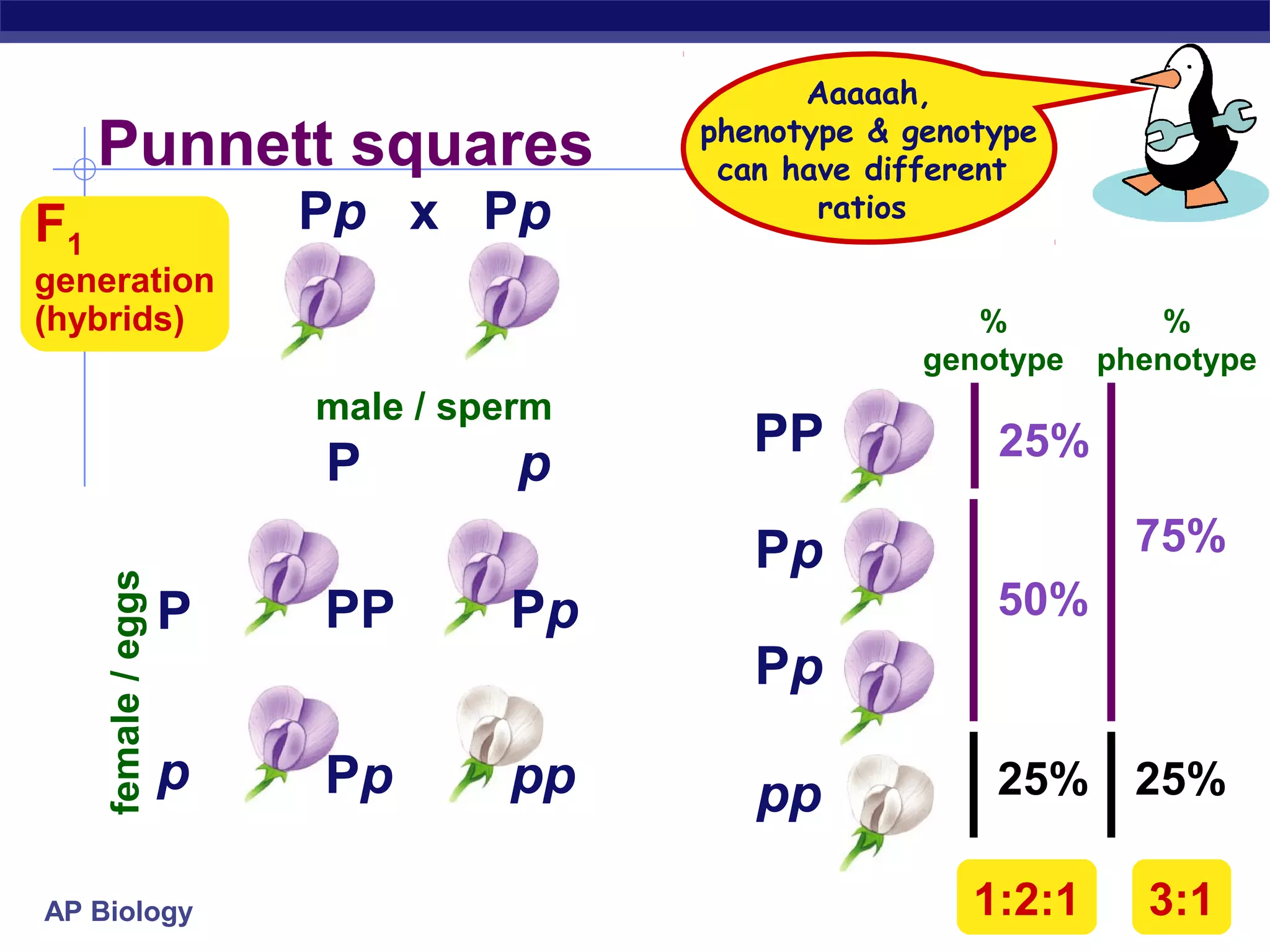
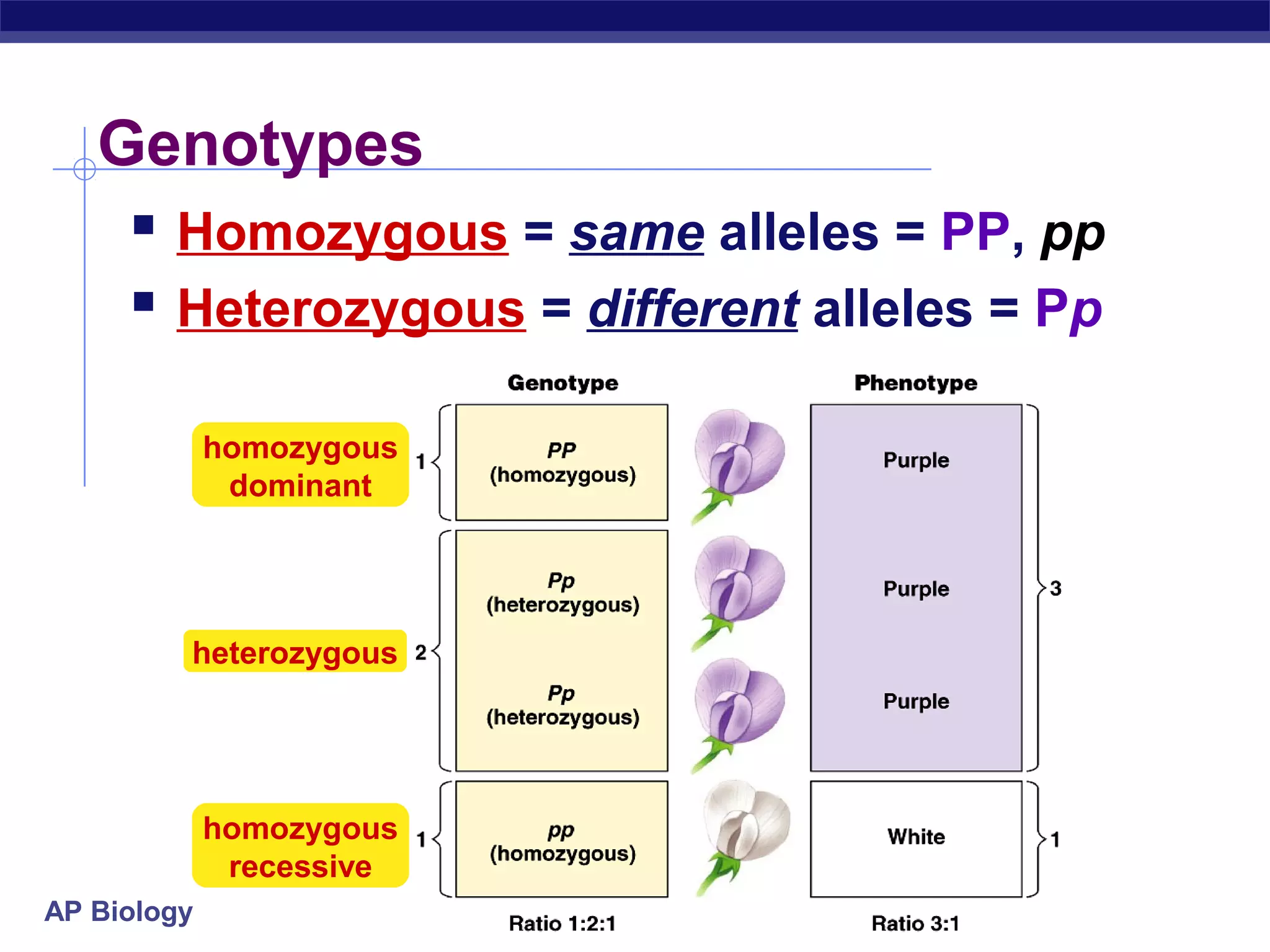
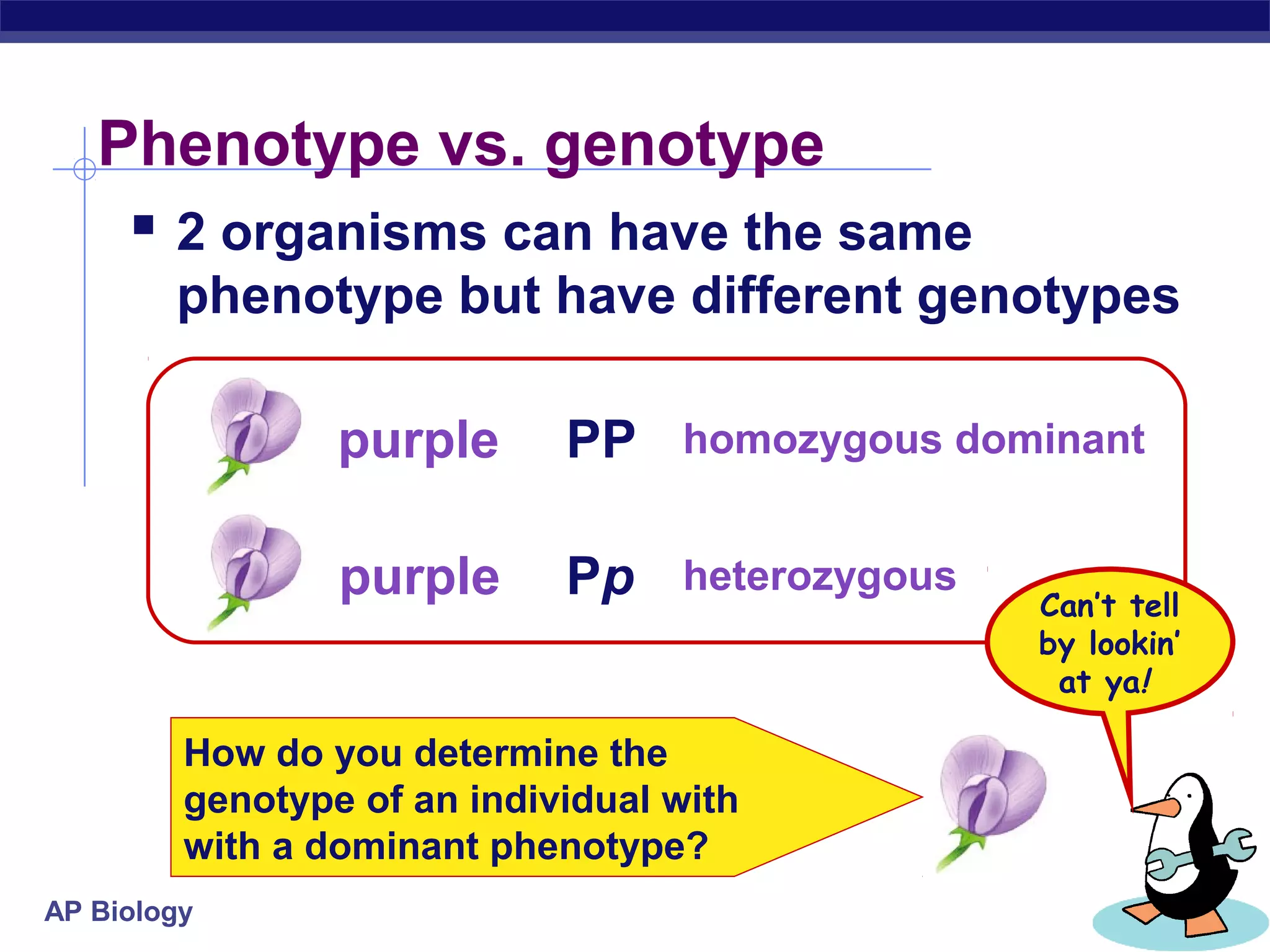
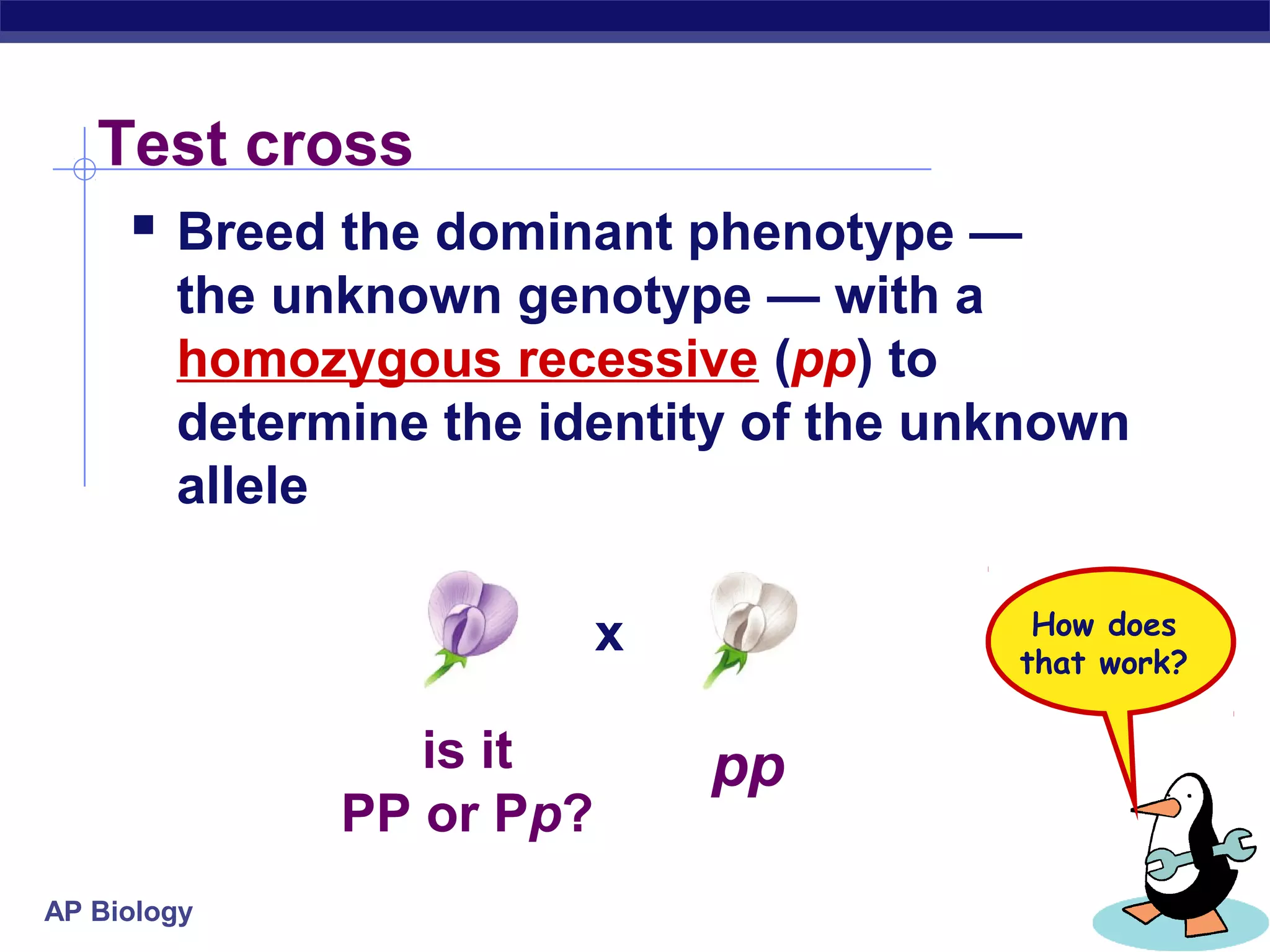
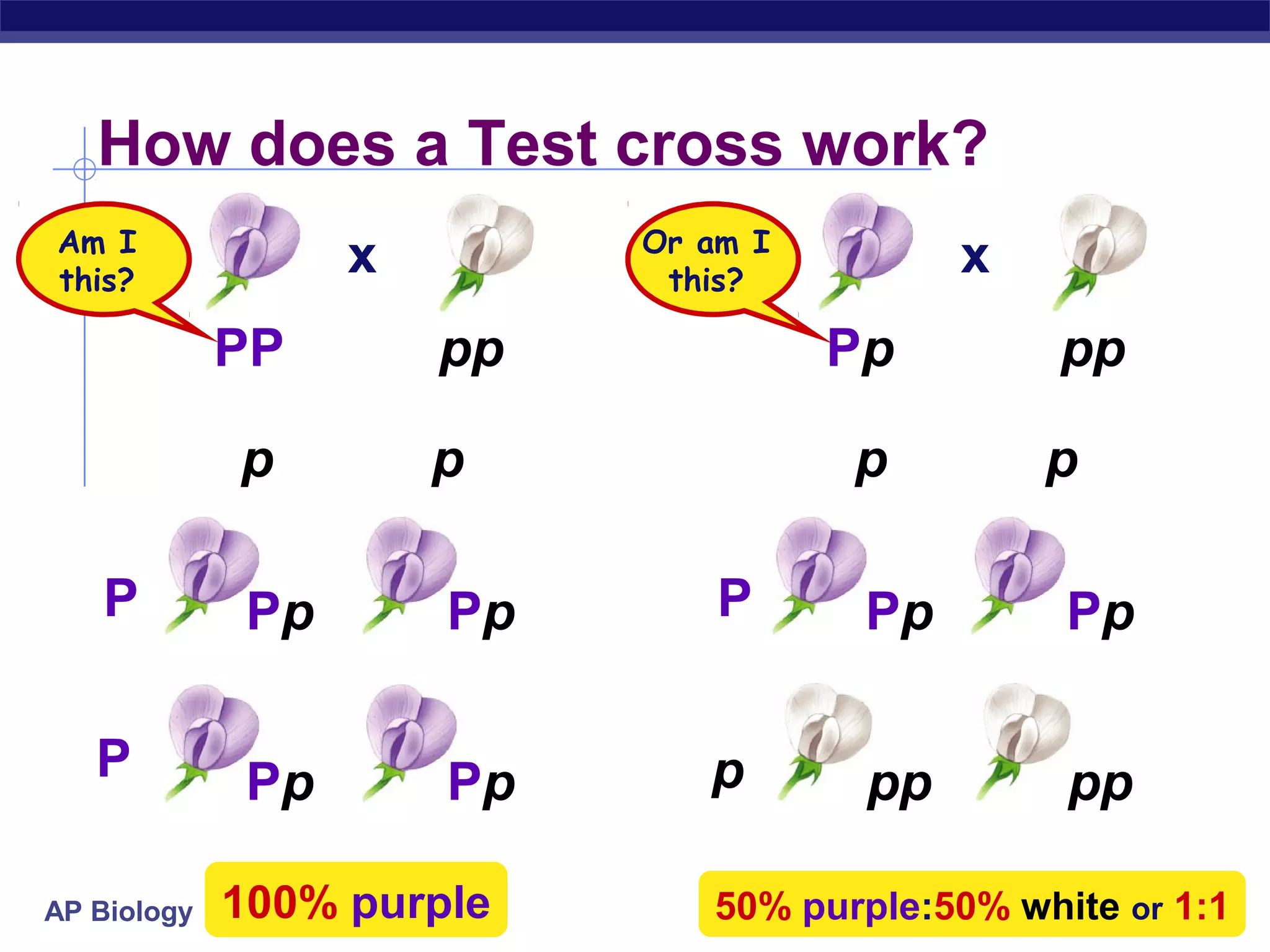
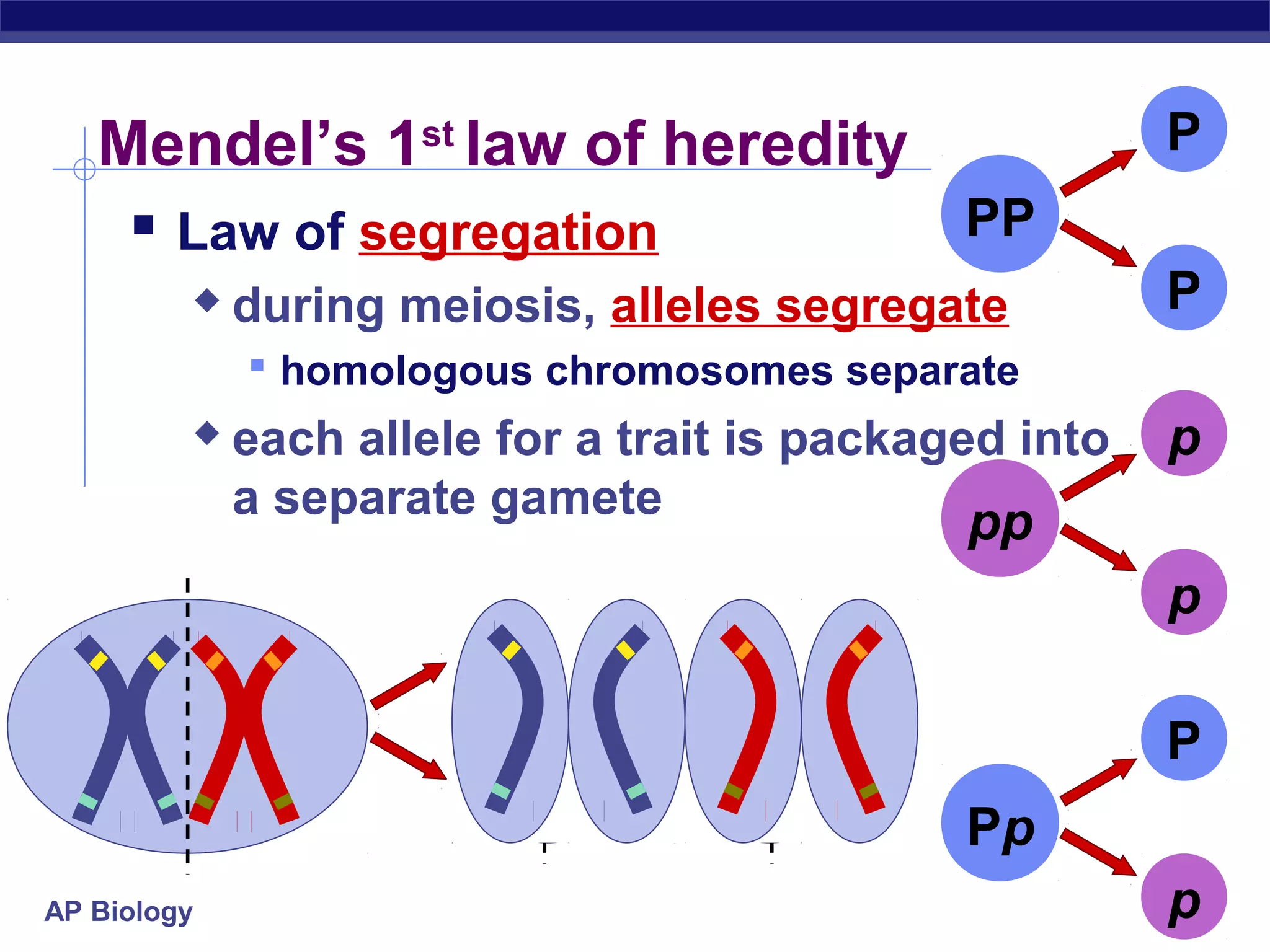
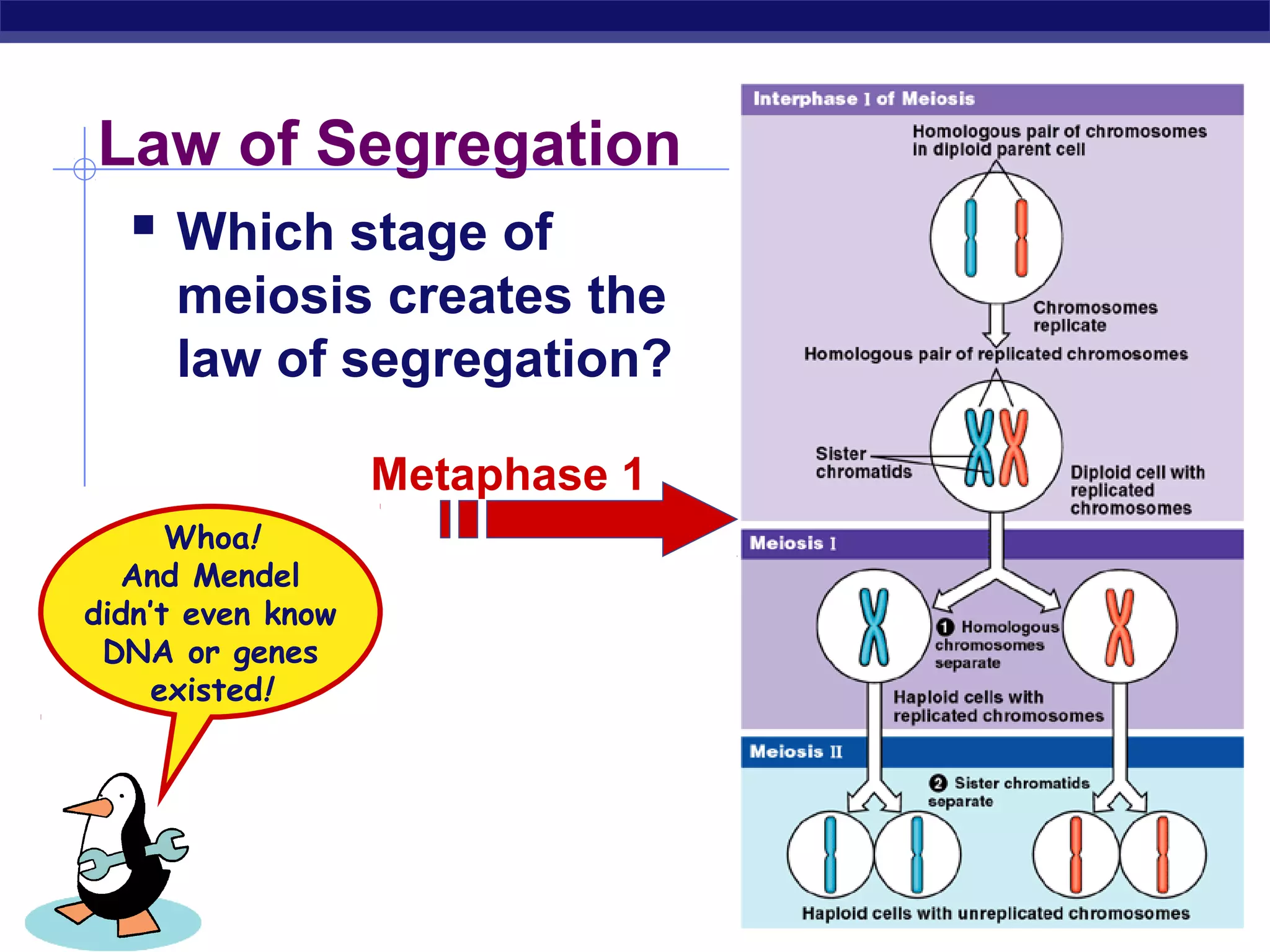
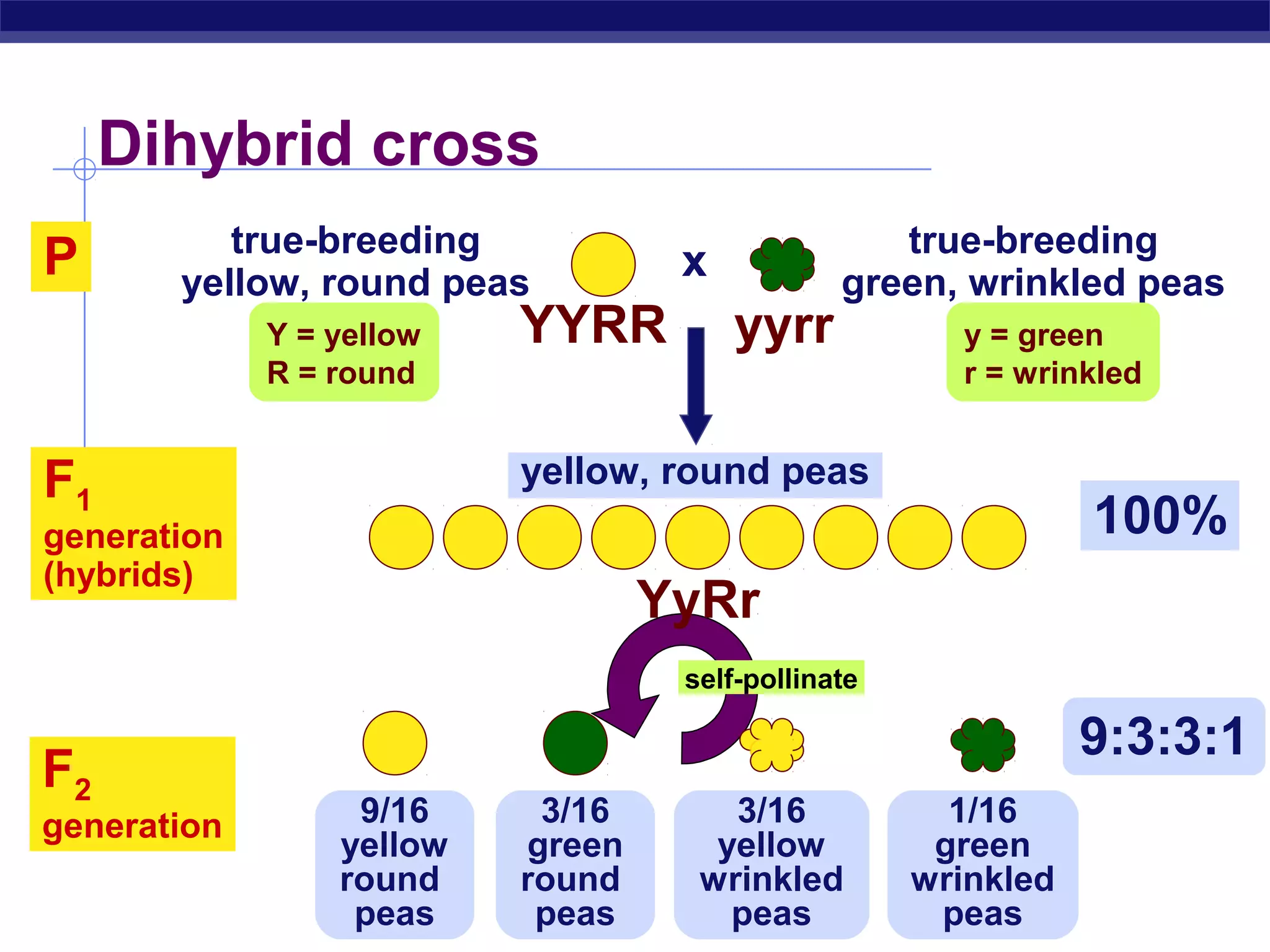
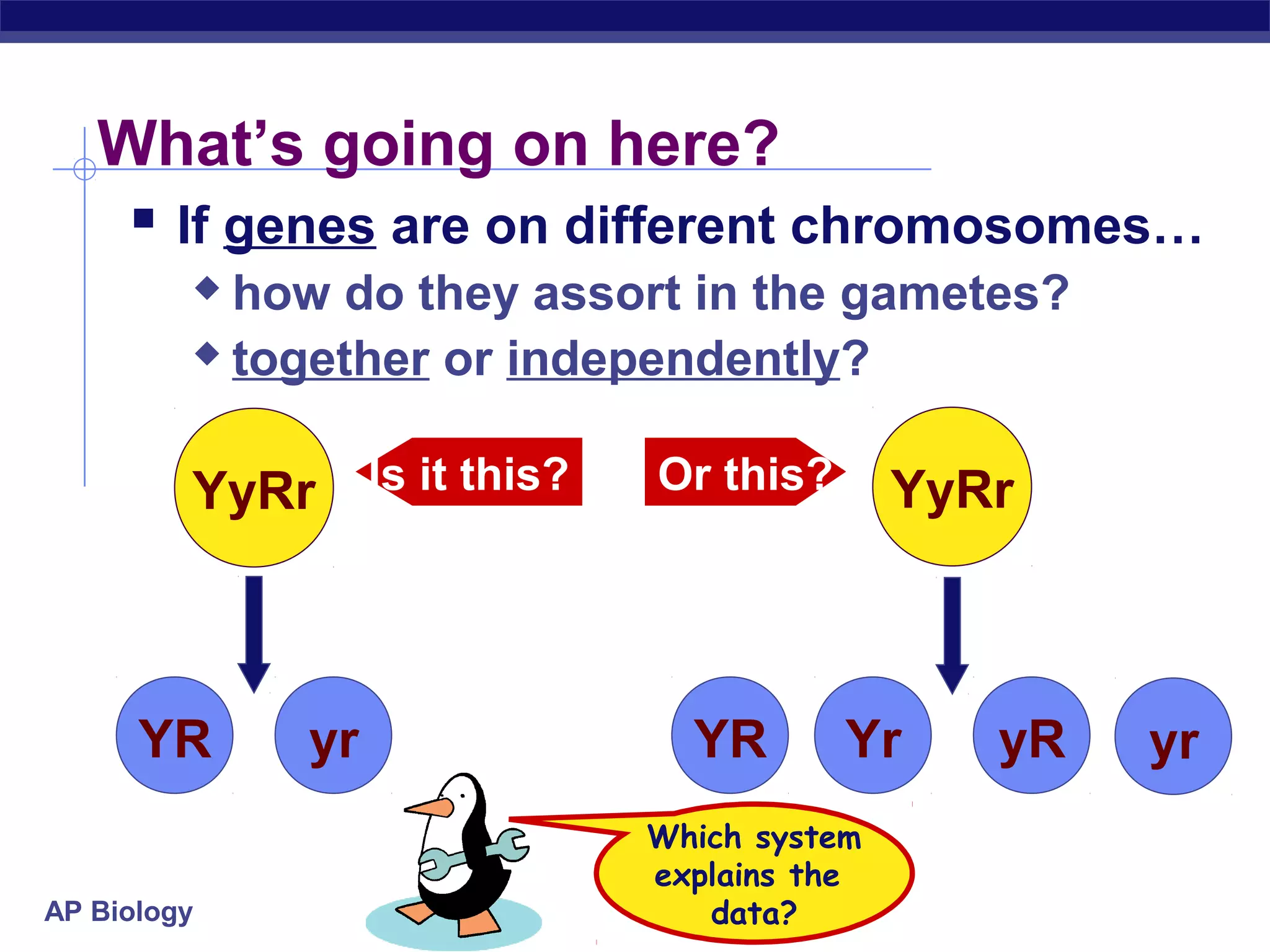
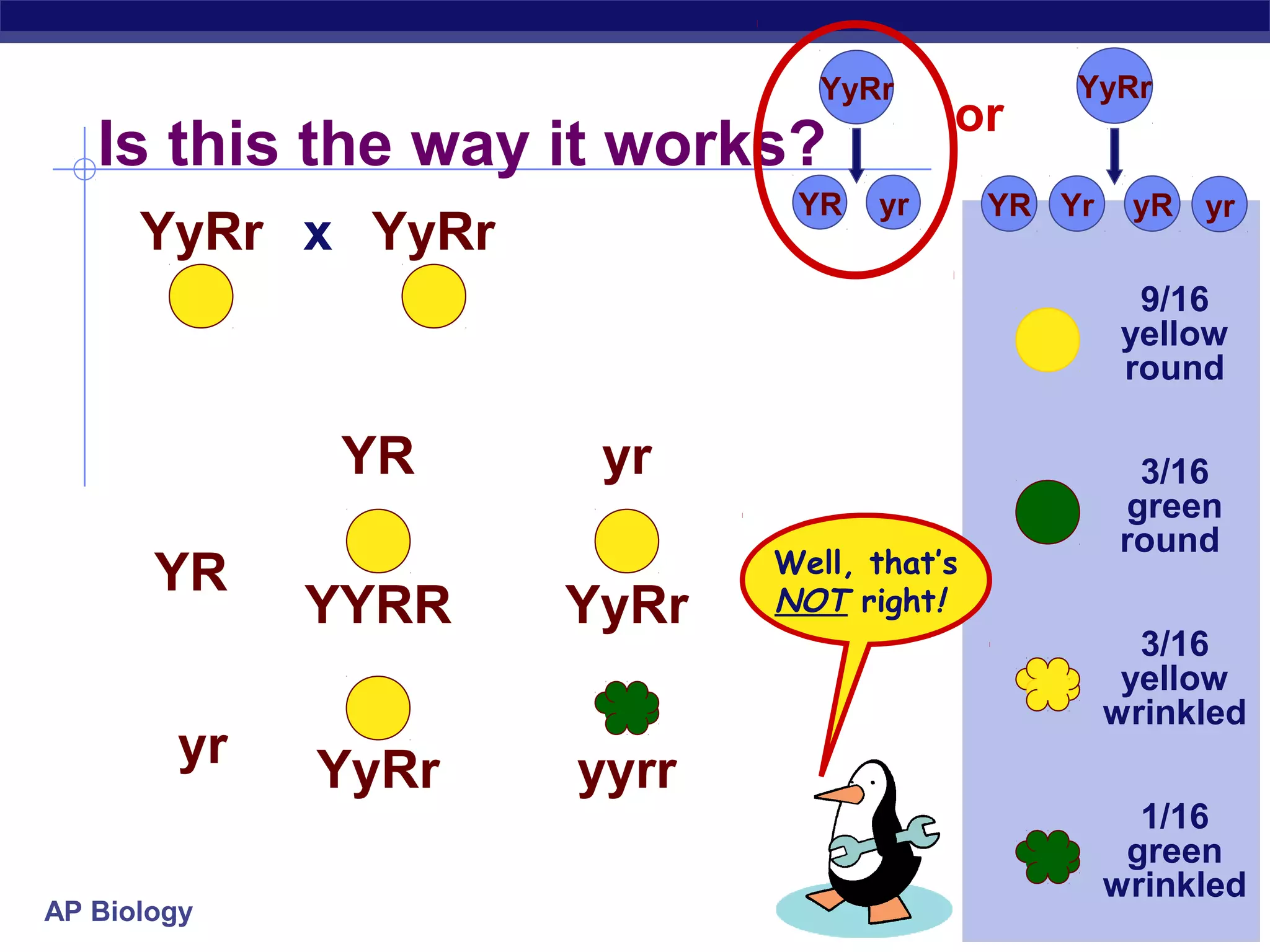
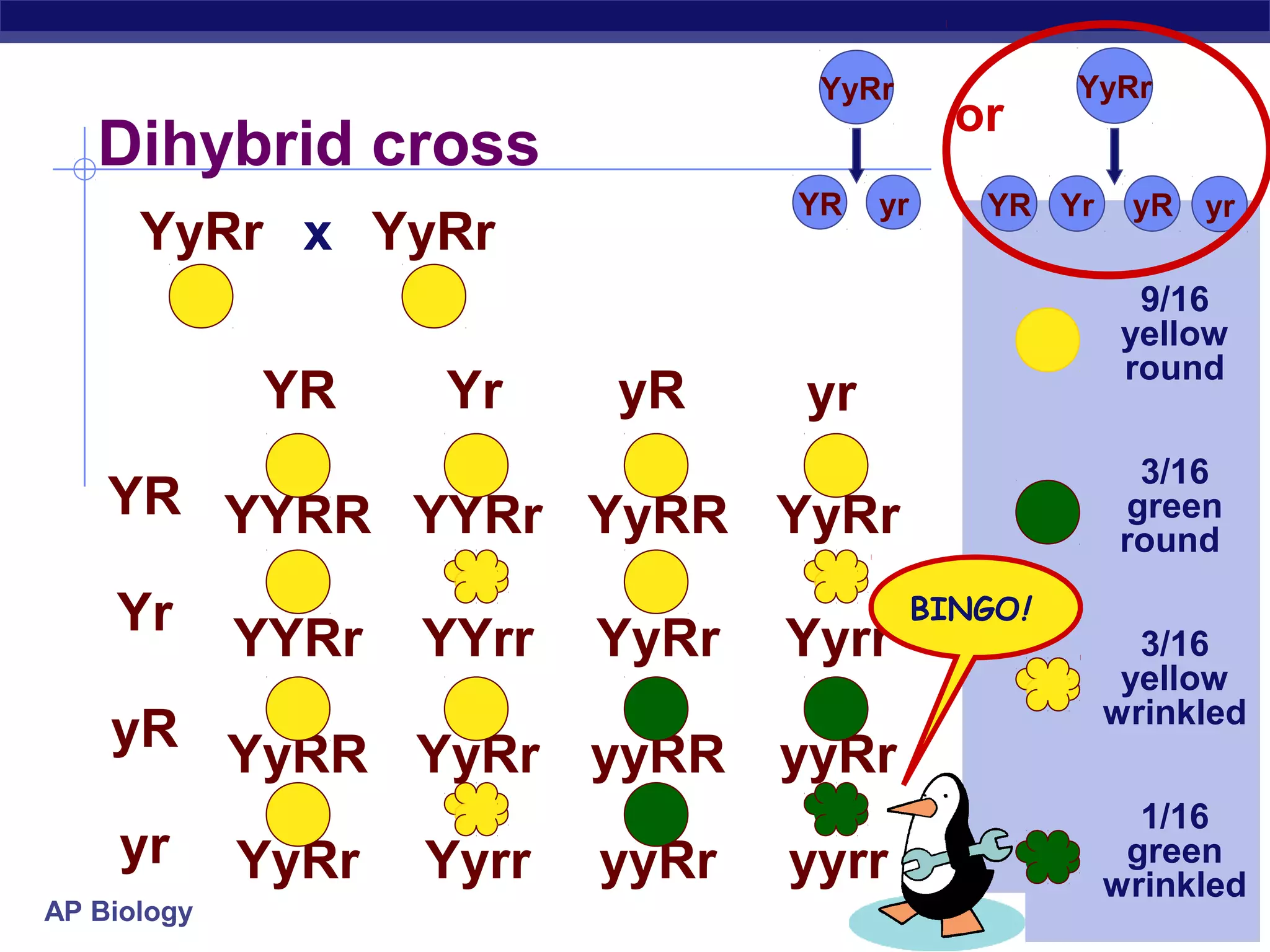
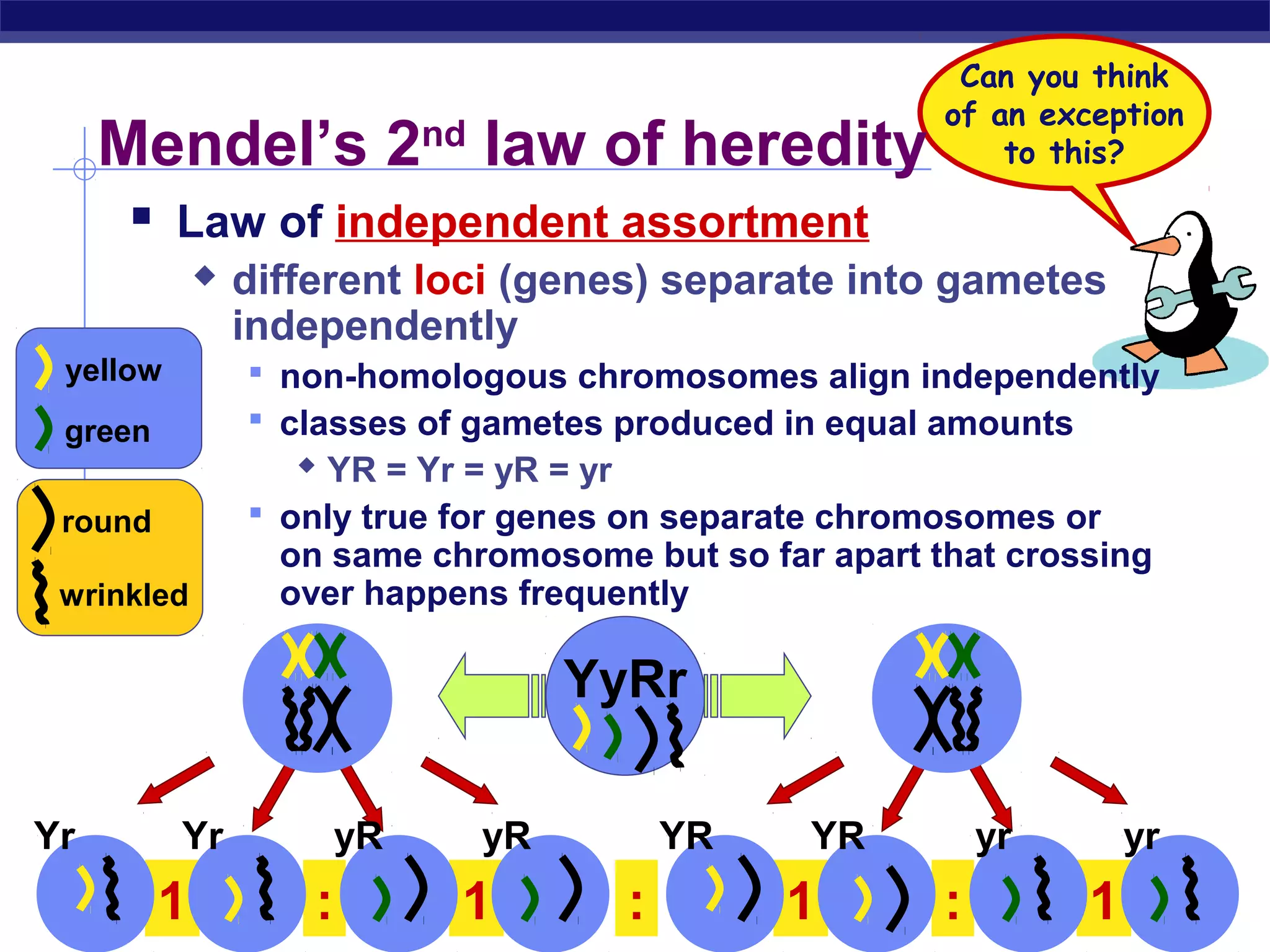
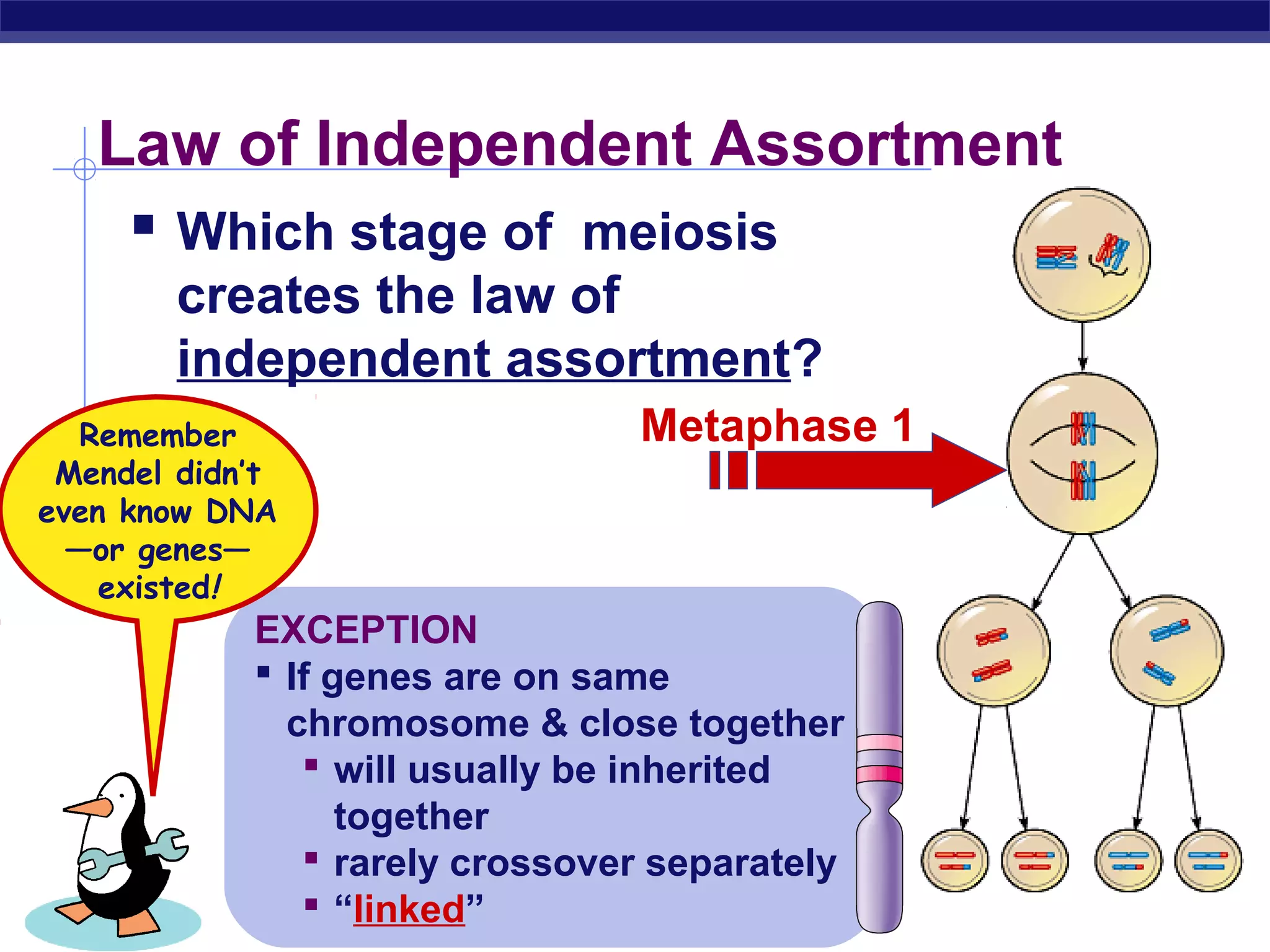
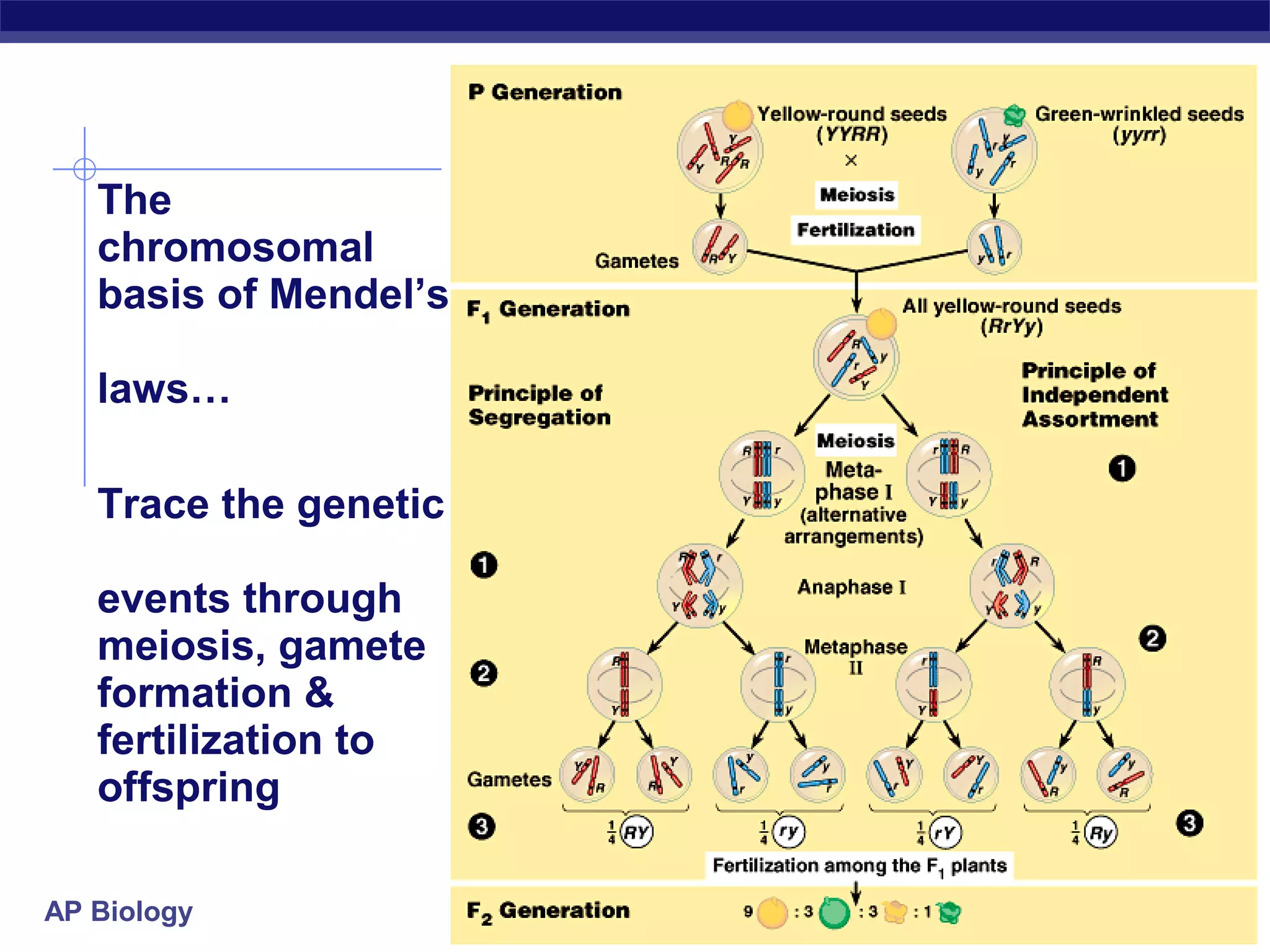
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments in the mid-1800s using pea plants to study inheritance patterns of traits such as flower color, seed shape, and seed color. Through quantitative analysis and use of the scientific method, he discovered that traits are inherited as discrete units and can be dominant or recessive. His findings established the laws of segregation and independent assortment, which explained that alleles separate independently during gamete formation and that different genes assort independently. Mendel's work laid the foundation for modern genetics.