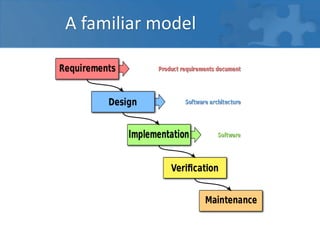
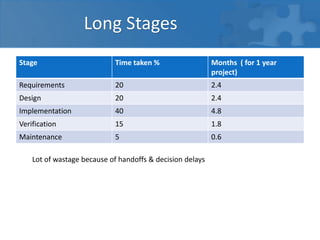
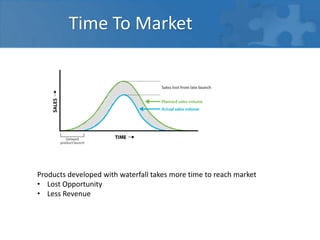
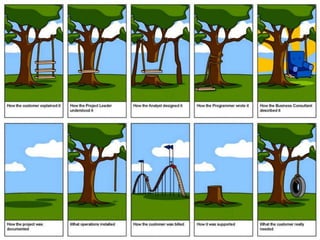
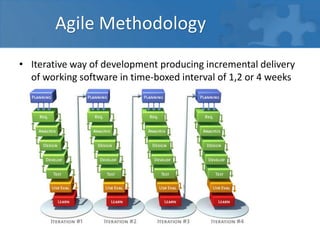
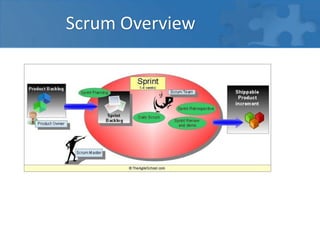
This document provides an overview of agile software development and the Scrum framework. It discusses the limitations of traditional waterfall models and how agile methods address these through iterative development, collaboration between cross-functional teams, and frequent delivery of working software. The key aspects of Scrum are described, including roles like the Product Owner and Scrum Master, meetings like Sprint Planning and Review, and artifacts like the Product Backlog and Sprint Task Board. Agile principles emphasize individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change.