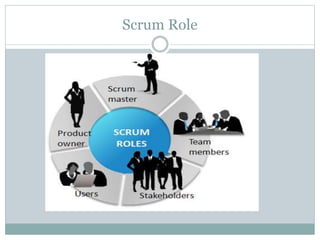
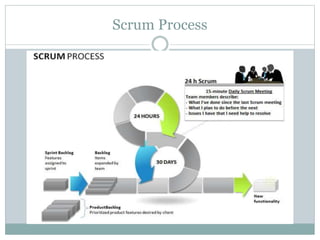
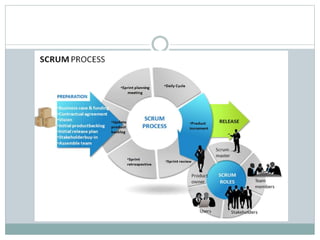
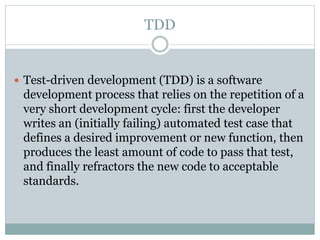
This document provides an overview of agile software development methods. It defines agile as developing software incrementally in rapid cycles with close customer collaboration. The agile manifesto values individuals, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. Popular agile methods described include scrum, extreme programming (XP), test-driven development (TDD), and lean. Scrum uses short iterations called sprints, with roles like product owner and scrum master. XP advocates frequent releases and pair programming. TDD involves writing tests before code. Lean aims to maximize value while minimizing waste. Agile frameworks help teams deliver faster with less risk by focusing on customer value.