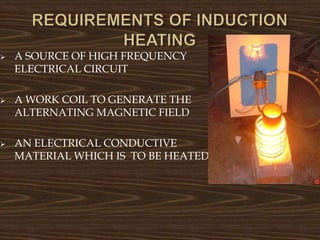
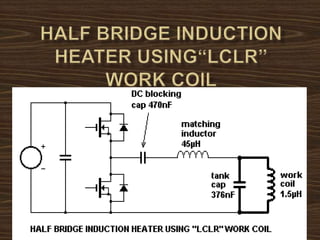
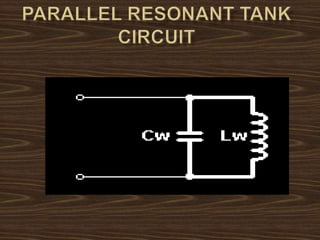
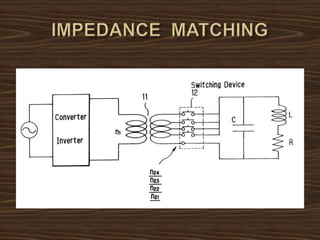
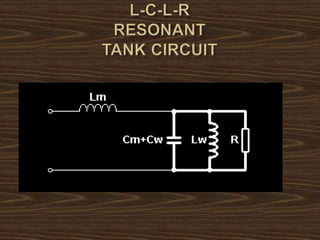
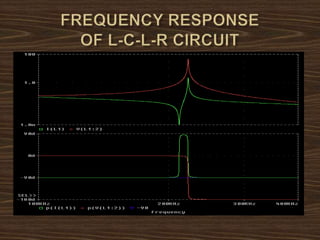
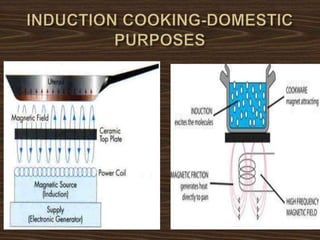
This document provides an overview of induction heating, including its working principle, requirements, and applications. It discusses how induction heating works by generating eddy currents in conductive materials using a high-frequency alternating magnetic field. This causes heating through hysteresis and eddy current losses. Key applications mentioned include induction cooking, welding, brazing, plastic processing, and sealing of food containers.