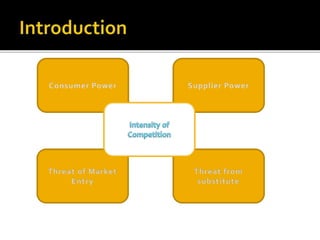
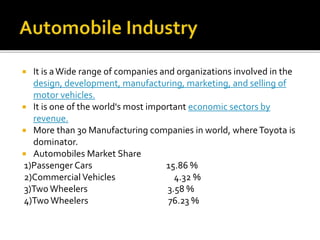
The document discusses the five forces model of competitive strategy - supplier power, buyer power, competitive rivalry, threat of substitution, and threat of new entry. It analyzes each of these forces in the automotive industry context. Specifically, it notes that there are many global automotive manufacturers with over 30 brands and 700 models available, creating high competitive rivalry. It also discusses that while the industry has high barriers to entry due to costs and expertise required, established brands from other locations could potentially enter the market. Overall, the automotive industry exhibits strong competitive forces.