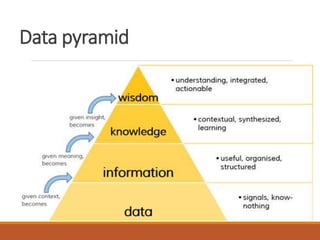
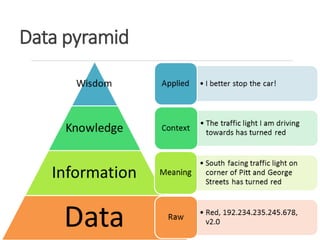
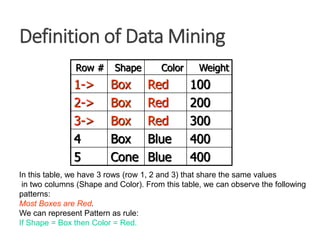
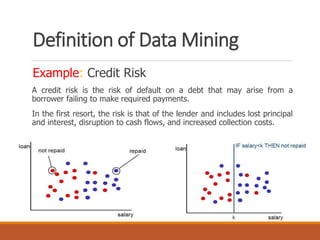
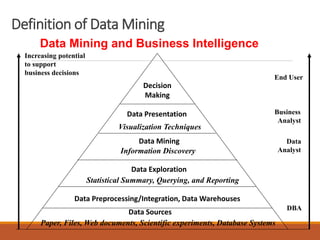
The document provides an introduction to data mining, defining it as the process of discovering valid, novel, and actionable patterns in large datasets. It distinguishes between data mining and knowledge discovery in databases (KDD), detailing the data mining process, its tasks, challenges, and applications. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding the discovered patterns for informed decision-making in various fields such as finance.