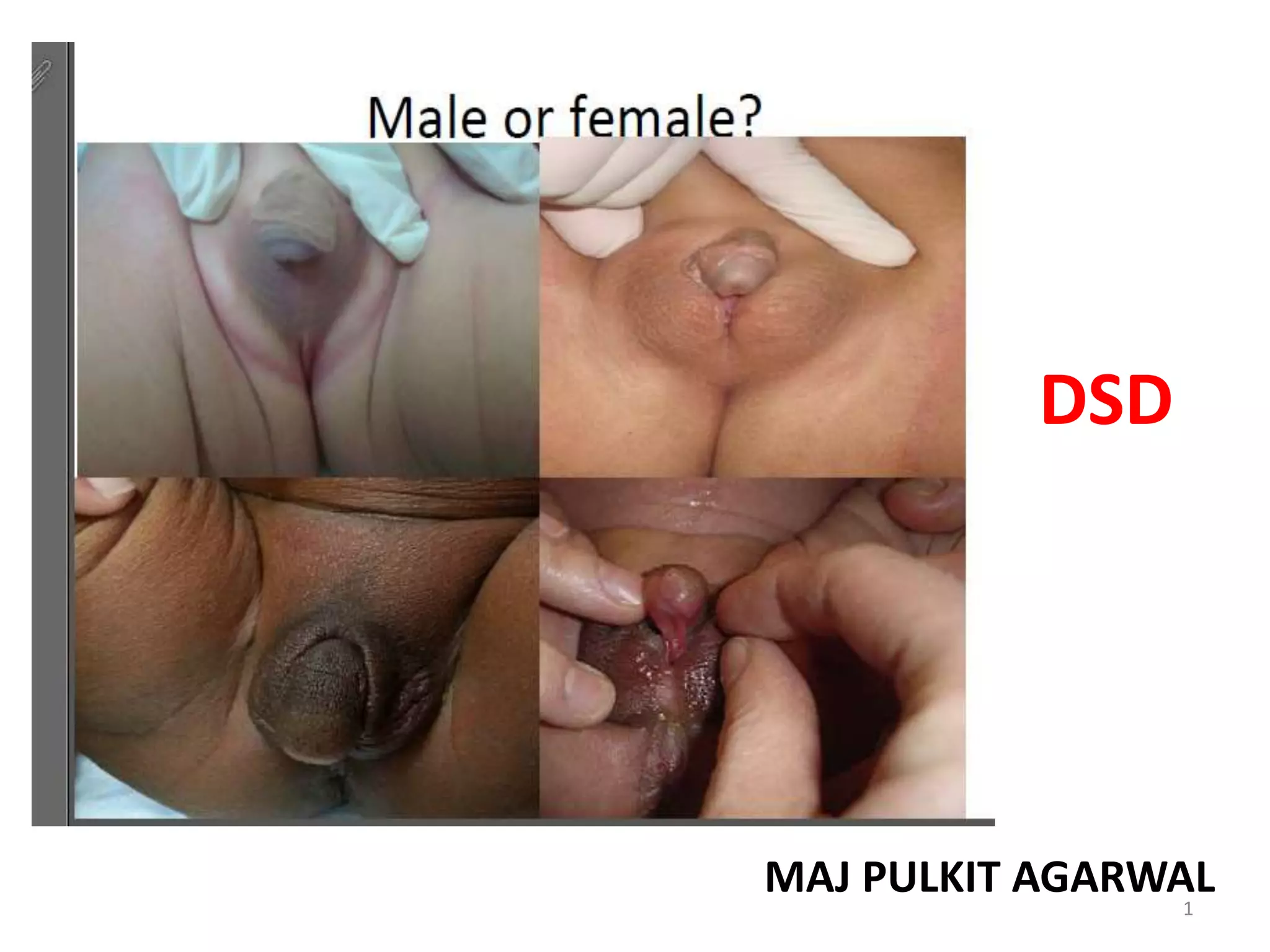
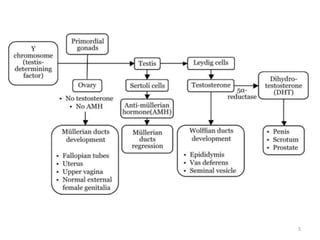
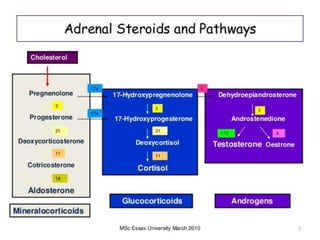
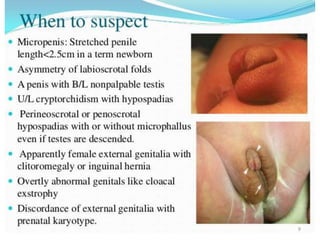
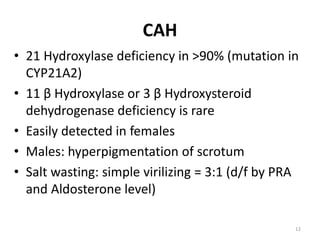
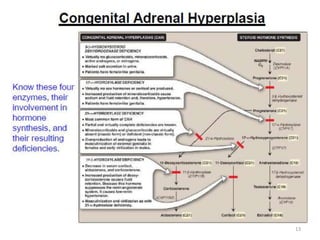
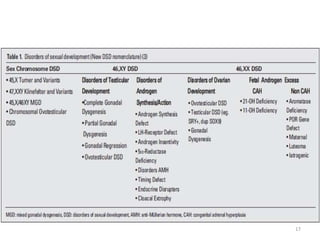
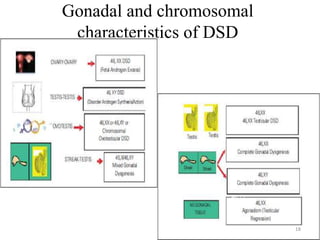
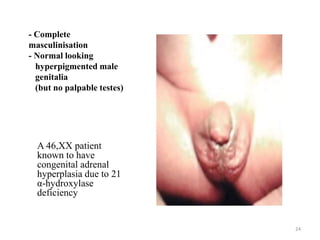
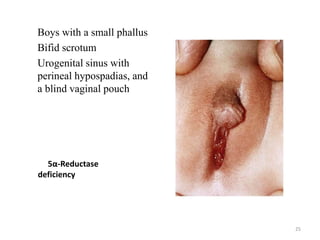
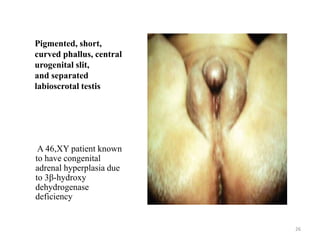
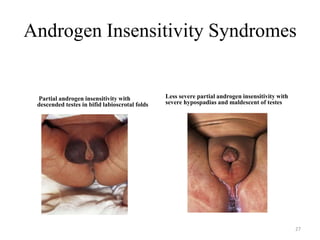
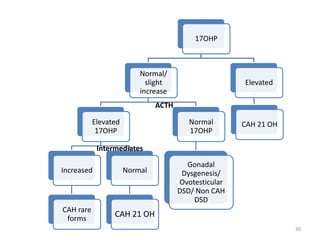
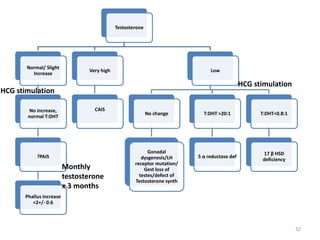
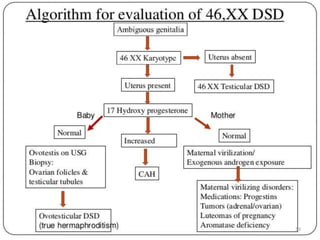
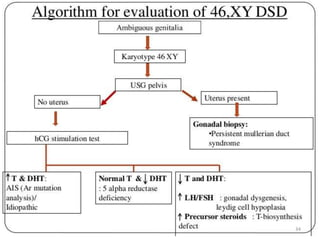
This document discusses normal sexual differentiation and disorders of sexual differentiation (DSD). It begins by outlining the three main steps in normal sexual differentiation: establishment of chromosomal sex at fertilization, development of gonads into testes or ovaries, and subsequent differentiation of internal and external genitalia due to gonadal endocrine functions. It then discusses how gender is assigned based on genetic sex, external genitalia, gonads/reproductive organs, and psychosocial factors. The majority of the document focuses on DSDs, including definitions, causes such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia and gonadal differentiation disorders, associated genetic and physical characteristics, evaluations including history, exams, imaging and hormonal assays, and examples of