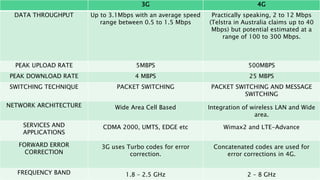
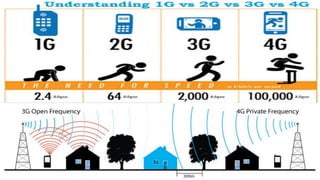
This document compares 3G and 4G mobile technologies. It notes that 3G provides data speeds up to 3.1 Mbps on average, while 4G can provide speeds up to 10 times faster at 100-300 Mbps. It outlines some key differences like 4G supporting higher peak upload/download speeds and quality of service features. Usage statistics are provided showing 3G has over 3 billion users worldwide compared to under 500 million for 4G currently. Potential advantages and drawbacks of both standards are also examined.