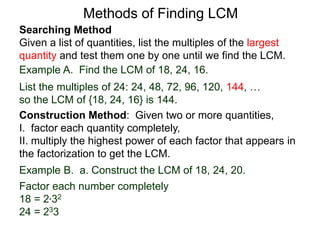
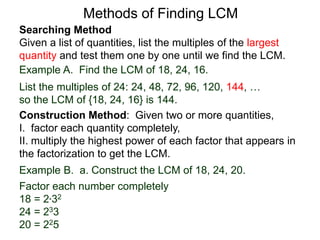
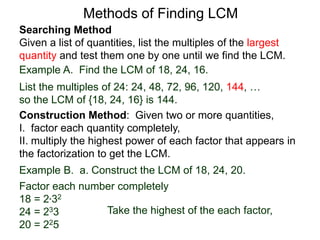
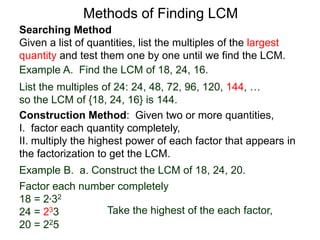
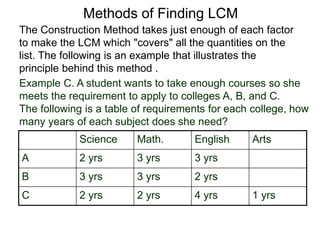
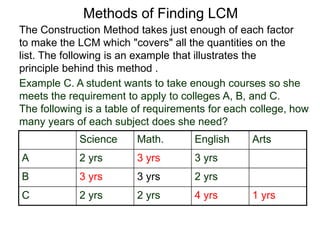
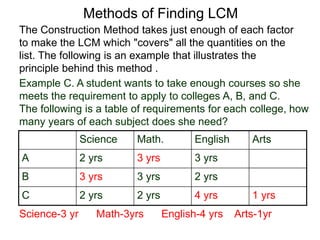
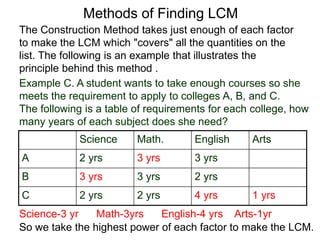
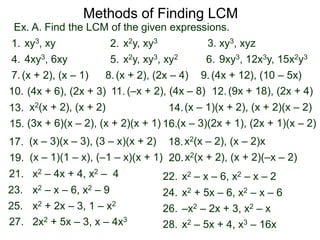
The document discusses methods for finding the least common multiple (LCM) of numbers. It defines a multiple as a number that can be divided evenly by another number. The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of all numbers given. Two methods are described: the searching method which tests multiples of the largest number, and the construction method which factors each number and multiplies the highest powers of common factors. Examples are provided to illustrate both methods.