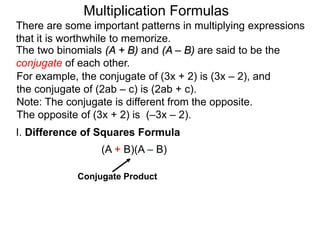
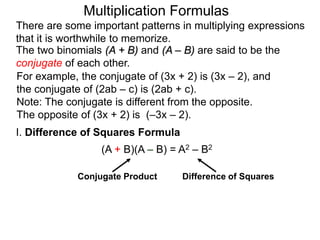
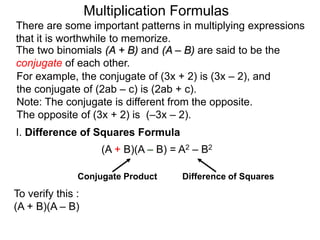
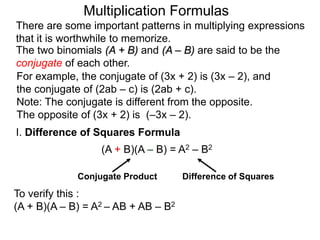
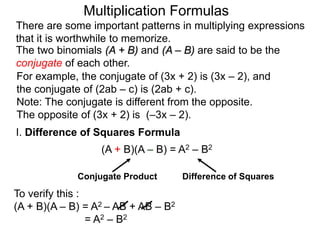
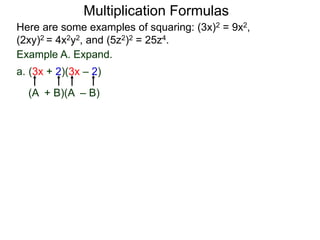
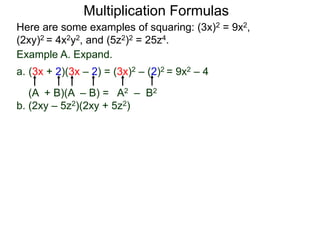
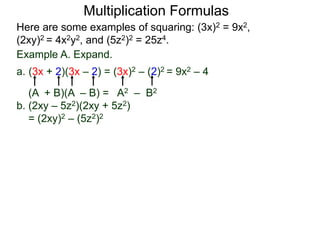
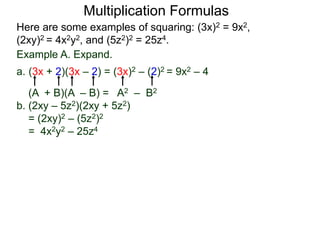
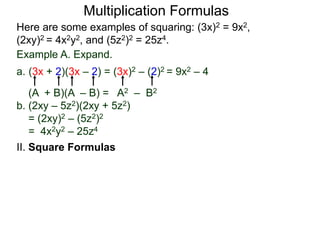
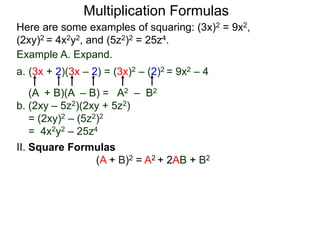
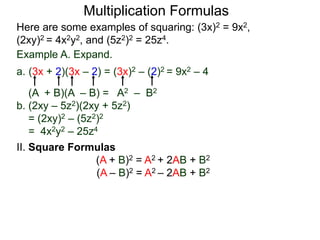
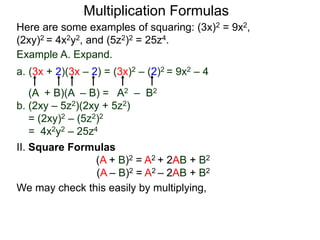
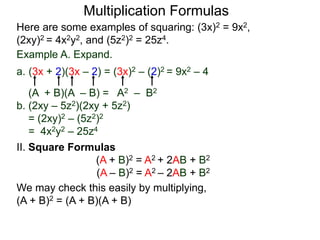
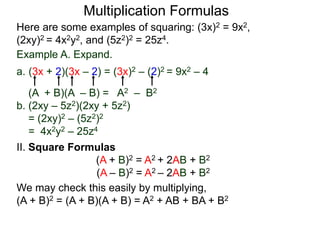
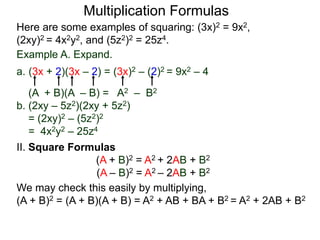
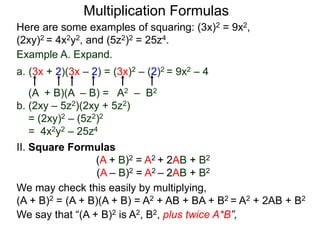
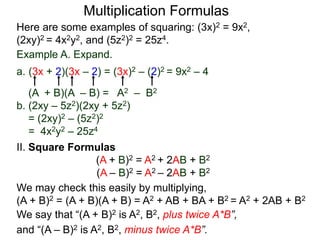
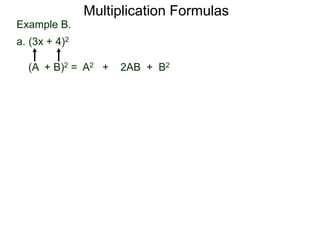
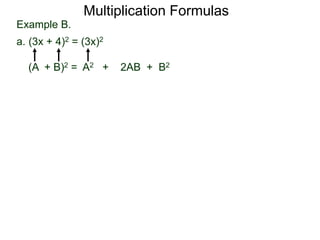
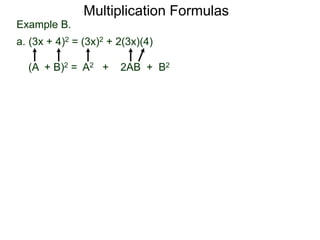
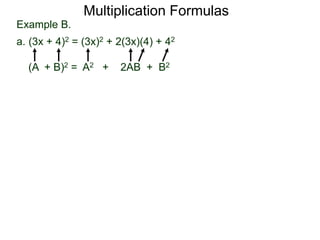
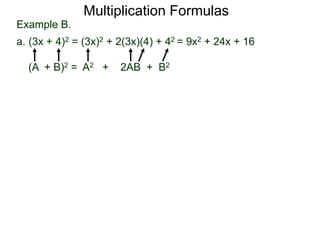
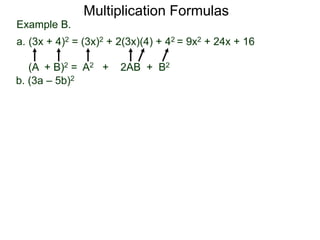
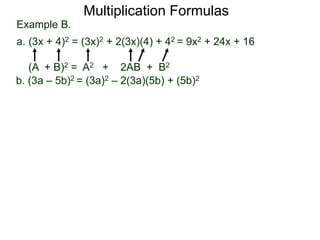
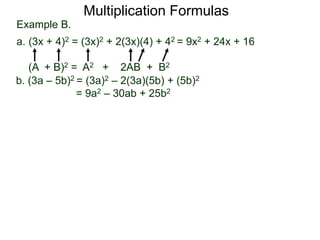
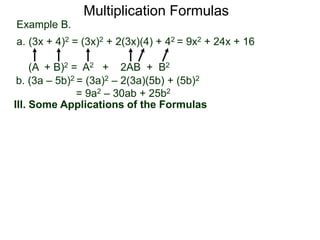
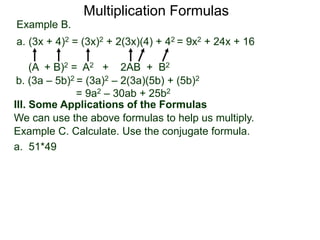
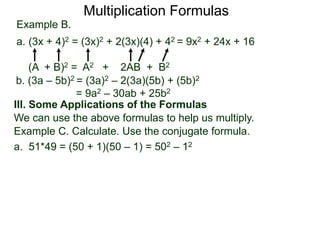
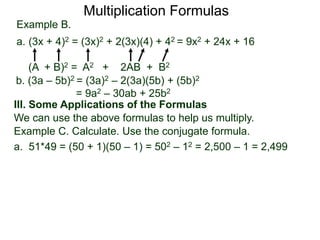
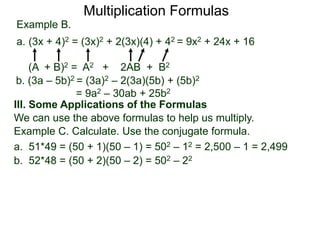
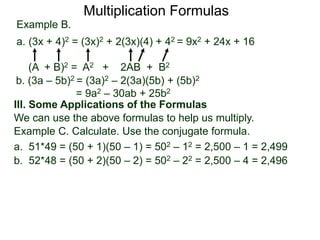
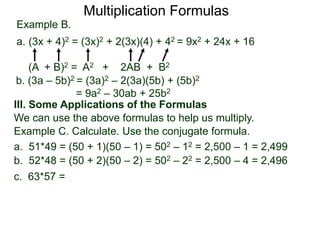
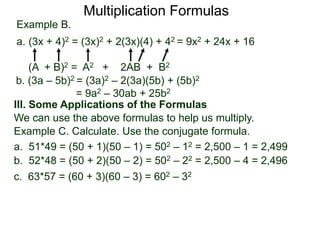
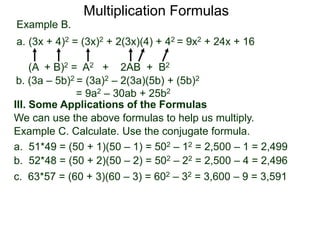
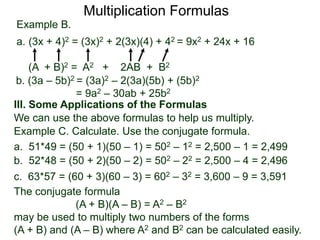
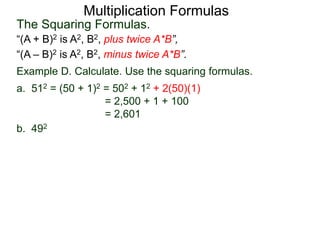
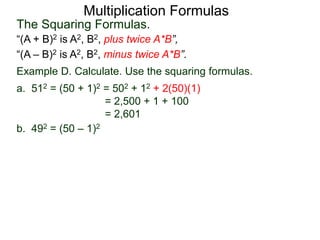
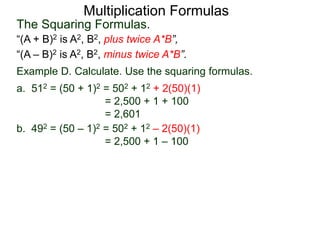
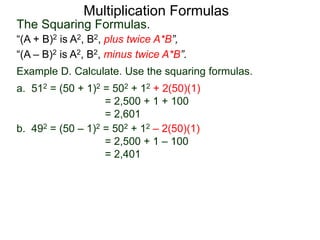
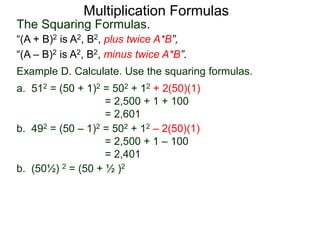
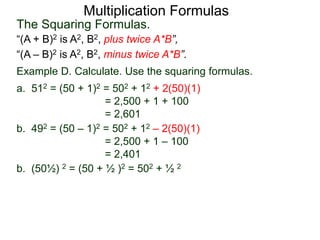
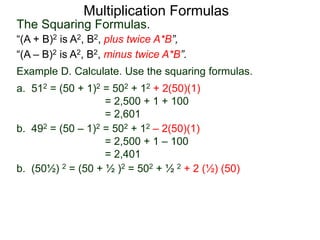
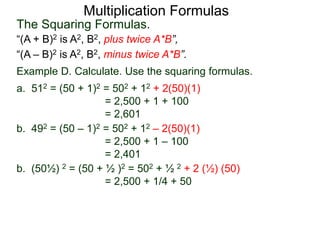
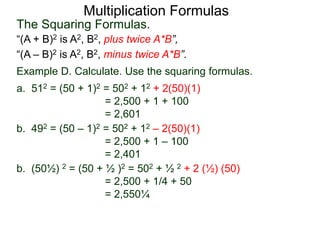
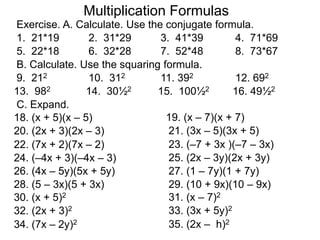
The document discusses formulas for multiplying binomial expressions. It states that the conjugate of expressions like (A + B) is (A - B). The difference of squares formula is given as (A + B)(A - B) = A^2 - B^2. Examples of expanding expressions using this formula and the square formulas (A + B)^2 = A^2 + 2AB + B^2 and (A - B)^2 = A^2 - 2AB + B^2 are provided.