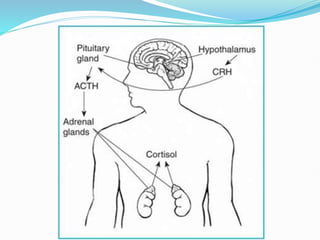
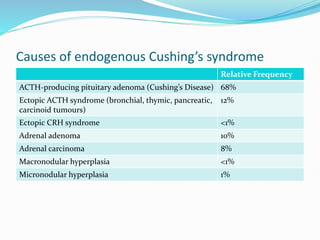
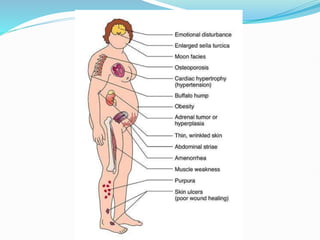
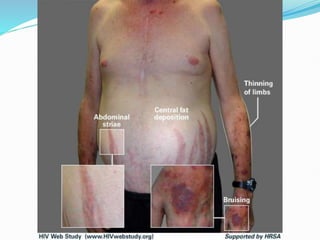
Cushing's syndrome is caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol and can be exogenous from medications or endogenous from tumors. It is characterized by upper body obesity, moon face, skin changes, muscle wasting and bone problems. Diagnosis involves urine and blood tests to detect high cortisol levels that do not suppress normally. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include surgery to remove tumors or gradually lowering medication doses. Without treatment, complications can include diabetes, infections, fractures and high blood pressure.