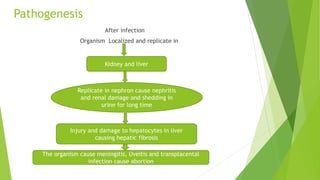
Leptospirosis is a waterborne, contagious disease of dogs caused by Leptospira interrogans bacteria. The bacteria infect the kidneys and liver, causing nephritis, renal damage, and hepatic fibrosis. Clinical signs include fever, depression, abdominal pain, vomiting, and signs of renal and hepatic failure. Diagnosis is made through microscopic examination of urine, blood tests, culture, and serological tests. Treatment involves antibiotics such as penicillin and supportive care. Control relies on vaccination, isolation of infected animals, hygienic disposal of waste, and prevention of contact with infected urine.