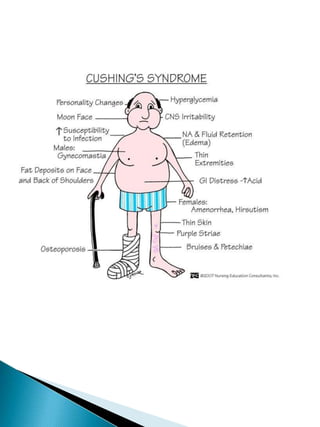
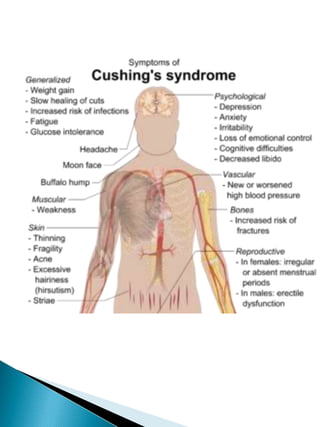
Cushing's syndrome is caused by excessive cortisol production and can be difficult to diagnose due to shared symptoms with other conditions. It may be endogenous from pituitary or adrenal tumors, or exogenous from long-term high-dose corticosteroid use. Diagnosis involves ruling out other conditions through tests and assessing cortisol levels in blood and urine over 24 hours. Treatment aims to normalize cortisol levels and depends on the underlying cause, such as surgery to remove tumors or medication to reduce cortisol production. Left untreated, Cushing's syndrome can cause serious health issues.





![ Cushing's disease is a cause of Cushing's
syndrome characterised by increased secretion
of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from
the anterior
pituitary (secondary hypercortisolism). This is
most often as a result of a
pituitary adenoma (specifically pituitary
basophilism) or due to excess production of
hypothalamus CRH (Corticotropin releasing
hormone) (tertiary
hypercortisolism/hypercorticism) that stimulates
the synthesis of cortisol by the adrenal glands.
Pituitary adenomas are responsible for 80% of
endogenous Cushing's syndrome,[3] when
excluding Cushing's syndrome from exogenously
administered corticosteroids.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-170517160031/85/Project-6-320.jpg)