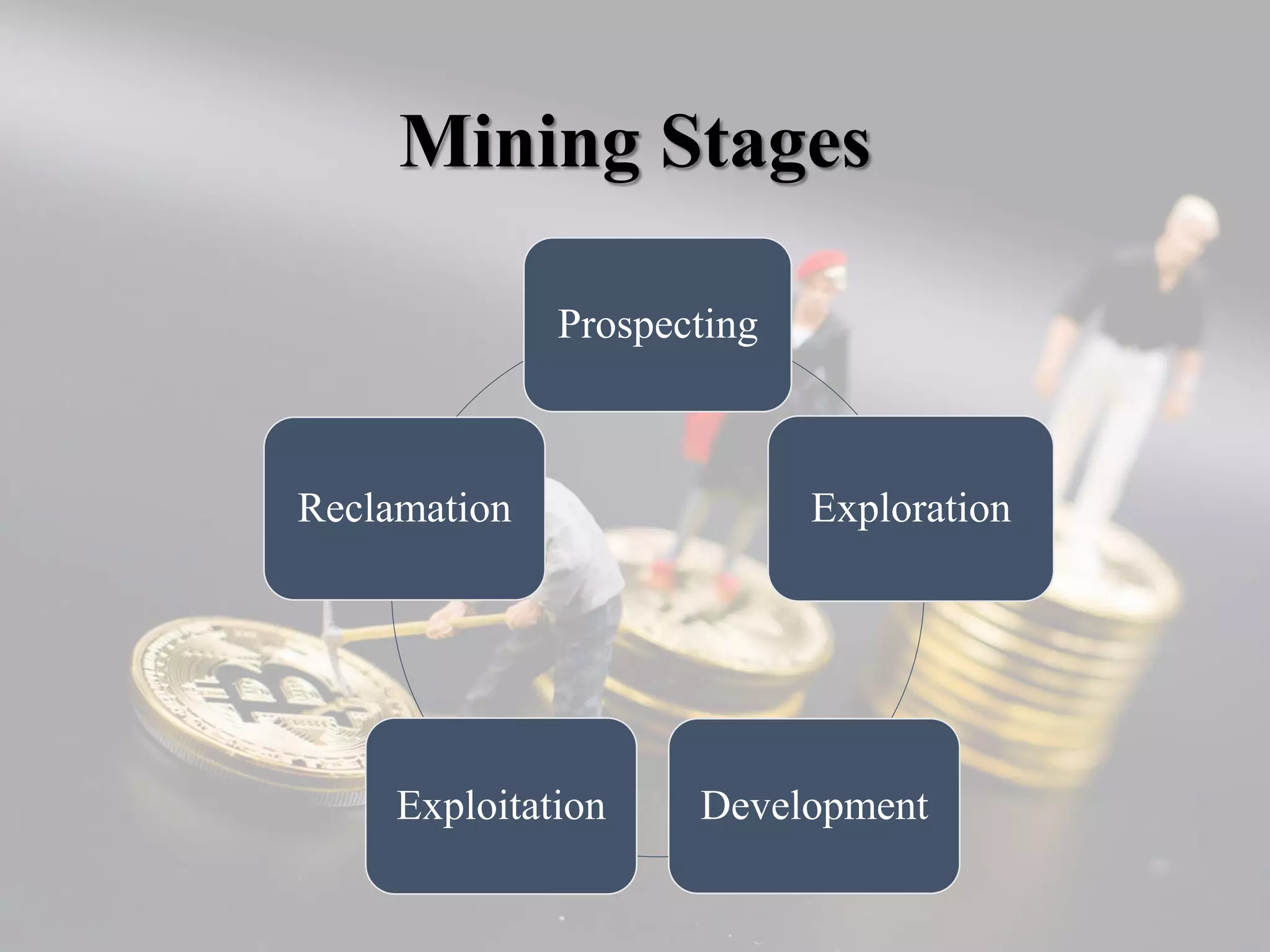
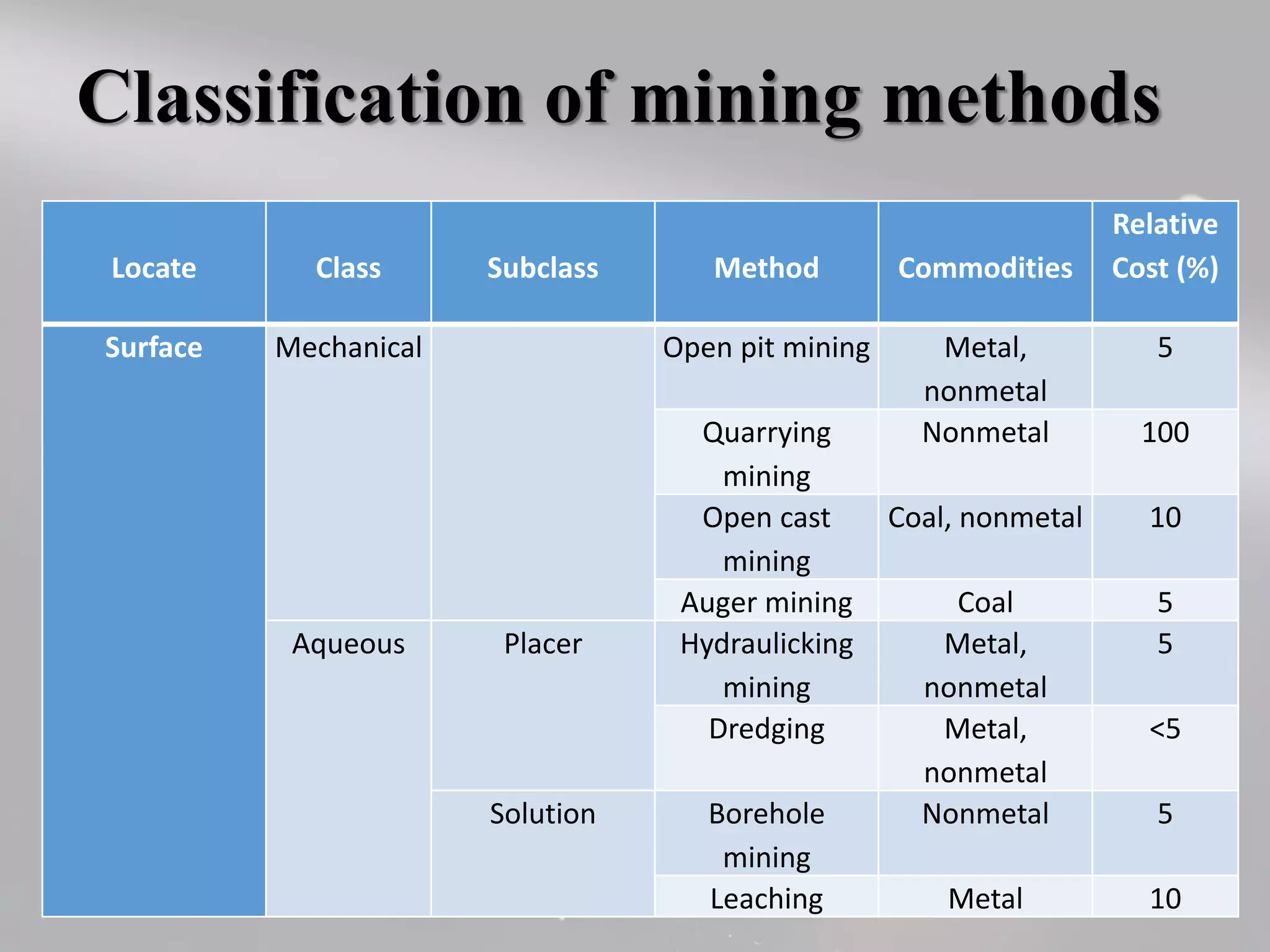
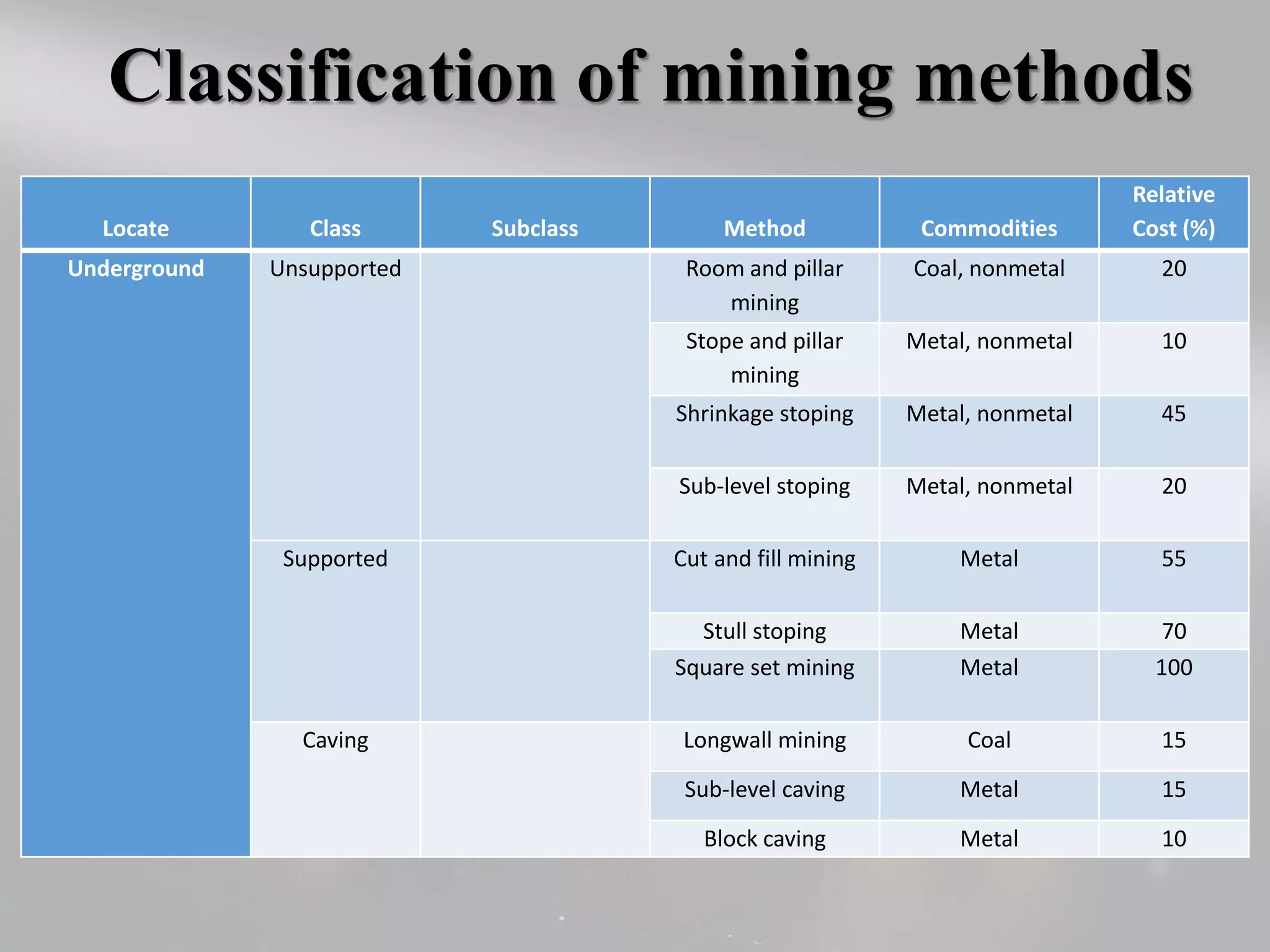
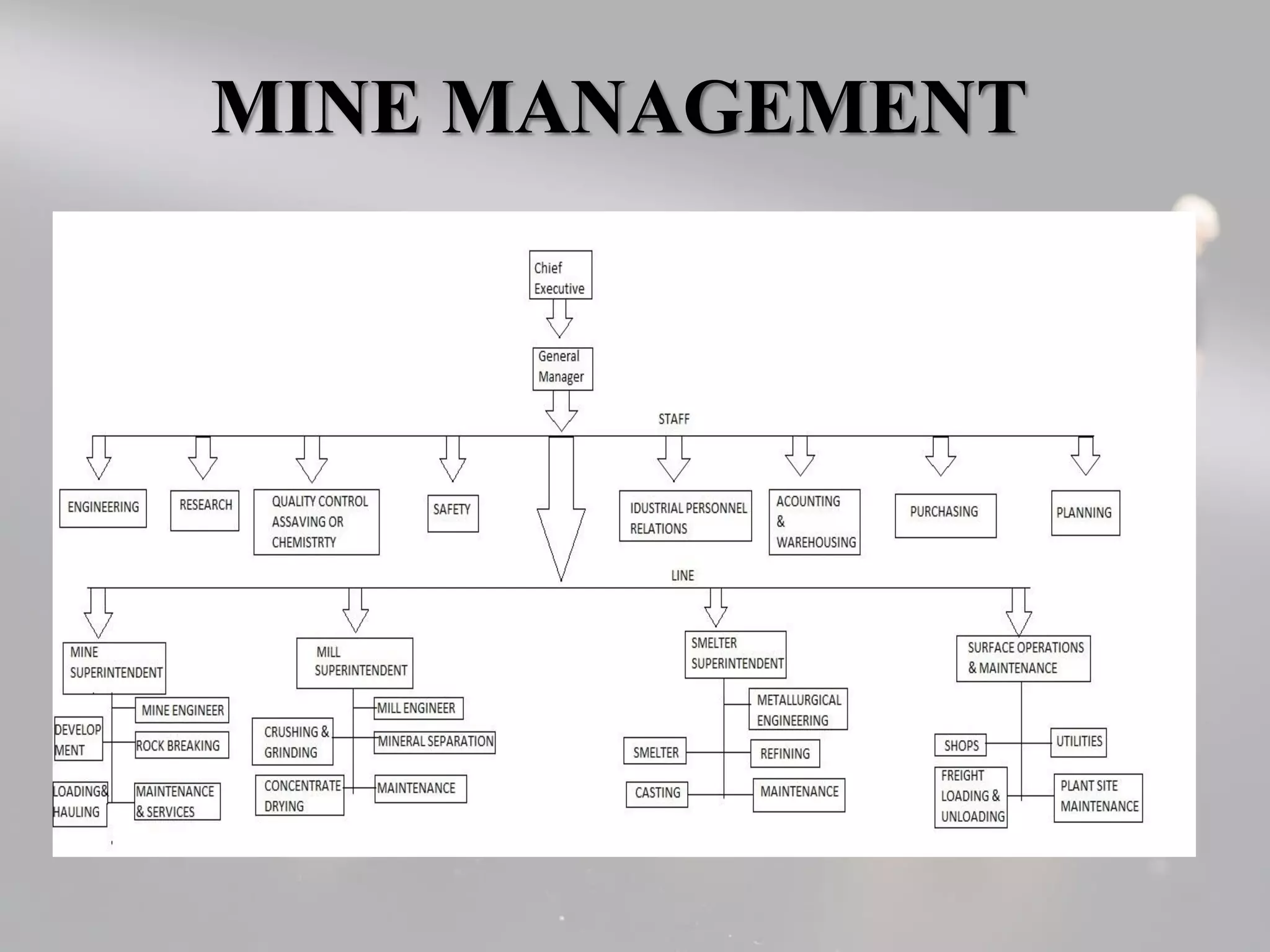
The document presents a comprehensive overview of the stages of mining, focusing on development and exploitation. It outlines the processes involved in mine development, including environmental regulations, financing, and the selection of mining methods based on various factors. Additionally, it discusses cost estimation, management, and strategies for effective mineral exploitation.