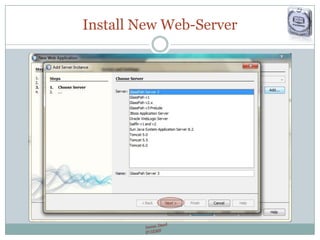
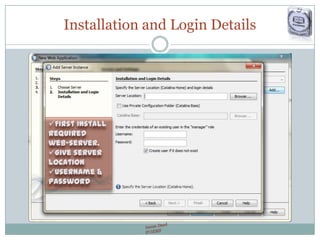
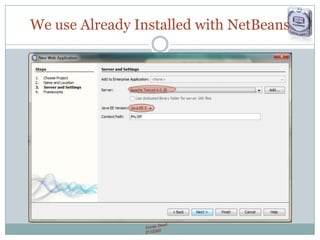
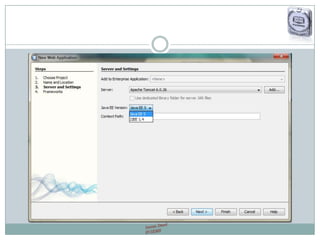
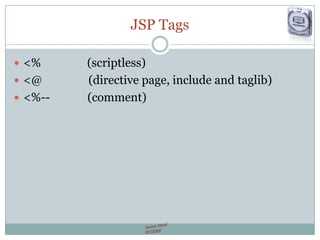
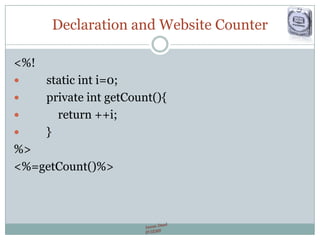
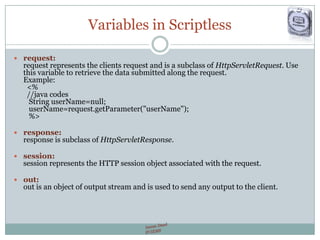
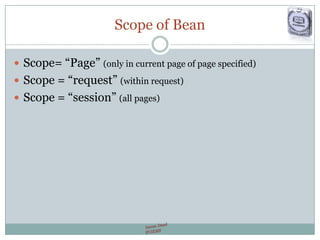
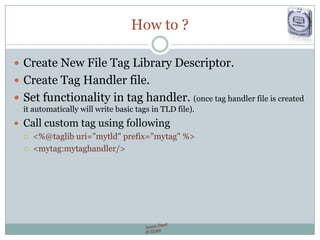
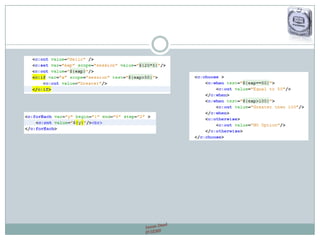
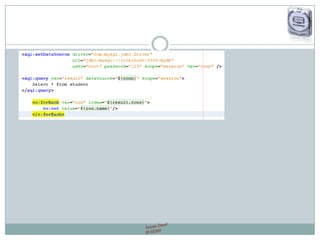
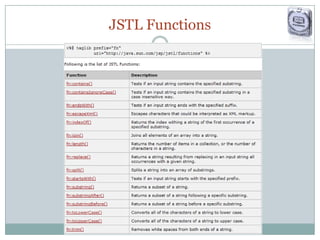
The document provides a comprehensive guide on JSP (JavaServer Pages) for web development, covering topics such as setting up a JSP environment, essential JSP tags, handling requests, and managing sessions. It explains how to use JSP beans and custom tags effectively, alongside practical examples for implementing forms and database connections. Additionally, the document highlights the integration of JSTL (JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library) for enhanced functionality.